Abstract
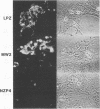
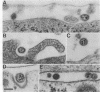
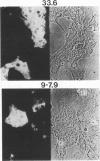
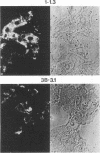
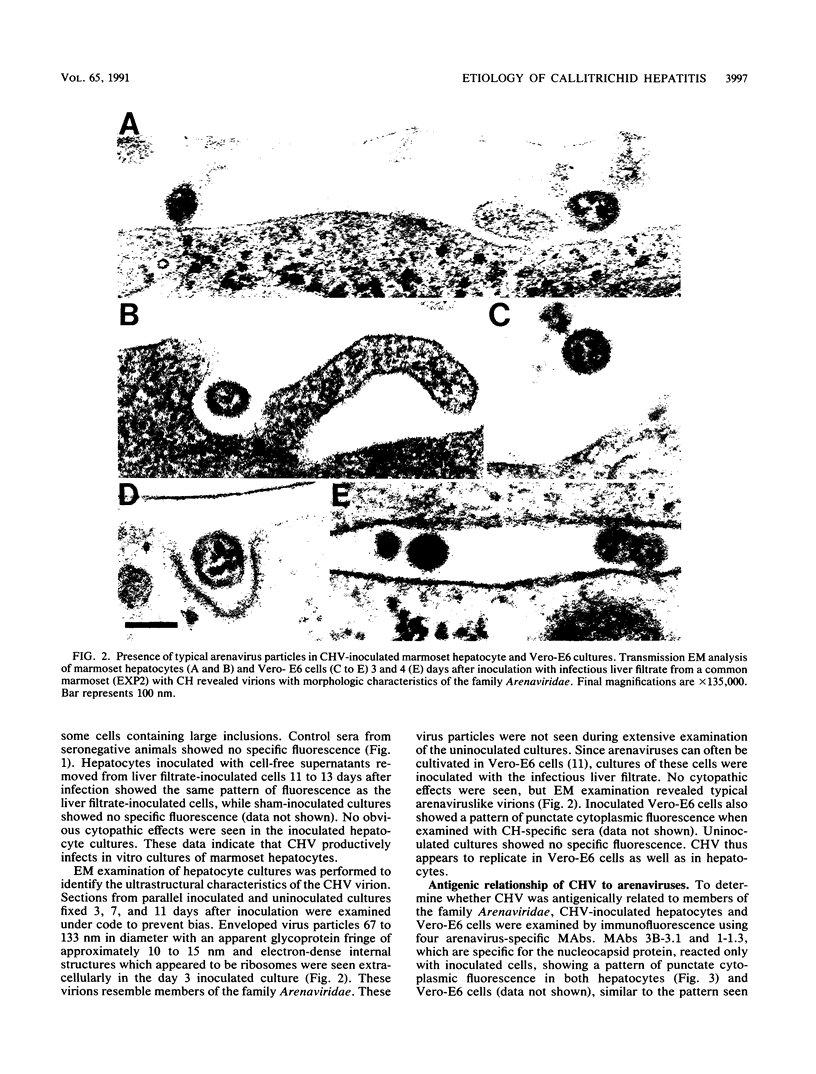
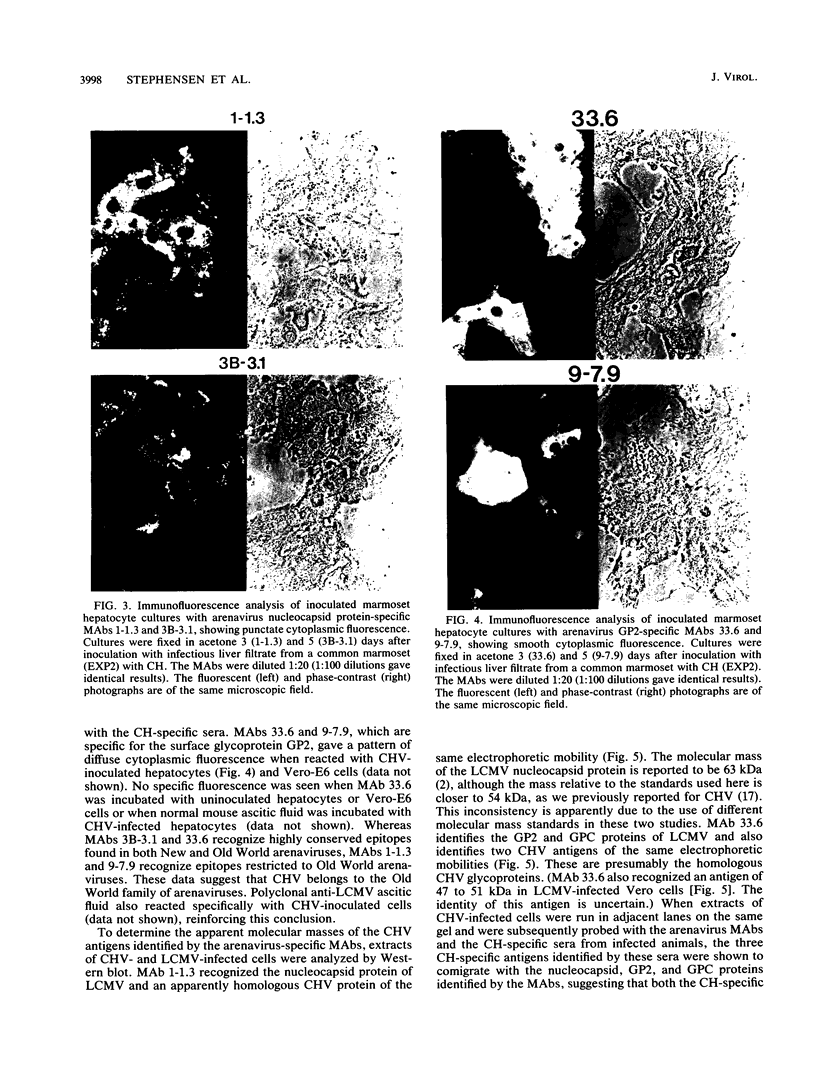
Callitrichid hepatitis (CH) is an acute, often fatal viral infection of New World primates from the family Callitrichidae. The etiologic agent of CH is unknown. We report here the isolation of an arenavirus from a common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) with CH by using in vitro cultures of marmoset hepatocytes and Vero-E6 cells. Enveloped virions 67 to 133 nm in diameter with ribosomelike internal structures were seen in infected cultures. Immunofluorescence and Western immunoblot analysis using CH-specific antisera (principally from animals exposed to CH during zoo outbreaks) revealed three antigens in cells infected with this CH-associated virus (CHV). These antigens had the same electrophoretic mobilities on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels as did the nucleocapsid, GP2, and GPC proteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). Monoclonal antibodies specific for these arenavirus proteins also reacted with the three CHV antigens. Conversely, the CH-specific antisera reacted with the nucleocapsid, GP2, and GPC proteins of LCMV. CHV thus appears to be a close antigenic relative of LCMV. The serologic association of CHV with several CH outbreaks implicate it as the etiologic agent of this disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchmeier M. J., Elder J. H., Oldstone M. B. Protein structure of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: identification of the virus structural and cell associated polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Tomori O., Johnson K. M. Monoclonal antibodies to lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus react with pathogenic arenaviruses. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):486–487. doi: 10.1038/288486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Tomori O., Oldstone M. B. Monoclonal antibodies to lymphocytic choriomeningitis and pichinde viruses: generation, characterization, and cross-reactivity with other arenaviruses. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton A. J., Rowe W. P., Smith G. H., Wilsnack R. E., Pugh W. E. Morphological and cytochemical studies on lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1968 Dec;2(12):1465–1478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.12.1465-1478.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J. R., Burk K. H., Eichberg J. W., Dreesman G. R., Lanford R. E. Expression of infectious viral particles by primary chimpanzee hepatocytes isolated during the acute phase of non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1121–1127. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob J. R., Eichberg J. W., Lanford R. E. In vitro replication and expression of hepatitis B virus from chronically infected primary chimpanzee hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1989 Dec;10(6):921–927. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Carey K. D., Estlack L. E., Smith G. C., Hay R. V. Analysis of plasma protein and lipoprotein synthesis in long-term primary cultures of baboon hepatocytes maintained in serum-free medium. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Feb;25(2):174–182. doi: 10.1007/BF02626175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montali R. J., Ramsay E. C., Stephensen C. B., Worley M., Davis J. A., Holmes K. V. A new transmissible viral hepatitis of marmosets and tamarins. J Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;160(5):759–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.5.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters C. J., Jahrling P. B., Liu C. T., Kenyon R. H., McKee K. T., Jr, Barrera Oro J. G. Experimental studies of arenaviral hemorrhagic fevers. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;134:5–68. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71726-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Murphy F. A., Bergold G. H., Casals J., Hotchin J., Johnson K. M., Lehmann-Grube F., Mims C. A., Traub E., Webb P. A. Arenoviruses: proposed name for a newly defined virus group. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):651–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.651-652.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephensen C. B., Montali R. J., Ramsay E. C., Holmes K. V. Identification, using sera from exposed animals, of putative viral antigens in livers of primates with callitrichid hepatitis. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6349–6354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6349-6354.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanzee B. E., Douglas R. G., Betts R. F., Bauman A. W., Fraser D. W., Hinman A. R. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis in university hospital personnel. Clinical features. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90635-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Murphy F. A. Pathology and pathogenesis of arenavirus infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;133:89–113. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71683-6_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E. L., Buchmeier M. J. Fine mapping of a peptide sequence containing an antigenic site conserved among arenaviruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90616-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]