Abstract
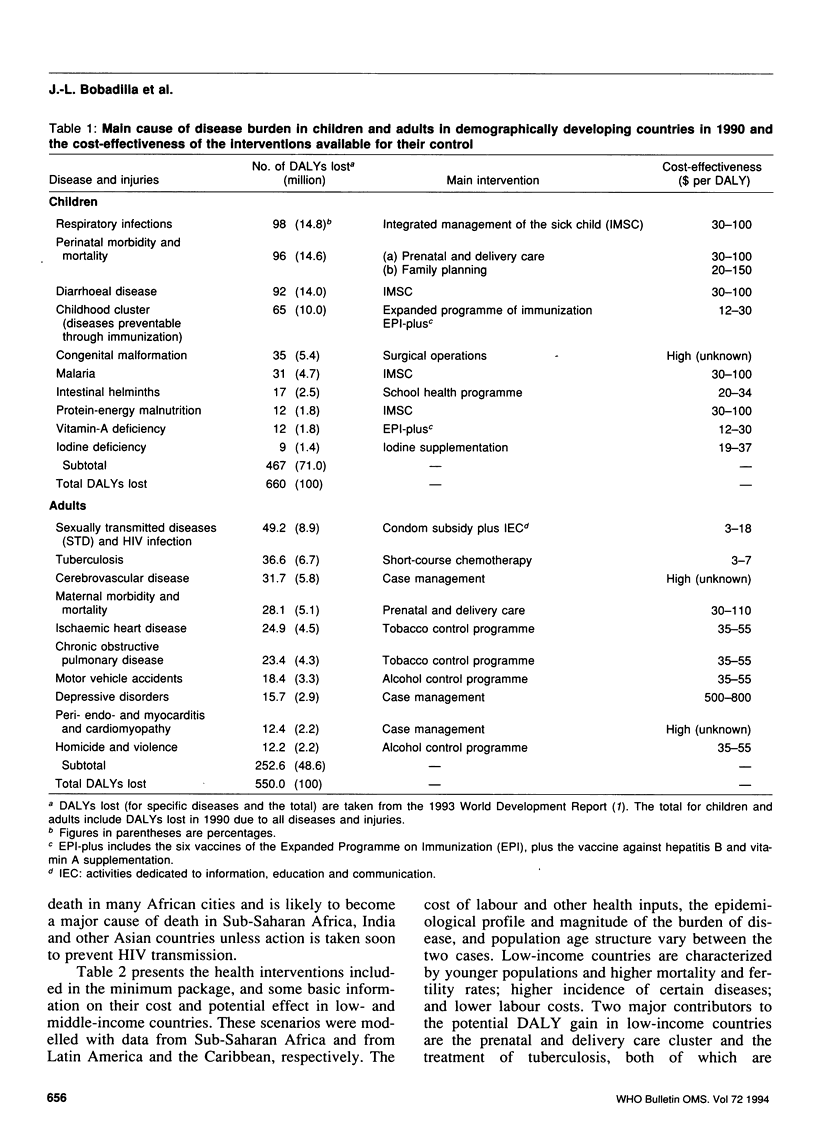
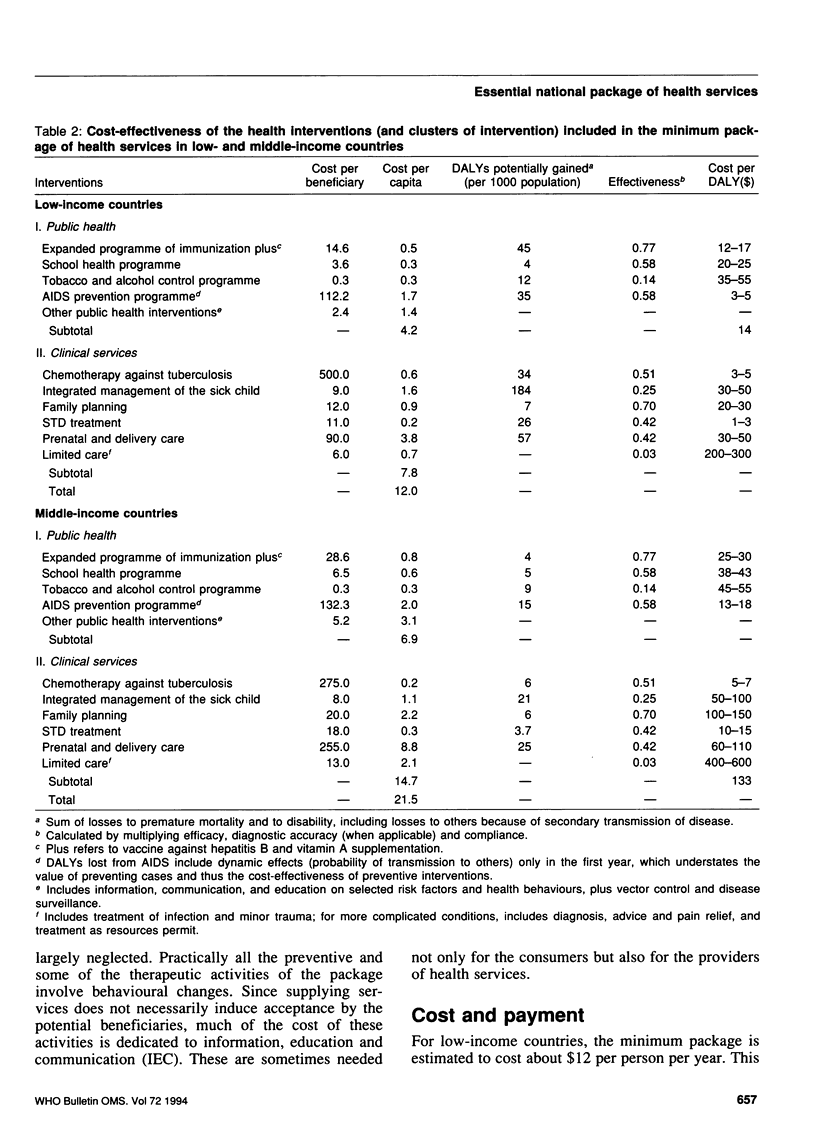
A minimum package of public health and clinical interventions, which are highly cost-effective and deal with major sources of disease burden, could be provided in low-income countries for about US$ 12 per person per year, and in middle-income countries for about $22. Properly delivered, this package could eliminate 21% to 38% of the burden of premature mortality and disability in children under 15 years and 10-18% of the burden in adults. The cost would exceed what governments now spend on health in the poorest countries but would be easily affordable in middle-income countries. Governments should ensure that, at the least, poor populations have access to these services. Additional public expenditure should then go either to extending coverage to the non-poor or to expansion beyond the minimum collection of services to an essential national package of health care, including somewhat less cost-effective interventions against a larger number of diseases and conditions.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elo I. T., Preston S. H. Effects of early-life conditions on adult mortality: a review. Popul Index. 1992 Summer;58(2):186–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J. Quantifying the burden of disease: the technical basis for disability-adjusted life years. Bull World Health Organ. 1994;72(3):429–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. A., Warren K. S. Selective primary health care: an interim strategy for disease control in developing countries. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 1;301(18):967–974. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911013011804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


