Abstract
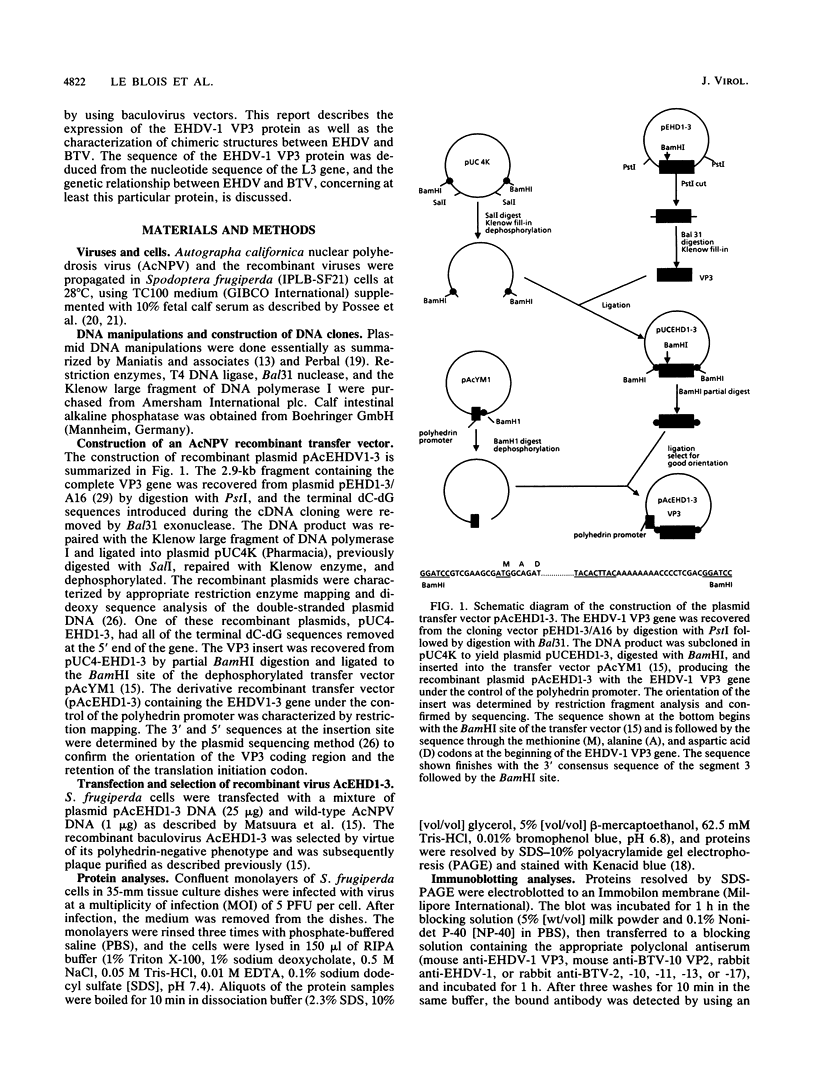
A functional assay has been developed to determine the conservative nature of the interacting sites of various structural proteins of orbiviruses by using baculovirus expression vectors. For this investigation, proteins of two serologically related orbiviruses, bluetongue virus (BTV) and the less studied epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV), were used to synthesize chimeric particles. The results demonstrate that the inner capsid protein VP3 of EHDV-1 can replace VP3 protein of BTV in formation of the single-shelled corelike particles and the double-shelled viruslike particles. Moreover, we have demonstrated that all three minor core proteins (VP1, VP4, and VP6) can be incorporated into the homologous and chimeric corelike and viruslike particles, indicating that the functional epitopes of the VP3 protein are conserved for the morphological events of the virus. This is the first evidence of assembly of seven structural proteins of the virus by a baculovirus expression system. Confirmation at the molecular level was obtained by determining the EHDV-1 L3 gene nucleic sequence and by comparing it with sequences available for BTV. The analysis revealed a high degree homology between the two proteins: 20% difference, 50% of which is conservative. The consequences for Orbivirus phylogeny and the possibility of gene reassortments are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown S. E., Gonzalez H. A., Bodkin D. K., Tesh R. B., Knudson D. L. Intra- and inter-serogroup genetic relatedness of orbiviruses. II. Blot hybridization and reassortment in vitro of epizootic haemorrhagic disease serogroup, bluetongue type 10 and Pata viruses. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):135–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French T. J., Marshall J. J., Roy P. Assembly of double-shelled, viruslike particles of bluetongue virus by the simultaneous expression of four structural proteins. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5695–5700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5695-5700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French T. J., Roy P. Synthesis of bluetongue virus (BTV) corelike particles by a recombinant baculovirus expressing the two major structural core proteins of BTV. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1530–1536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1530-1536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi H., Purdy M. A., Roy P. The complete sequence of bluetongue virus serotype 10 segment 3 and its predicted VP3 polypeptide compared with those of BTV serotype 17. Virus Res. 1985 Sep;3(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould A. R. The complete nucleotide sequence of bluetongue virus serotype 1 RNA3 and a comparison with other geographic serotypes from Australia, South Africa and the United States of America, and with other orbivirus isolates. Virus Res. 1987 Apr;7(2):169–183. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Bremer C. W., Barber T. L. The nucleic acid and proteins of epizootic haemorrhagic disease virus. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1979 Jun;46(2):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt A. D., Eaton B. T. Ultrastructural distribution of the major capsid proteins within bluetongue virus and infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1988 Apr;69(Pt 4):805–815. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-4-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inumaru S., Ghiasi H., Roy P. Expression of bluetongue virus group-specific antigen VP3 in insect cells by a baculovirus vector: its use for the detection of bluetongue virus antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1627–1635. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon P. T., Roy P. Assembly of five bluetongue virus proteins expressed by recombinant baculoviruses: inclusion of the largest protein VP1 in the core and virus-like proteins. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):798–802. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90094-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. J., Roy P. High level expression of the two outer capsid proteins of bluetongue virus serotype 10: their relationship with the neutralization of virus infection. Virus Res. 1990 Mar;15(3):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens P. P., Burroughs J. N., Anderson J. Purification and properties of virus particles, infectious subviral particles, and cores of bluetongue virus serotypes 1 and 4. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield S., Adachi A., Urakawa T., Hirasawa T., Roy P. Purification and characterization of the major group-specific core antigen VP7 of bluetongue virus synthesized by a recombinant baculovirus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2649–2656. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton H. A., Ihara T., Bishop D. H. Identification of the N and NSS proteins coded by the ambisense S RNA of Punta Toro phlebovirus using monospecific antisera raised to baculovirus expressed N and NSS proteins. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):338–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possee R. D. Cell-surface expression of influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. Virus Res. 1986 Jul;5(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possee R. D., Howard S. C. Analysis of the polyhedrin gene promoter of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10233–10248. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy M., Petre J., Roy P. Cloning of the bluetongue virus L3 gene. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):754–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.754-759.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. D., Kiuchi A., Roy P. Homologous terminal sequences of the genome double-stranded RNAs of bluetongue virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):378–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.378-383.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter D. G., Roy P. Genetic relationships of bluetongue virus serotypes isolated from different parts of the world. Virus Res. 1988 Aug;11(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Ritter G. D., Jr, Akashi H., Collisson E., Inaba Y. A genetic probe for identifying bluetongue virus infections in vivo and in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1613–1619. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mecham J. O., Holbrook F. R. Isolation and characterization of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus from sheep and cattle in Colorado. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1050–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwoerd D. W., Els H. J., De Villiers E. M., Huismans H. Structure of the bluetongue virus capsid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):783–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.783-794.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. C., Fukusho A., Roy P. Diagnostic complementary DNA probes for genome segments 2 and 3 of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 1. Am J Vet Res. 1990 Jun;51(6):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]