Abstract
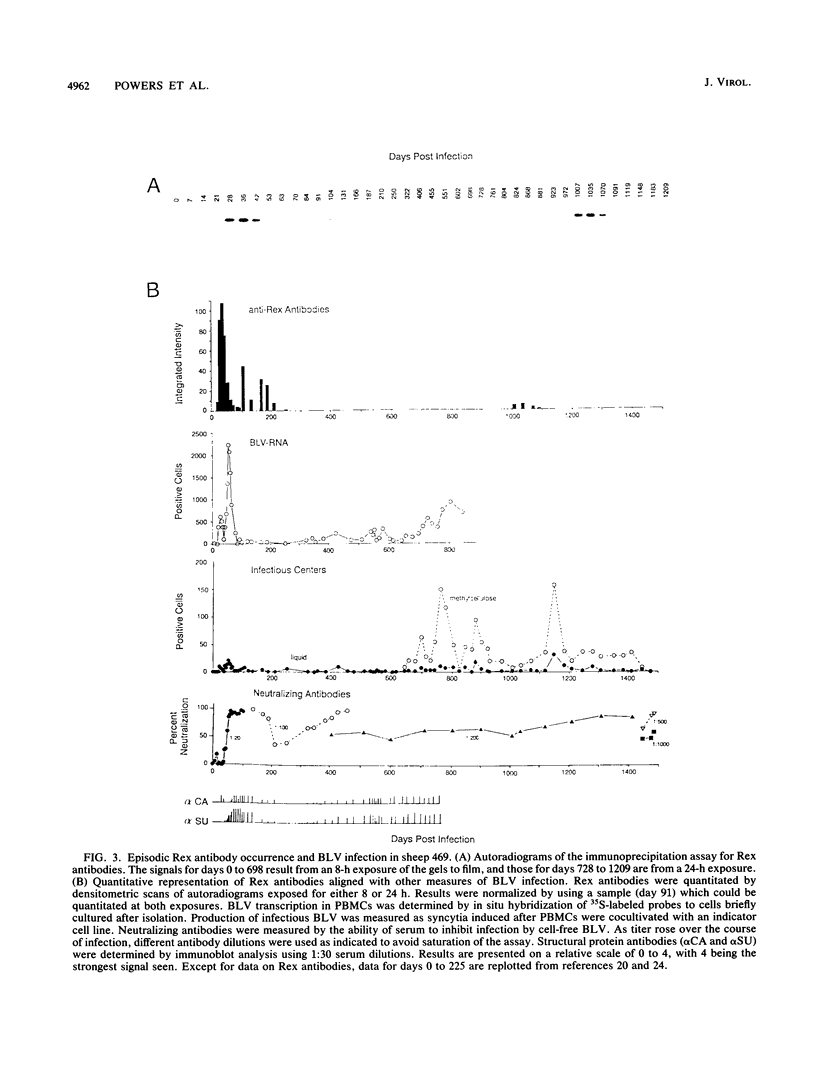
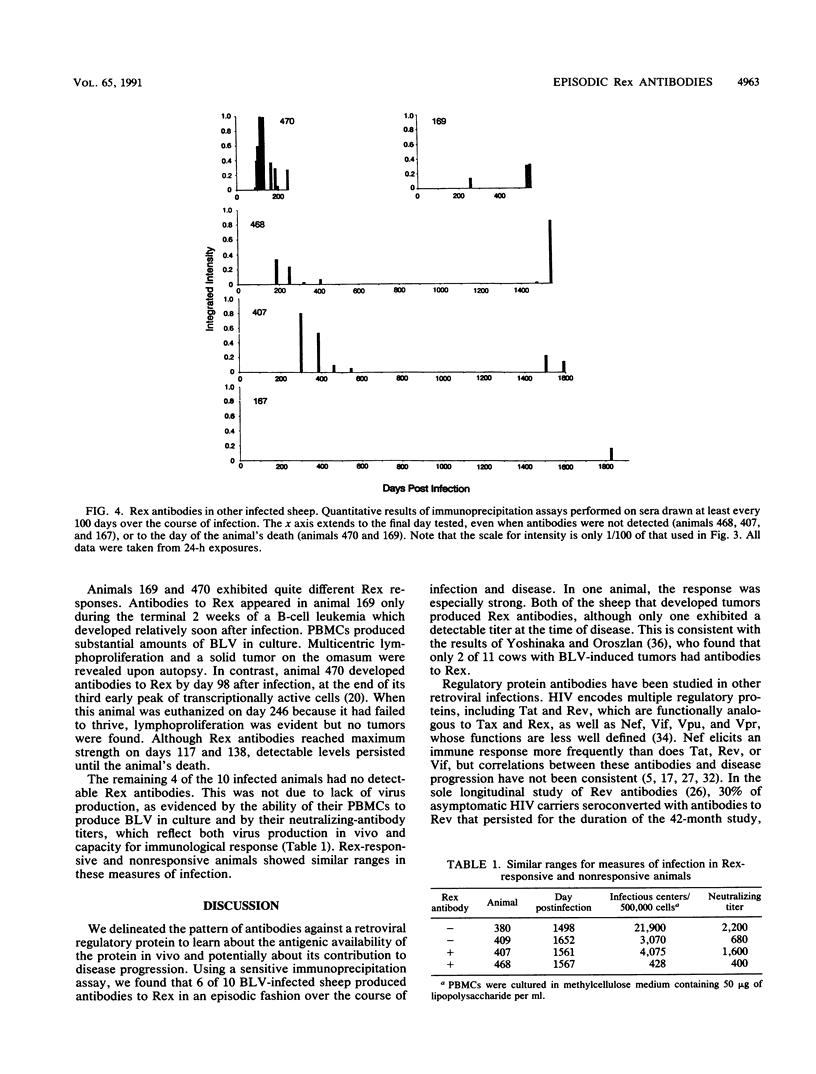
Infection by bovine leukemia virus (BLV) is characterized by a long clinical latency after which some individuals develop B-cell tumors. The contributions of the viral regulatory proteins Tax and Rex during clinical latency and disease are incompletely understood. To learn about Rex expression in the host, we used a sensitive immunoprecipitation assay to detect Rex antibodies throughout the course of BLV infection in sheep. Sixty percent of the infected animals produced Rex antibodies in intermittent episodes. This pattern differed markedly from that of antibodies to virion structural proteins, which were maintained in all animals throughout infection. Only one of two animals that developed tumors had detectable Rex antibodies at the time, although the other had previously demonstrated an especially strong Rex antibody response. We examined the Rex response in the context of BLV infection by comparing it with the frequency of circulating mononuclear blood cells that could transcribe BLV RNA or produce infectious virus. Episodes of Rex antibody occurrence followed some but not all increases in the number of BLV-transcribing cells. Since the appearance of circulating antibodies requires that the intracellular Rex protein be available to serve as antigen, the episodic pattern of occurrence of Rex antibodies could result from intermittent killing by virus-specific cytotoxic cells. Fluctuations in titer that were observed during some episodes of Rex response could be due to antibody retention by antigen present in lymphoid tissue.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burny A., Cleuter Y., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Marbaix G., Portetelle D., van den Broeke A., Willems L., Thomas R. Bovine leukaemia: facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Jul;17(3):197–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Okayama A., Lee T. H., Tachibana N., Mueller N., Essex M. Sexual transmission of human T-cell leukemia virus type I associated with the presence of anti-Tax antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Kettmann R., Burny A. Experiments with cloned complete tumor-derived bovine leukemia virus information prove that the virus is totally exogenous to its target animal species. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):605–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.605-609.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devash Y., Reagan K., Wood D., Turner J., Parrington M., Kang C. Y. Antibodies against AIDS proteins. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):581–581. doi: 10.1038/345581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich G. D., Glaser J. B., Abbott M. A., Slamon D. J., Keith D., Sliwkowski M., Brandis J., Keitelman E., Teramoto Y., Papsidero L. Detection of anti-HTLV-I Tax antibodies in HTLV-I enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-negative individuals. