Abstract
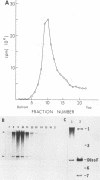
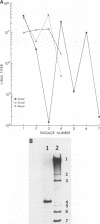
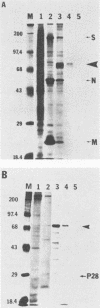
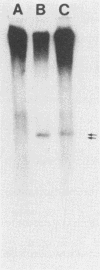
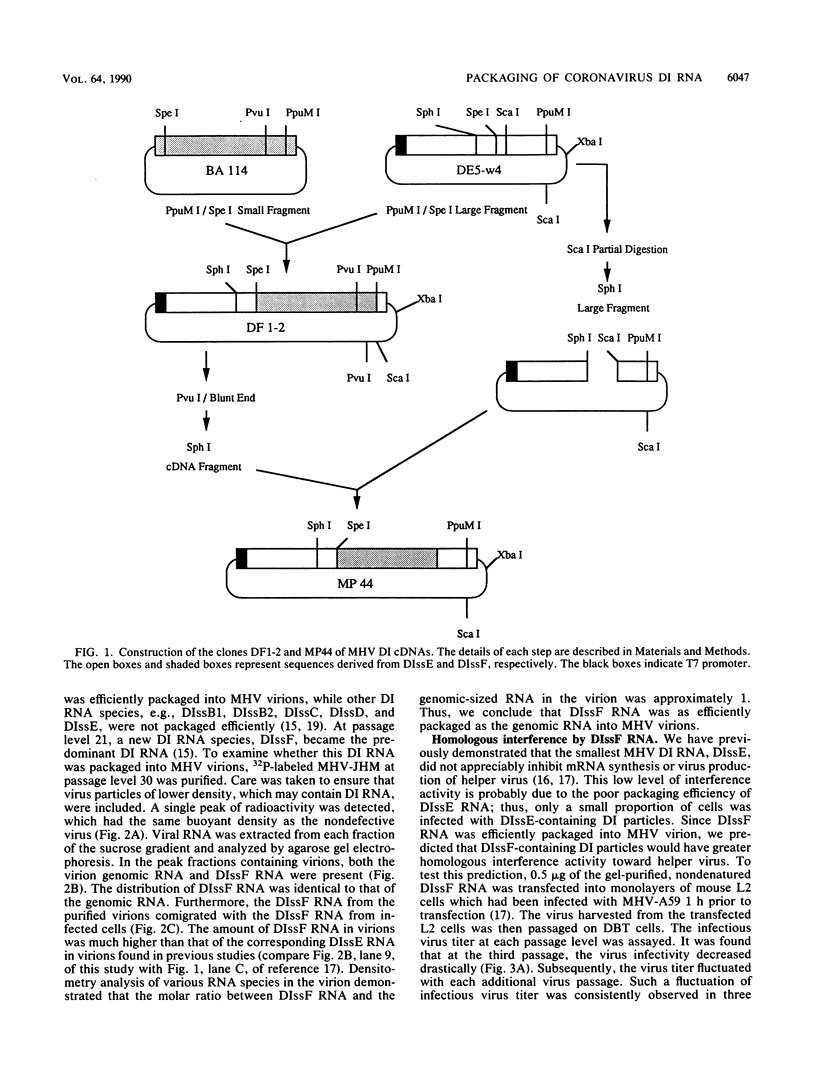
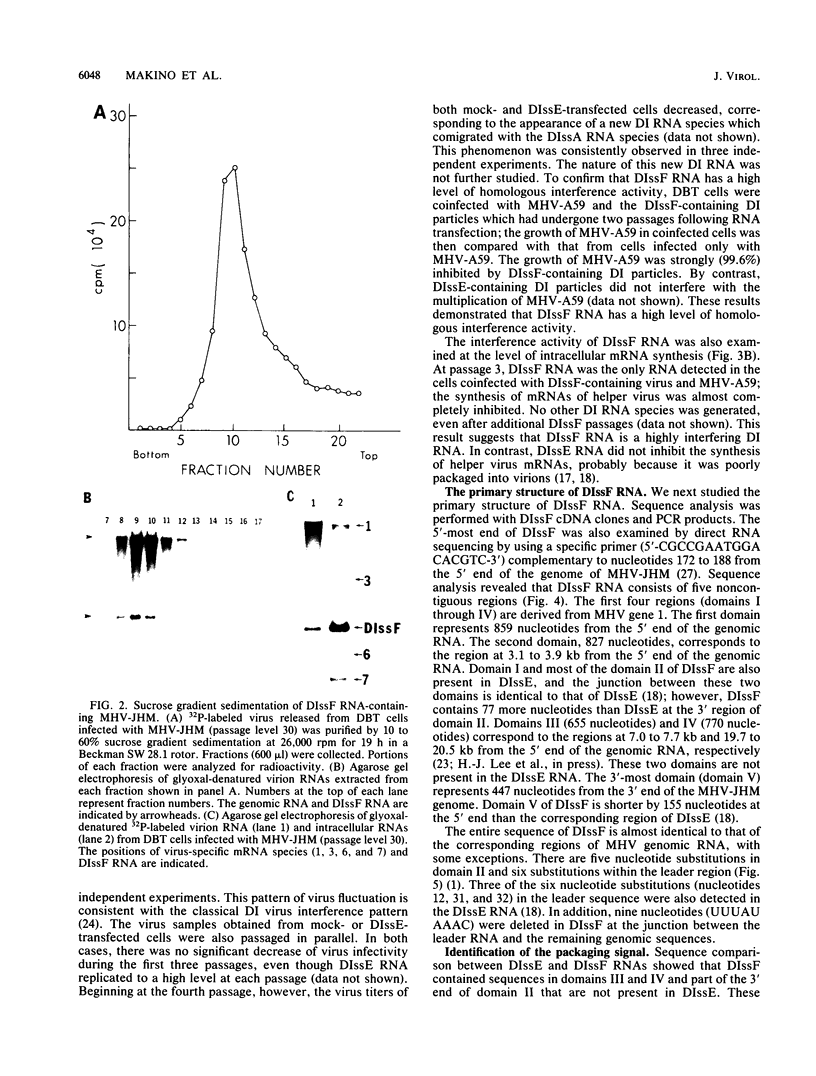
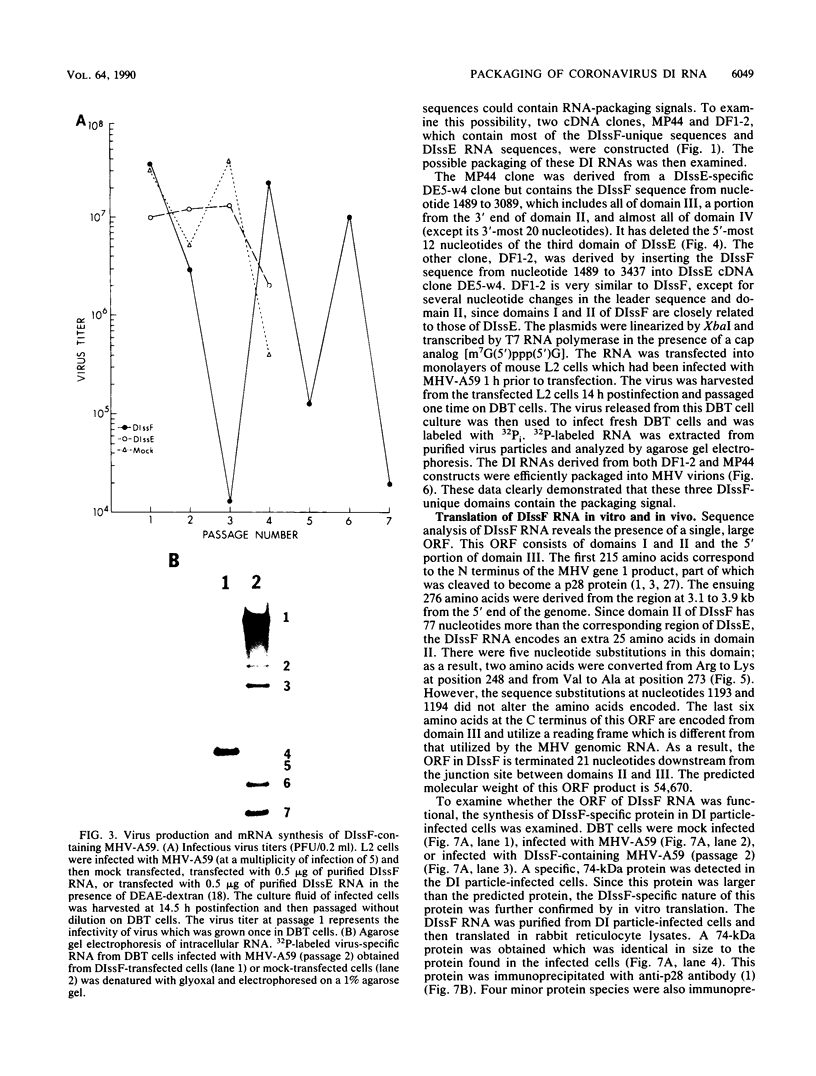
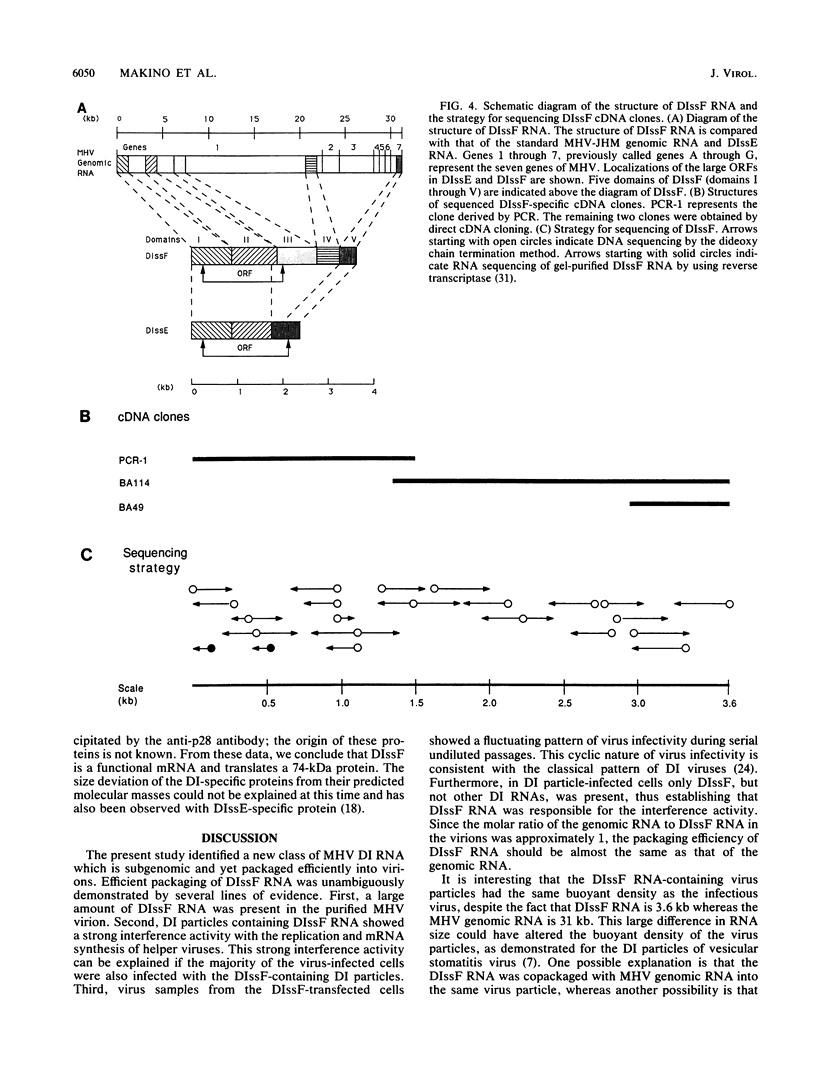
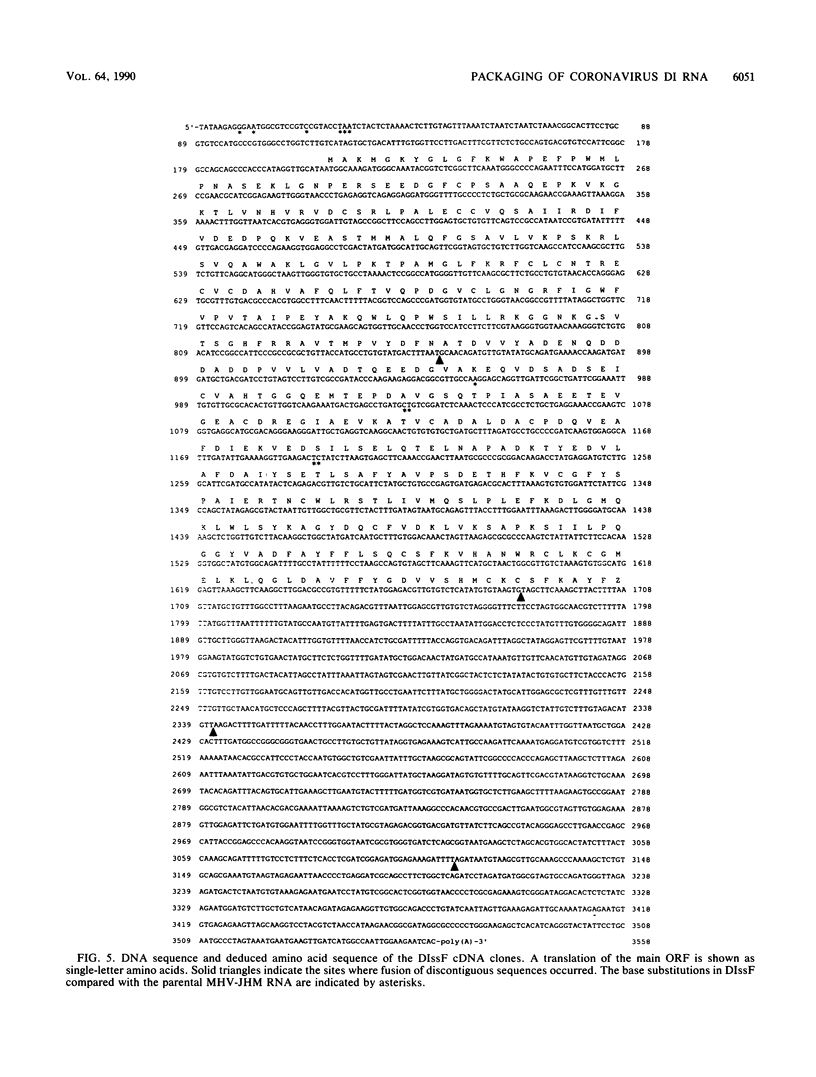
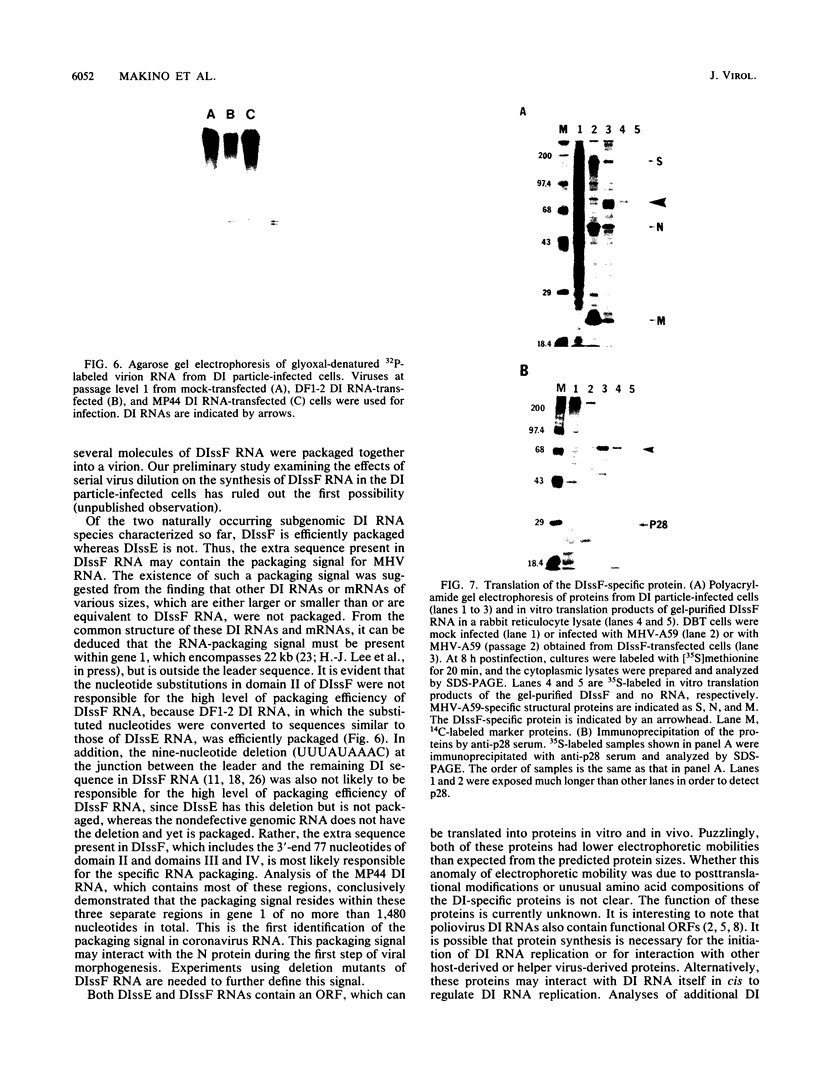
We have previously shown that most of the defective interfering (DI) RNA of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) are not packaged into virions. We have now identified, after 21 serial undiluted passages of MHV, a small DI RNA, DIssF, which is efficiently packaged into virions. The DIssF RNA replicated at a high efficiency on its transfection into the helper virus-infected cells. The virus released from the transfected cells interfered strongly with mRNA synthesis and growth of helper virus. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of DIssF RNA revealed that it is 3.6 kb and consists of sequences derived from five discontinuous regions of the genome of the nondefective virus. The first four regions (domains I to IV) from the 5' end are derived from gene 1, which presumably encodes the RNA polymerase of the nondefective virus. The entire domain I (859 nucleotides) and the first 750 nucleotides of domain II are also present in a previously characterized DI RNA, DIssE, which is not efficiently packaged into virions. Furthermore, the junction between these two domains is