Abstract
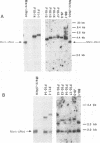
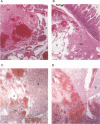
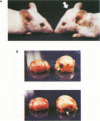
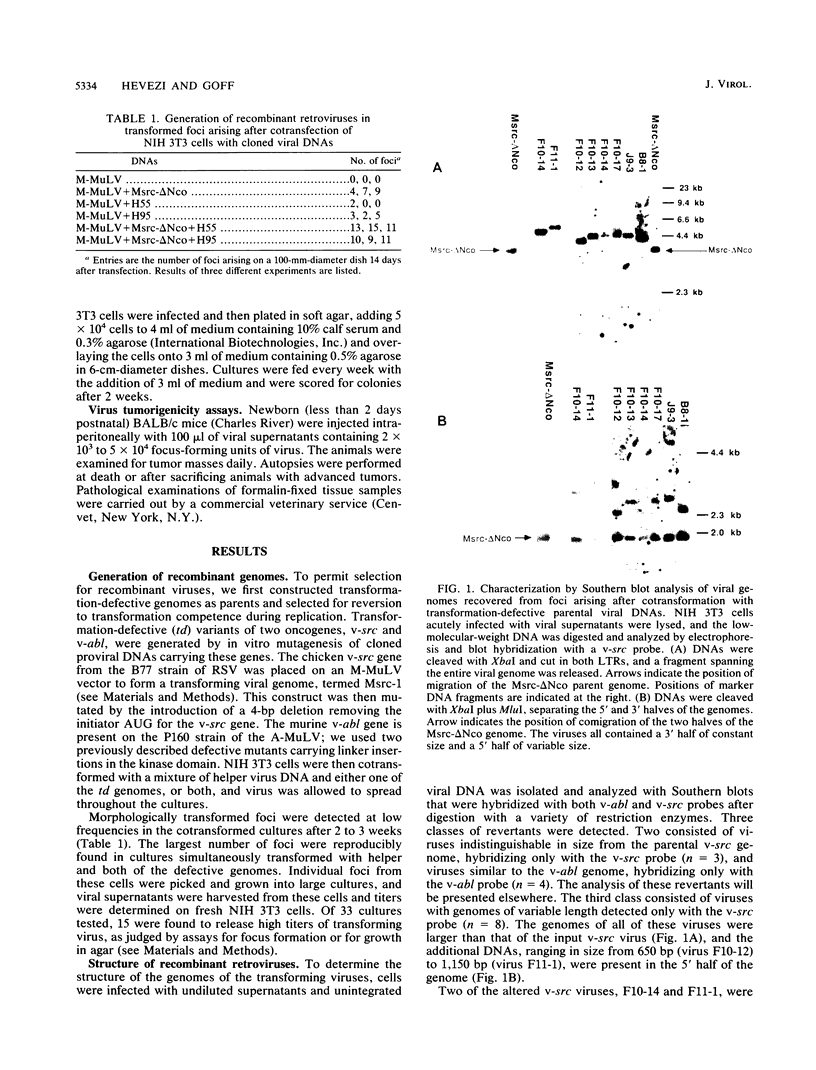
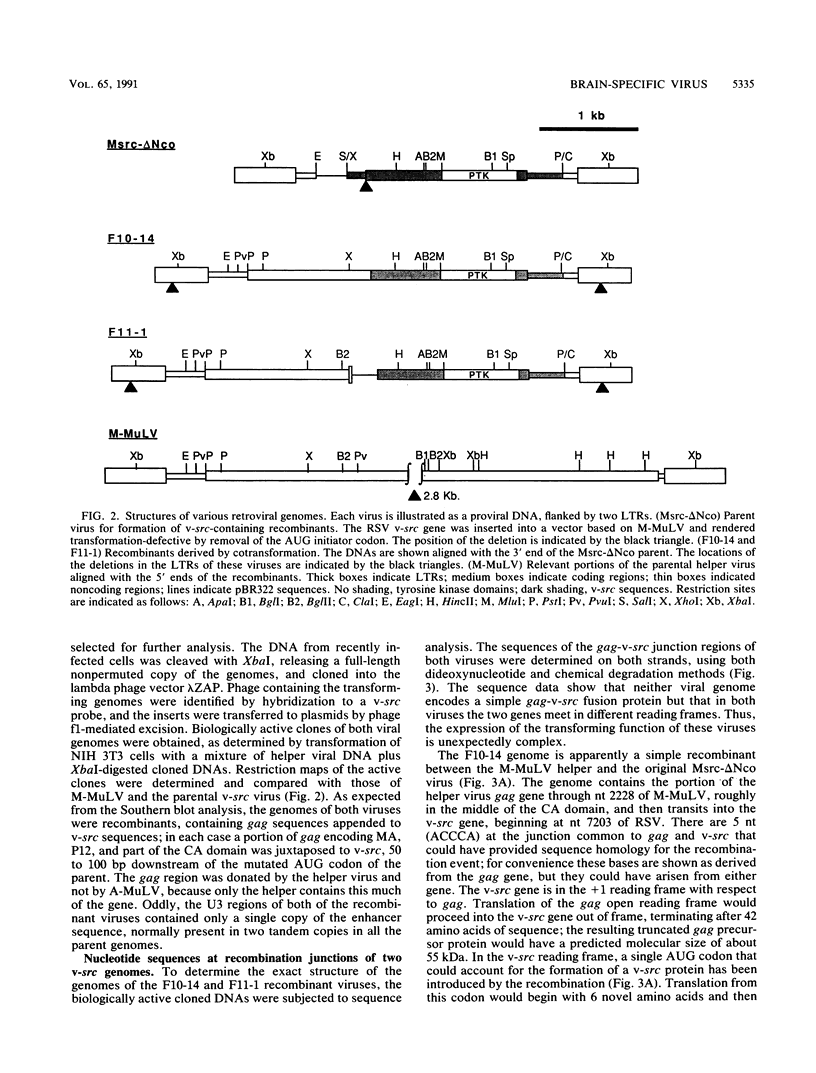
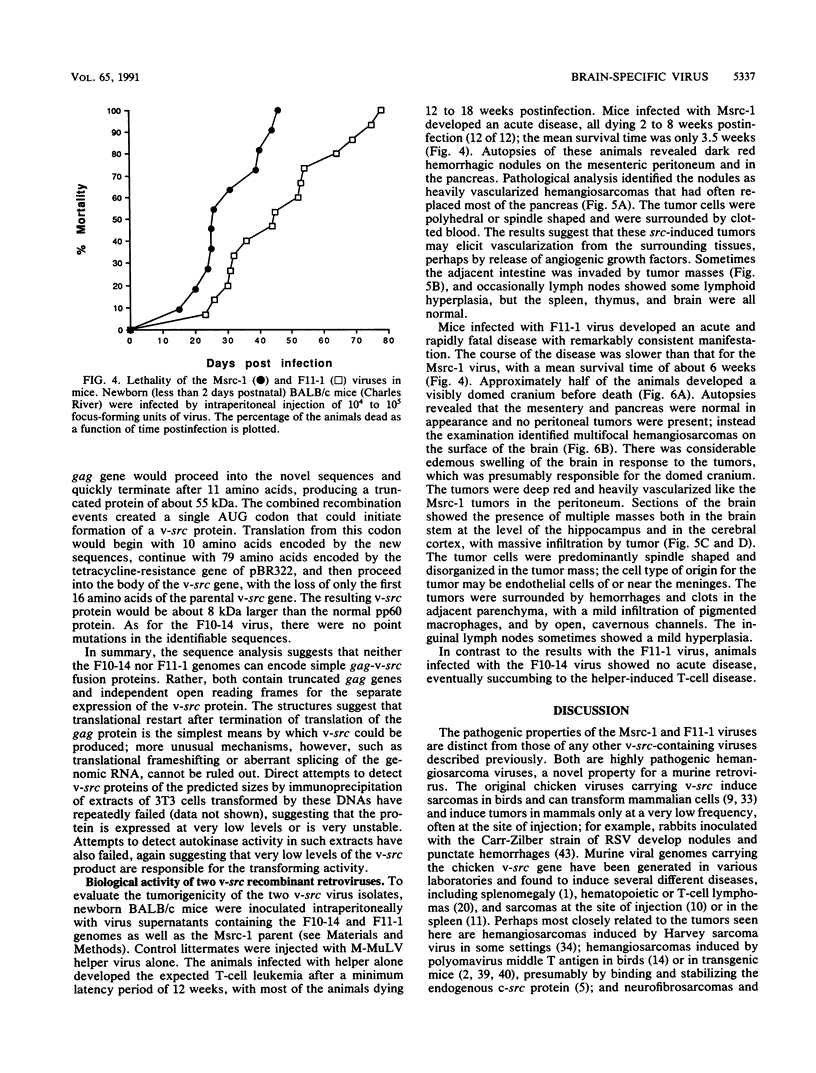
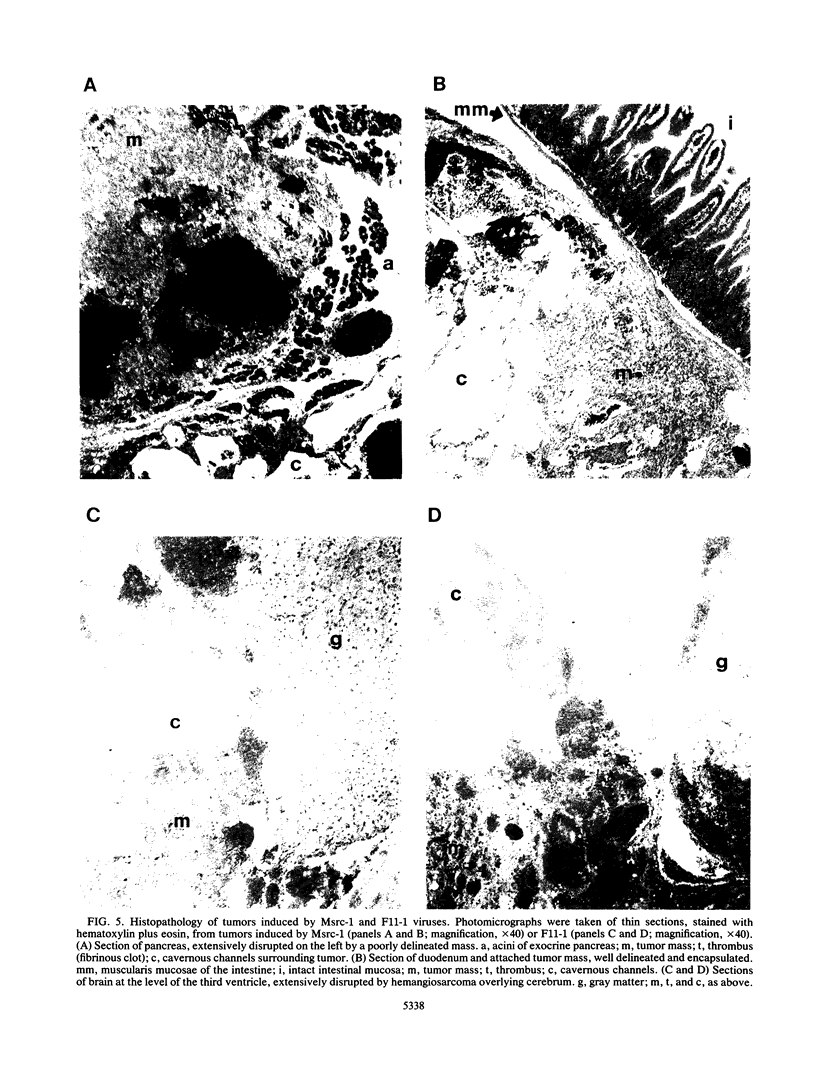
A series of recombinant retroviral genomes was generated by cotransformation of NIH 3T3 cells with a mixture of cloned DNAs: a proviral copy of the wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus, and Moloney-based vectors containing defective copies of the chicken v-src and the murine v-abl oncogenes. Morphologically transformed foci, appearing at low frequencies in these cultures, released high titers of transforming viruses. Analysis of one group of these viruses showed that the genomes were recombinants containing portions of the viral gag gene juxtaposed to the v-src oncogene. Biologically active cloned DNAs of two of these viruses were obtained and mapped in detail. One of these viruses did not cause disease after inoculation into newborn mice, but the other induced rapidly fatal hemangiosarcomas located exclusively in the brain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. M., Scolnick E. M. Construction and isolation of a transforming murine retrovirus containing the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):594–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.594-605.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L., Toda S., Hassell J. A., Hanahan D. Endothelial cell tumors develop in transgenic mice carrying polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):529–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterman F. C., Harvey J. J., Dourmashkin R. R., Salaman M. H. The pathology of tumors and other lesions induced in rodents by virus derived from a rat with Moloney leukemia. Cancer Res. 1966 Aug;26(8):1759–1768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Barrette M., Jolicoeur P. Physical mapping of the paralysis-inducing determinant of a wild mouse ecotropic neurotropic retrovirus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.356-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced spongiform encephalopathy: the 3'-end long terminal repeat-containing viral sequences influence the incidence of the