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):1066–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farzadegan H., Polis M. A., Wolinsky S. M., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Sninsky J. J., Kwok S., Griffith R. L., Kaslow R. A., Phair J. P., Polk B. F. Loss of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) antibodies with evidence of viral infection in asymptomatic homosexual men. A report from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jun;108(6):785–790. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-6-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. L., Chen I. S. Regulation of human T cell leukemia virus expression. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):169–175. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Gotoh Y., Sugamura K., Nagata K., Goto T., Nakai M., Kamada N., Matsumoto T., Kinoshita K. A retrovirus associated with human adult T-cell leukemia: in vitro activation. Gan. 1982 Apr;73(2):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Shida H., McFarlin D. E., Fauci A. S., Koenig S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurological disease. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):245–248. doi: 10.1038/348245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamihira S., Toriya K., Amagasaki T., Momita S., Ikeda S., Yamada Y., Tomonaga M., Ichimaru M., Kinoshita K., Sawada T. Antibodies against p40tax gene product of human T-lymphotropic virus type-I (HTLV-I) under various conditions of HTLV-I infection. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 Nov;80(11):1066–1071. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb02260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi S., Kajiyama W., Hayashi J., Noguchi A., Nakashima K., Nomura H., Ikematsu H., Sawada T., Kida S., Koide A. Antibody to p40tax protein of human T cell leukemia virus 1 and infectivity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):426–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Marbaix G., Cleuter Y., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus and lack of viral RNA expression in the target cells of cattle with different responses to BLV infection. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krone W. J., Debouck C., Epstein L. G., Heutink P., Meloen R., Goudsmit J. Natural antibodies to HIV-tat epitopes and expression of HIV-1 genes in vivo. J Med Virol. 1988 Nov;26(3):261–270. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890260306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias D. M., Radke K. Transcriptional activation of bovine leukemia virus in blood cells from experimentally infected, asymptomatic sheep with latent infections. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2099–2107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2099-2107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias D. M., Radke K. Transient increases of blood mononuclear cells that could express bovine leukemia virus early after experimental infection of sheep. Microb Pathog. 