Abstract
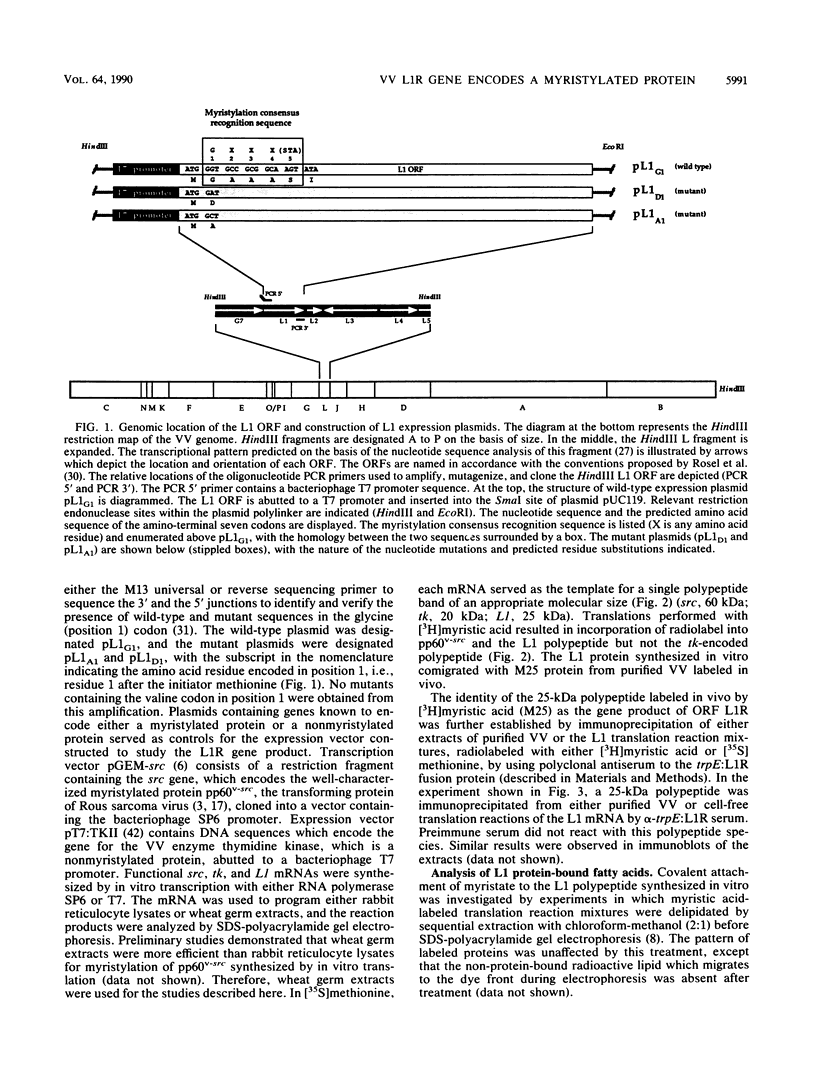
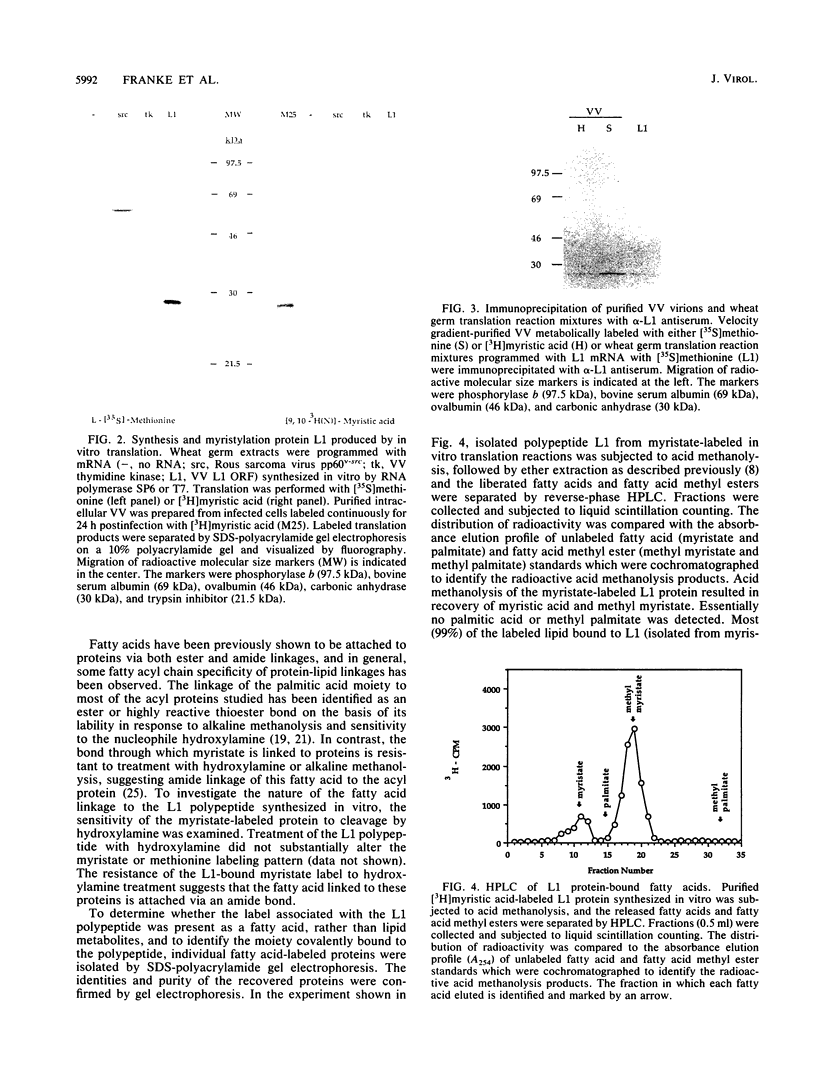
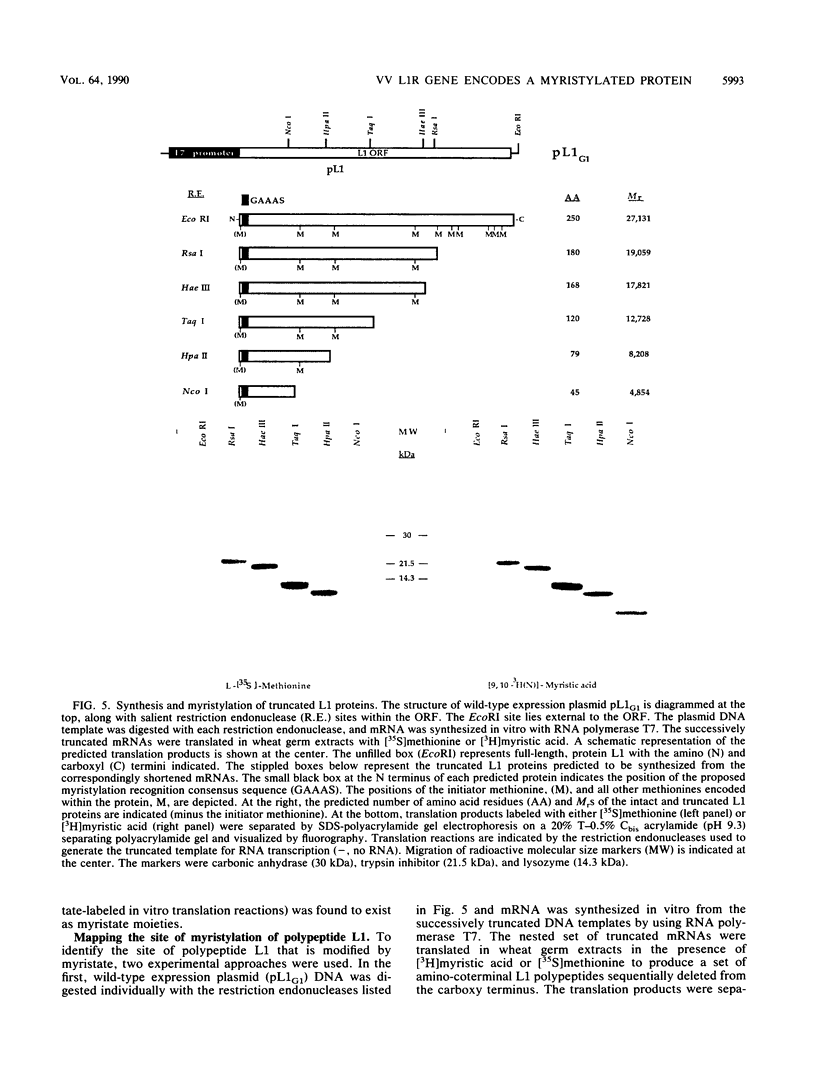
A 25-kDa vaccinia virus (VV) virion protein, designated M25, is modified in vivo by covalent addition of myristic acid. The predicted amino acid sequences of all VV open reading frames which have been reported were searched for the sequence M-G-X-X-X-(S/T/A), which has been proposed to be the consensus recognition signal for cotranslational modification of proteins by N-myristyltransferase. This conserved signal was found at the amino terminus of a single locus, which corresponded to the leftmost rightward-reading open reading frame (L1R) initiating within the VV HindIII L DNA fragment. By using synthetic oligonucleotides in concert with polymerase chain reaction techniques, a chimeric gene consisting of open reading fram L1R fused to a bacteriophage T7 promoter was constructed and cloned into a plasmid vector. Transcripts derived from the wild-type expression plasmid (designated pL1G1) were translated in vitro in a wheat germ extract to yield a polypeptide with an apparent molecular mass of 25 kDa. This polypeptide was labeled with either [35S]methionine or [3H]myristic acid and comigrated with in vivo-labeled protein M25 on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Polyclonal antiserum generated in rabbits against a trpE:L1R fusion protein immunoprecipitated a 25-kDa protein labeled either in vitro (the L1R gene product, designated protein L1) or in vivo (from purified VV, protein M25), identifying the M25 protein as the gene product of open reading frame L1R. Chromatographic analysis of the protein L1-bound fatty acid moieties liberated after acid methanolysis resulted in recovery of greater than 99% of the fatty acid as myristate-associated label. Cell-free translation of proteins derived from a set of deletions from the carboxy terminus of the open reading frame L1R suggested that the site of myristylation maps near the amino terminus of protein L1. This hypothesis was supported by cell-free translation of mutant L1R transcripts in which the penultimate glycine codon had been altered by site-directed mutagenesis to encode either an aspartic acid (pL1D1) or alanine (pL1A1) residue. In both cases, the mutant transcripts were translated into a 25-kDa protein which could be labeled in vitro with [35S]methionine but not with [3H]myristic acid. These data demonstrate that VV open reading frame L1R encodes a myristylated protein and provide evidence that the site of modification of protein L1 is the amino-terminal glycine residue.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deichaite I., Casson L. P., Ling H. P., Resh M. D. In vitro synthesis of pp60v-src: myristylation in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4295–4301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essani K., Dugre R., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: involvement of spicules of the envelope during virion assembly examined by means of conditional lethal mutants and serology. Virology. 