Abstract
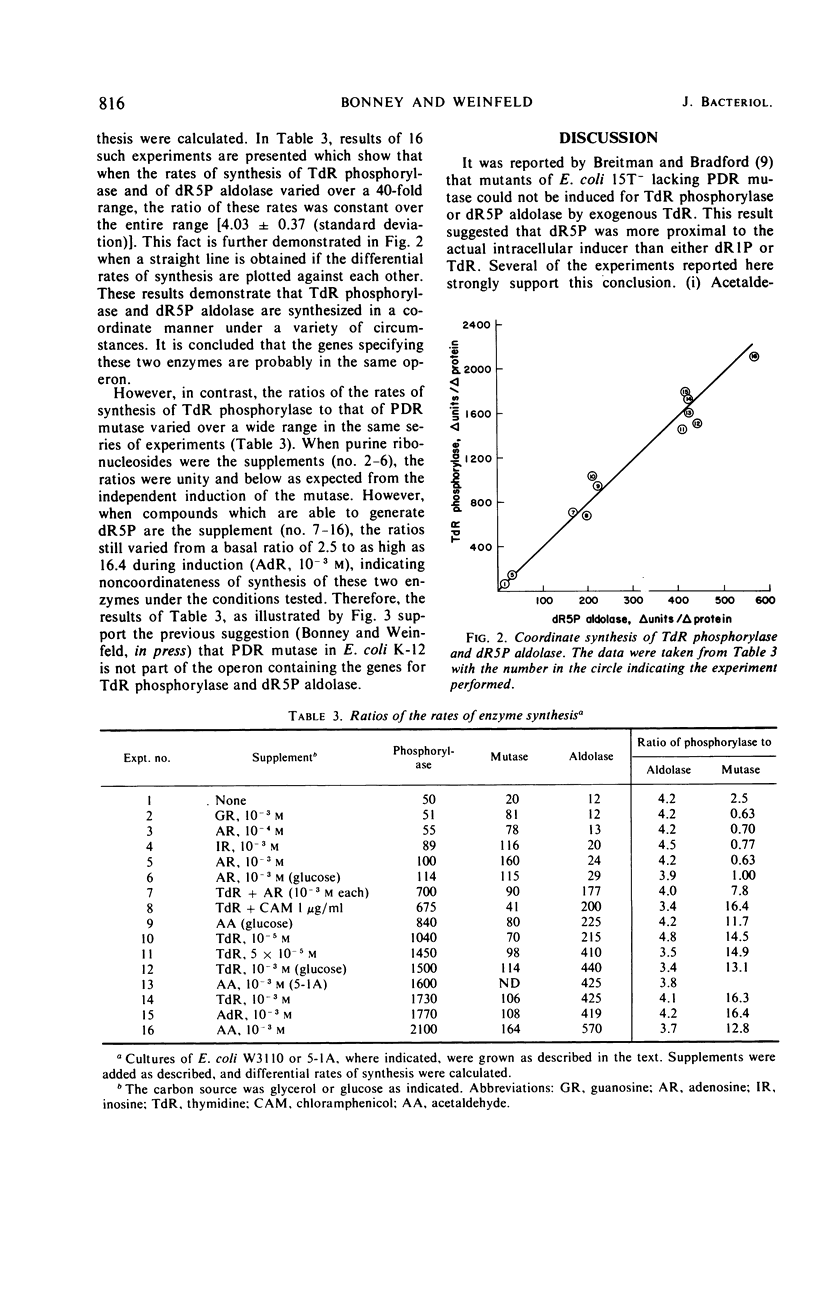
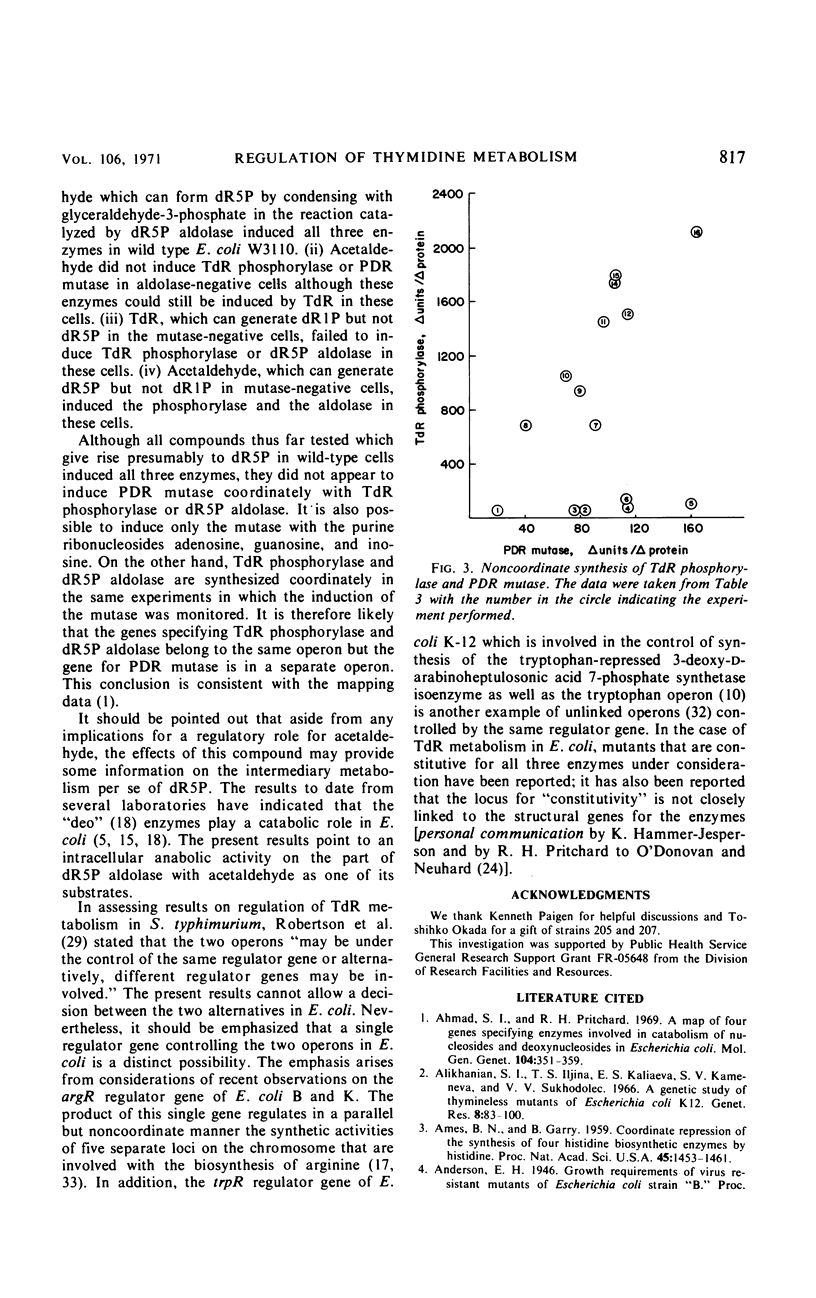
A study was made of the regulation of three enzymes that act sequentially in the metabolism of thymidine in Escherichia coli K-12. Under a variety of conditions, two of the enzymes, thymidine phosphorylase and deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase, were found to be synthesized coordinately. However, the third enzyme, phosphodeoxyribomutase, was synthesized noncoordinately with the other two enzymes under the same conditions. In addition, the mutase could be fully induced, whereas basal levels of the phosphorylase and the aldolase were maintained. These findings indicate that two operons comprise the genes concerned with the reversible pathway leading from thymidine to acetaldehyde and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. In addition to thymidine, it was found that acetaldehyde was an external inducer of these enzymes. The results of induction experiments performed on wild-type cells and mutants defective in the mutase or the aldolase, with thymidine or acetaldehyde as exogenous inducers, strongly suggest that deoxyribose-5-phosphate is more proximal to the intracellular inducer than is thymidine, deoxyribose-1-phosphate, or acetaldehyde.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S. I., Pritchard R. H. A map of four genes specifying enzymes involved in catabolism of nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1969 Aug 15;104(4):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00334234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alikhanian S. I., Iljina T. S., Kaliaeva E. S., Kameneva S. V., Sukhodolec V. V. A genetical study of thymineless mutants of E. coli K12. Genet Res. 1966 Aug;8(1):83–100. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Garry B. COORDINATE REPRESSION OF THE SYNTHESIS OF FOUR HISTIDINE BIOSYNTHETIC ENZYMES BY HISTIDINE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Oct;45(10):1453–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.10.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKWITH J. R., PARDEE A. B., AUSTRIAN R., JACOB F. Coordination of the synthesis of the enzymes in the pyrimidine pathway of E. coli. J Mol Biol. 1962 Dec;5:618–634. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Beacham I. R., Ahmad S. I., Pritchard R. H. The inducer of the deoxynucleoside phosphorylases and deoxyriboaldolase in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 23;161(2):554–557. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beacham I. R., Barth P. T., Pritchard R. H. Constitutivity of thymidine phosphorylase in deoxyriboaldolase negative strains: dependence on thymine requirement and concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):589–592. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonney R. J., Weinfeld H. Regulation of thymidine metabolism in Escherichia coli K-12: optimal conditions for the assay of 1,5-phosphodeoxyribomutase in ultrasonic extracts. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):650–655. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.650-655.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Bradford R. M. Inability of low thymine-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli lacking phosphodeoxyribomutase to be induced for deoxythymidine phosphorylase and deoxyriboaldolase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2434–2435. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2434-2435.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D. Regulation of aromatic amino acid biosynthesis Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1968 Sep;60(1):31–48. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDKIN M., KALCKAR H. M. Desoxyribose-1-phosphate: I. The phosphorolysis and resynthesis of purine desoxyribose nucleoside. J Biol Chem. 1950 Jun;184(2):437–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDKIN M., ROBERTS D. The enzymatic synthesis of nucleosides. I. Thymidine phosphorylase in mammalian tissue. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):245–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN C. E., LAMPEN J. O. Products of desoxyribose degradation by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):885–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffee P. A., Robertson B. C. 2-Deoxyribose gene-enzyme complex in Salmonella typhimurium: regulation of phosphodeoxyribomutase. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1386–1396. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1386-1396.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Gorini L. A unitary account of the repression mechanism of arginine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. I. The genetic evidence. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):73–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax M. S., Greenberg G. R. Characteristics of the deo operon: role in thymine utilization and sensitivity to deoxyribonucleosides. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):501–514. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.501-514.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANSON L. A., LAMPEN J. O. The metabolism of desoxyribose nucleosides in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1951 Dec;193(2):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch-Petersen A. On the catabolism of deoxyribonucleosides in cells and cell extracts of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Nov;6(3):432–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch-Petersen A. Thymineless mutants of Escherichia coli with deficiencies in deoxyribomutase and deoxyriboaldolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan G. A., Neuhard J. Pyrimidine metabolism in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Sep;34(3):278–343. doi: 10.1128/br.34.3.278-343.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACHMELER M., GERHART J., ROSNER J. Limited thymidine uptake in Escherichia coli due to an inducible thymidine phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:222–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Enzymatic synthesis and breakdown of desoxyribose phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1952 May;196(1):347–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. C., Jargiello P., Blank J., Hoffee P. A. Genetic regulation of ribonucleoside and deoxyribonucleoside catabolism in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):628–635. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.628-635.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STACEY K. A., SIMSON E. IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION OF THYMINE-REQUIRING MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:554–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.554-555.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. L. Current linkage map of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Jun;34(2):155–175. doi: 10.1128/br.34.2.155-175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaka S. Isolation of the arginine repressor in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1970 Oct 24;228(5269):336–338. doi: 10.1038/228336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