identical between the two DI RNAs. The remaining 77 nucleotides at the 3' end of domain II and all of domains III (655 nucleotides) and IV (770 nucleotides) are not present in DIssE RNA. These four domains are derived from gene 1. In contrast, the 3'-most domain (domain V, 447 nucleotides) is derived from the 3' end of the genomic RNA and is also present in DIssE. The comparison of primary sequences and packaging properties between DIsse and DIssF RNAs suggested that domains III and IV and part of the 3' end of domain II contain the packaging signal for MHV RNA. This conclusion was confirmed by inserting these DIssF-unique sequences into a DIssE cDNA construct; the in vitro-transcribed RNA from this hybrid construct was efficiently packaged into virion particles. DIssF RNA also contains an open reading frame, which begins from domain I and ends at the 5'-end 20 bases of domain III. In vitro translation of DIssF RNA and metabolic labeling of the virus-infected cells showed that this open reading frame is indeed translated into a 75-kDa protein. The structures of both DIssE and DIssF RNAs suggest that a protein-encoding capability is a common characteristic of MHV DI RNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. C., Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Chang M. F., Vannier D. M., Lai M. M. Identification of a domain required for autoproteolytic cleavage of murine coronavirus gene A polyprotein. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3693–3699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3693-3699.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Perlman S. Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.12-18.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino-Yamagishi K., Nomoto A. In vitro construction of poliovirus defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5386–5392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5386-5392.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Fujiwara K., Hino S., Matumoto M. Replication and plaque formation of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-2) in mouse cell line DBT culture. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01240618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of leader RNA sequences on the virion and mRNAs of mouse hepatitis virus, a cytoplasmic RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3626–3630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Brayton P. R., Armen R. C., Patton C. D., Pugh C., Stohlman S. A. Mouse hepatitis virus A59: mRNA structure and genetic localization of the sequence divergence from hepatotropic strain MHV-3. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.823-834.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Makino S., Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Keck J. G., Fleming J. O. Coronavirus: a jumping RNA transcription. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:359–365. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Wilhelmsen K. C., Bond C. W. The virus-specific intracellular RNA species of two murine coronaviruses: MHV-a59 and MHV-JHM. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Fujioka N., Fujiwara K. Structure of the intracellular defective viral RNAs of defective interfering particles of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.329-336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Lai M. M. High-frequency leader sequence switching during coronavirus defective interfering RNA replication. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5285–5292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5285-5292.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Shieh C. K., Keck J. G., Lai M. M. Defective-interfering particles of murine coronavirus: mechanism of synthesis of defective viral RNAs. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90237-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Baker S. C., Lai M. M. Primary structure and translation of a defective interfering RNA of murine coronavirus. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):550–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90526-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Fujiwara K. Defective interfering particles of mouse hepatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Hirano N., Fujiwara K. Analysis of genomic and intracellular viral RNAs of small plaque mutants of mouse hepatitis virus, JHM strain. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90335-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma E. L., Huang A. Cyclic production of vesicular stomatitis virus caused by defective interfering particles. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):402–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Makino S., Chang M. F., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. The 5'-end sequence of the murine coronavirus genome: implications for multiple fusion sites in leader-primed transcription. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Baker S. C., Chang M. F., Lai M. M. Sequence and translation of the murine coronavirus 5'-end genomic RNA reveals the N-terminal structure of the putative RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3968–3976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3968-3976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Phosphoproteins of murine hepatitis viruses. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):672–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.672-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V., Behnke J. Isolation of coronavirus envelope glycoproteins and interaction with the viral nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):449–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.449-462.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., La Monica N., Makino S., Shieh C. K., Lai M. M. Biosynthesis, structure, and biological activities of envelope protein gp65 of murine coronavirus. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90581-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]