1990 Sep;9(3):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90018-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Paul D. A., de Wolf F., Coutinho R. A., Goudsmit J. Viral gene expression, antibody production and immune complex formation in human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1987 May;1(1):15–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Grossman D., Kidd L. C. Humoral immune response of experimentally infected sheep defines two early periods of bovine leukemia virus replication. Microb Pathog. 1990 Sep;9(3):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90019-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss P., De Ronde A., Lange J. M., De Wolf F., Dekker J., Danner S. A., Debouck C., Goudsmit J. Low antigenicity of HIV-1 rev: rev-specific antibody response of limited value as correlate of rev gene expression and disease progression. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Dec;5(6):621–628. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss P., de Ronde A., Lange J. M., de Wolf F., Dekker J., Debouck C., Goudsmit J. Antibody response to the viral negative factor (nef) in HIV-1 infection: a correlate of levels of HIV-1 expression. AIDS. 1989 Apr;3(4):227–233. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198904000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock N. D., Ferrer J. F. Replicating C-type virus in phytohemagglutinin-treated buffy-coat cultures of bovine origin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Apr;48(4):985–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Plata F. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against HIV. AIDS. 1990 Mar;4(3):177–184. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199003000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. N., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Parker D., Roberts C., Duncan J., Weller I., Carne C., Tedder R. S., Pinching A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in two cohorts of homosexual men: neutralising sera and association of anti-gag antibody with prognosis. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland U., Kühn J. E., Jassoy C., Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Wolber V., Braun R. W. Antibodies to recombinant HIV-1 vif, tat, and nef proteins in human sera. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1990;179(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00190145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Bruck C., Portetelle D., Burny A., Kettmann R. Expression of a cDNA clone corresponding to the long open reading frame (XBL-I) of the bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Cho M. J., Tachibana N., McLane M. F., Takatsuki K., Lee T. H., Mueller N., Essex M. The prevalence of antibody to p42 of HTLV-I among ATLL patients in comparison with healthy carriers in Japan. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jun 15;43(6):970–974. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Oroszlan S. Bovine leukemia virus post-envelope gene coded protein: evidence for expression in natural infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91809-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]