1982 Apr 30;118(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C. A., Reynolds P. L., Hruby D. E. Fatty acid acylation of vaccinia virus proteins. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4285–4291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4285-4291.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke C. A., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Neomycin resistance as a dominant selectable marker for selection and isolation of vaccinia virus recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1918–1924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J. Acylation of viral and eukaryotic proteins. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):625–638. doi: 10.1042/bj2580625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuckeroth R. O., Towler D. A., Adams S. P., Glaser L., Gordon J. I. 11-(Ethylthio)undecanoic acid. A myristic acid analogue of altered hydrophobicity which is functional for peptide N-myristoylation with wheat germ and yeast acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2127–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. Golgi-derived membranes that contain an acylated viral polypeptide are used for vaccinia virus envelopment. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):651–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.651-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt P., Hiller G., Wittek R. Localization and fine structure of a vaccinia virus gene encoding an envelope antigen. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.757-764.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Guarino L. A., Kates J. R. Vaccinia virus replication. I. Requirement for the host-cell nucleus. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):705–715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.705-715.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G., Olson E. N. Fatty acylated proteins as components of intracellular signaling pathways. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2623–2634. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Simonds W. F., Merendino J. J., Jr, Brann M. R., Spiegel A. M. Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein alpha subunit is essential for its membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):568–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L. Cysteines in the transmembrane region of major histocompatibility complex antigens are fatty acylated via thioester bonds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7230–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid acylation of eucaryotic cell membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 30;694(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90008-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Drugeon G., Haenni A. L., Girard M., van der Werf S. Role of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid protein VP4 as determined by site-directed mutagenesis of its N-terminal sequence. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. N., Hruby D. E. Rifampicin prevents virosome localization of L65, an essential vaccinia virus polypeptide. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Prevention of NH2-terminal acetylation of proteins synthesized in cell-free systems. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8781–8783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plucienniczak A., Schroeder E., Zettlmeissl G., Streeck R. E. Nucleotide sequence of a cluster of early and late genes in a conserved segment of the vaccinia virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):985–998. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosel J. L., Earl P. L., Weir J. P., Moss B. Conserved TAAATG sequence at the transcriptional and translational initiation sites of vaccinia virus late genes deduced by structural and functional analysis of the HindIII H genome fragment. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):436–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.436-449.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Fatty acylation of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:611–647. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Adams S. P., Eubanks S. R., Towery D. S., Jackson-Machelski E., Glaser L., Gordon J. I. Myristoyl CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase activities from rat liver and yeast possess overlapping yet distinct peptide substrate specificities. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1784–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Adams S. P., Eubanks S. R., Towery D. S., Jackson-Machelski E., Glaser L., Gordon J. I. Purification and characterization of yeast myristoyl CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D., Glaser L. Acylation of cellular proteins with endogenously synthesized fatty acids. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 25;25(4):878–884. doi: 10.1021/bi00352a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D., Glaser L. Protein fatty acid acylation: enzymatic synthesis of an N-myristoylglycyl peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2812–2816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Moss B. Regulation of expression and nucleotide sequence of a late vaccinia virus gene. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):662–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.662-669.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. M., Franke C. A., Black M. E., Hruby D. E. Expression vector pT7:TKII for the synthesis of authentic biologically active RNA encoding vaccinia virus thymidine kinase. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






