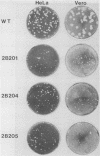
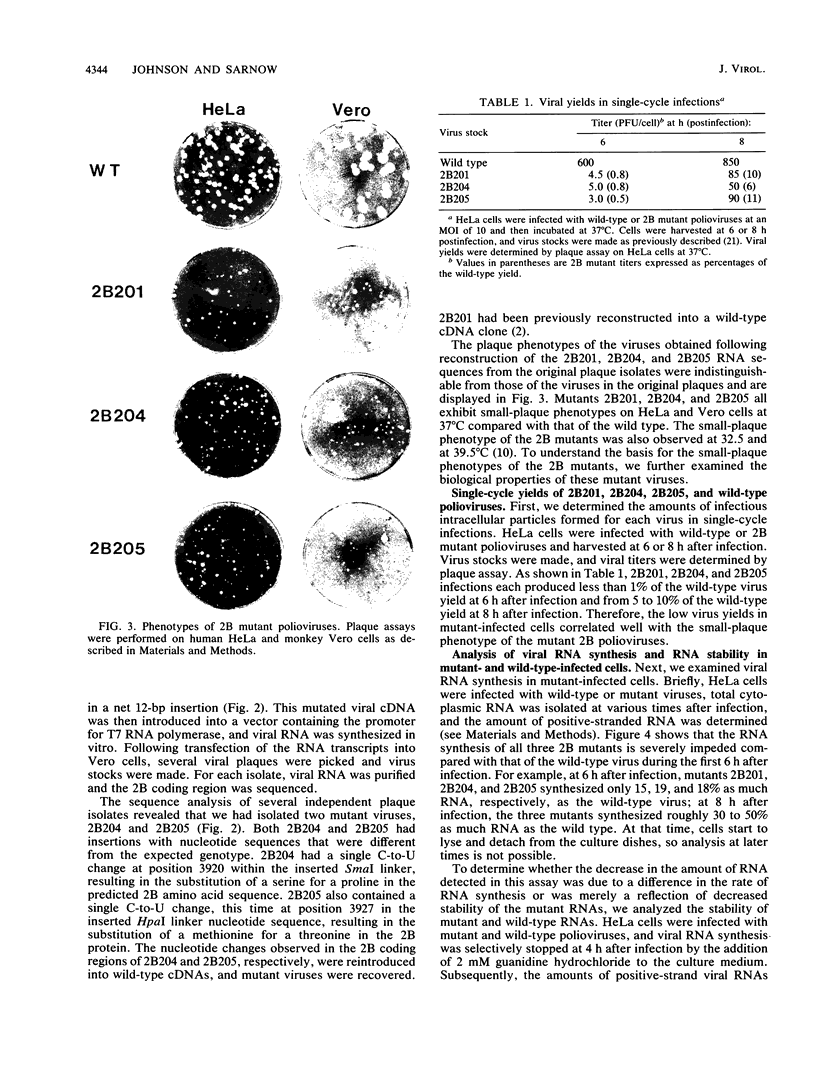
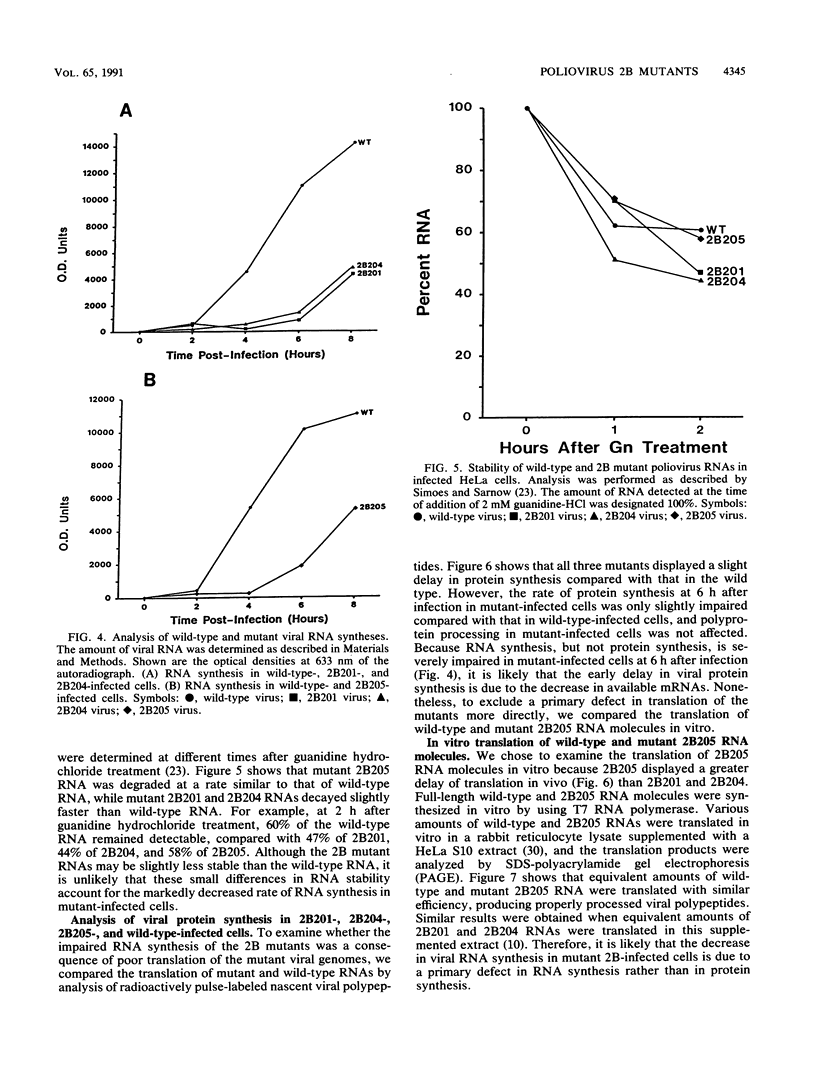
Abstract
Many functions of the poliovirus genome in virally infected cells have been elucidated. However, the role of 2B (and of its precursor polypeptide, 2BC), encoded by the P2 region in the poliovirus genome, remains unknown. We have employed a genetic approach to examine the role of 2B in poliovirus-infected cells. We report here the phenotype of one previously isolated mutant in the 2B coding region, 2B201. In addition, we have constructed one additional mutation in the 2B coding region of an infectious poliovirus cDNA clone. Upon transfection into monkey Vero cells we could recover two 2B mutant polioviruses, 2B204 and 2B205. All three mutants exhibited small-plaque phenotypes on monkey Vero and human HeLa cells and displayed primary defects in viral RNA synthesis. None of the 2B mutants could be complemented by wild-type virus. Instead, the mutants exhibited a dosage-dependent dominance over wild-type poliovirus. Thus, the phenotypes of these 2B mutants implicate 2B and possibly its precursor, 2BC, in viral RNA amplification in poliovirus-infected cells, and the dominance of the 2B mutants suggests a structural role for 2B in viral replication complexes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Pasamontes L. Association of polioviral proteins of the P2 genomic region with the viral replication complex and virus-induced membrane synthesis as visualized by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry and autoradiography. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Rasser Y., Bossart W. Intracellular distribution of poliovirus proteins and the induction of virus-specific cytoplasmic structures. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Troxler M., Pasamontes L. Structural organization of poliovirus RNA replication is mediated by viral proteins of the P2 genomic region. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1156-1163.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalbadie-McFarland G., Cohen L. W., Riggs A. D., Morin C., Itakura K., Richards J. H. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis as a general and powerful method for studies of protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Baltimore D. The mechanism of RNA recombination in poliovirus. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K. Mutations in VP1 of poliovirus specifically affect both encapsidation and release of viral RNA. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):195–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.195-206.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomax N. B., Yin F. H. Evidence for the role of the P2 protein of human rhinovirus in its host range change. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2396–2399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2396-2399.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Wimmer E. Production of guanidine-resistant and -dependent poliovirus mutants from cloned cDNA: mutations in polypeptide 2C are directly responsible for altered guanidine sensitivity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):793–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.793-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Picornaviral structure and assembly. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):287–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.287-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Role of 3'-end sequences in infectivity of poliovirus transcripts made in vitro. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.467-470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoes E. A., Sarnow P. An RNA hairpin at the extreme 5' end of the poliovirus RNA genome modulates viral translation in human cells. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):913–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.913-921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H., Lomax N. B. Host range mutants of human rhinovirus in which nonstructural proteins are altered. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):410–418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.410-418.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]