disease and the specificity of the neurological syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8818–8822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diglio C. A., Wolfe D. E., Meyers P. Transformation of rat cerebral endothelial cells by Rous sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):15–21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Davis B. R., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Generation of a recombinant Moloney murine leukemia virus carrying the v-src gene of avian sarcoma virus: transformation in vitro and pathogenesis in vivo. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):804–816. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.804-816.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Lee W. T., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Comparison of three recombinant murine leukemia viruses carrying the v-src oncogene of avian sarcoma virus: differences in in vitro transformation and in vivo pathogenicity. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(1):57–66. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., DesGroseillers L. Neurotropic Cas-BR-E murine leukemia virus harbors several determinants of leukemogenicity mapping in different regions of the genome. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):639–643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.639-643.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Cross F. R., Harbison M., Hanafusa H. Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts and tumor induction by the middle T antigen of polyomavirus carried in an avian retroviral vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1545–1551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumanishi T., Ikuta F., Yamamoto T. Brain tumors induced by Rous sarcoma virus, Schmidt-Ruppin strain. 3. Morphology of brain tumors induced in adult mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jan;50(1):95–109. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon G., Varmus H. E. Frameshift and intragenic suppressor mutations in a Rous sarcoma provirus suggest src encodes two proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):871–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Aaronson S. A., Anderson S. M. Hematopoietic cell transformation by a murine recombinant retrovirus containing the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABOTTI G. F., RAINE W. A. BRAIN TUMOURS INDUCED IN HAMSTERS INOCULATED INTRACEREBRALLY AT BIRTH WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1964 Nov 28;204:898–899. doi: 10.1038/204898a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABOTTI G. F., RAINE W. A., SELLERS R. L. BRAIN TUMORS (GLIOMAS) INDUCED IN HAMSTERS BY BRYAN'S STRAIN OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Science. 1965 Jan 29;147(3657):504–506. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3657.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabotti G. F., Grove A. S., Jr, Sellers R. L., Anderson W. R. Induction of multiple brain tumours (gliomata and leptomeningeal sarcomata) in dogs by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1966 Feb 26;209(5026):884–886. doi: 10.1038/209884a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabotti G. F., Sellers R. L., Anderson W. A. Leptomeningeal sarcomata and gliomata induced in rabbits by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1966 Jan 29;209(5022):524–526. doi: 10.1038/209524b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees-Jones R. W., Goff S. P. Insertional mutagenesis of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: identification of mutants with altered kinase activity and defective transformation ability. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):978–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.978-986.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. The viral and cellular forms of the Abelson (abl) oncogene. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:39–81. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60708-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Scolnick E. M., Siegler R. Induction of erythroid leukaemia by Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):225–226. doi: 10.1038/256225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. R., Aw E. J., Papadimitriou J. M., Simons P. J. In vivo and in vitro studies on the morphogenesis of tumors induced by murine sarcoma virus (Harvey). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1541–1549. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Beckson M., Anderson S. M., Hanafusa H. Identification of the viral sequence required for the generation of recovered avian sarcoma viruses and characterization of a series of replication-defective recovered avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):881–891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.881-891.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Edelstein B., Mayer B. J. Induction of tumors and generation of recovered sarcoma viruses by, and mapping of deletions in, two molecularly cloned src deletion mutants. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):904–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.904-913.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Avian sarcoma viruses. Virus Res. 1988 Feb;9(2-3):159–203. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Moscovici C., Karess R. E., Hanafusa H. Analysis of the src gene of sarcoma viruses generated by recombination between transformation-defective mutants and quail cellular sequences. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.546-556.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Courtneidge S. A., Wagner E. F. Embryonic lethalities and endothelial tumors in chimeric mice expressing polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Risau W., Zerwes H. G., Drexler H., Aguzzi A., Wagner E. F. Endothelioma cells expressing the polyoma middle T oncogene induce hemangiomas by host cell recruitment. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Mock D., Greer P., Maltby V., Rossant J., Bernstein A., Pawson T. Lymphoid and mesenchymal tumors in transgenic mice expressing the v-fps protein-tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5491–5499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Yamashita M., Nomoto A. Transformation-defective mutants of Rous sarcoma virus with longer sizes of genome RNA and their highly frequent occurrences. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):453–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.453-461.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilber L. A. Pathogenicity and oncogenicity of Rous sarcoma virus for mammals. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1965;7:1–48. doi: 10.1159/000391376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]