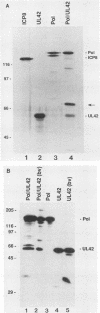
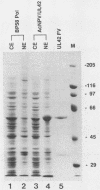
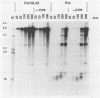
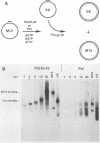
Abstract
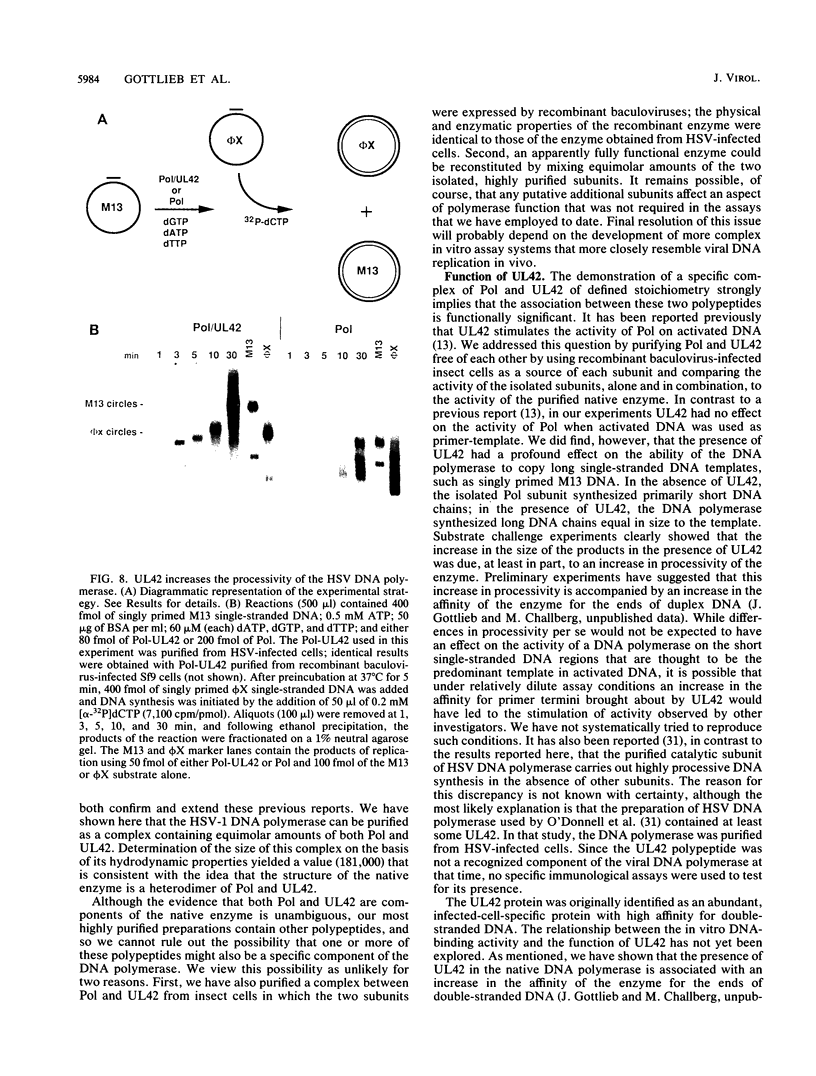
Genetic experiments have shown that the products of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) DNA polymerase (UL30) and UL42 genes are both required for viral DNA replication, and a number of studies have suggested that these two proteins specifically interact. We have confirmed and extended these findings. The viral DNA polymerase from HSV-1-infected cells has been purified as a complex containing equimolar quantities of the UL30 (Pol, the catalytic subunit) and UL42 polypeptides. Sedimentation and gel filtration analyses of this complex are consistent with the idea that the complex consists of a heterodimer of Pol and UL42. A complex with identical physical and functional properties was also purified from insect cells coinfected with recombinant baculoviruses expressing the two polypeptides. Therefore, the formation of the Pol-UL42 complex does not require the participation of any other HSV-encoded protein. We have compared the catalytic properties of the Pol-UL42 complex with those of the isolated subunits of the enzyme purified from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. The specific activity of the catalytic subunit alone was nearly identical to that of the complex when assayed on activated DNA. When assayed on a defined template such as singly primed M13 DNA, however, the combination of Pol and UL42 utilized fewer primers and formed larger products than Pol alone. Template challenge experiments demonstrated that the Pol-UL42 complex was more highly processive than Pol alone. Our data are consistent with the idea that the UL42 polypeptide is an accessory subunit of the DNA polymerase that acts to increase the processivity of polymerization.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. The yeast analog of mammalian cyclin/proliferating-cell nuclear antigen interacts with mammalian DNA polymerase delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7506–7510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet A., Simon M., Faye G., Bauer G. A., Burgers P. M. Structure and function of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC2 gene encoding the large subunit of DNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1849–1854. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael E. P., Kosovsky M. J., Weller S. K. Isolation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 host range mutants defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.91-99.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Aschman D. P., Gelep P. T., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Schaffer P. A. Fine mapping and molecular cloning of mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):236–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.236-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase. Identification of an intrinsic 5'----3' exonuclease with ribonuclease H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19266–19270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene by in vitro translation and effects of gene deletions on activity. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3224–3232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3224-3232.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Jackwood D. H., Murphy M., Marsden H. S., Parris D. S. Purification of the herpes simplex virus type 1 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein: properties of the protein and evidence of its association with the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2874–2883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2874-2883.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffey M. L., Stevens J. T., Terry B. J., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Wietstock S. M., Ruyechan W. T., Field A. K. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and detection of virus-specific enzyme activity in cell-free lysates. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4493–4498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4493-4498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin stabilizes complexes of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase and primed templates. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16224–16232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W. Properties of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase and characterization of its associated exonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):231–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Lehrach H., Goody R. S. DNA sequencing using alpha-thiodeoxynucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:166–177. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Tan C. K., Downey K. M., So A. G. Further studies on calf thymus DNA polymerase delta purified to homogeneity by a new procedure. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 24;23(9):1906–1913. doi: 10.1021/bi00304a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace D. C., Alberts B. M. Characterization of the stimulatory effect of T4 gene 45 protein and the gene 44/62 protein complex on DNA synthesis by T4 DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 5;177(2):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90459-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti M. E., Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. A temperature-sensitive mutation in a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene required for viral DNA synthesis maps to coordinates 0.609 through 0.614 in UL. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.715-721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Coen D. M. Enzymatic activities of overexpressed herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase purified from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1207–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. A., Korn D., Wang T. S. The evolutionary conservation of DNA polymerase alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7961–7973. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Elias P., Funnell B. E., Lehman I. R. Interaction between the DNA polymerase and single-stranded DNA-binding protein (infected cell protein 8) of herpes simplex virus 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4260–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Elias P., Lehman I. R. Processive replication of single-stranded DNA templates by the herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4252–4259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orberg P. K., Schaffer P. A. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 major DNA-binding protein, ICP8, in transformed cell lines: complementation of deletion mutants and inhibition of wild-type virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1136–1146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1136-1146.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Cross A., Haarr L., Orr A., Frame M. C., Murphy M., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S. Identification of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.818-825.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Littler E., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. II. Major virus-specific DNa-binding protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):894–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.894-902.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. I. Purification of the induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):618–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.618-626.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Lewis R. B., Powell K. L. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):621–623. doi: 10.1038/269621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants in two distinct complementation groups of herpes simplex virus type 1 specify thermolabile DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):219–222. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the genes for DNA polymerase and the major DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8143–8163. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Weir A. C. Interaction with nucleic acids and stimulation of the viral DNA polymerase by the herpes simplex virus type 1 major DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):727–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.727-733.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Huber H. E., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin confers processivity on the DNA polymerase activity of the gene 5 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16212–16223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Castillo C., So A. G., Downey K. M. An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12310–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. J., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding protein associated with herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):501–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.501-508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Kelly T. J. Requirement for two DNA polymerases in the replication of simian virus 40 DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9742–9746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Carmichael E. P., Aschman D. P., Goldstein D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of mutants in four essential genes that map to the left half of HSV-1 UL DNA. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):198–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Weller S. K. UL5, a protein required for HSV DNA synthesis: genetic analysis, overexpression in Escherichia coli, and generation of polyclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]