Abstract
Studies coordinated by the World Health Organization were conducted in seven clinical centres on the chemotherapy of human echinococcosis with mebendazole, albendazole, and flubendazole. The first phase of these ended with the following conclusions.
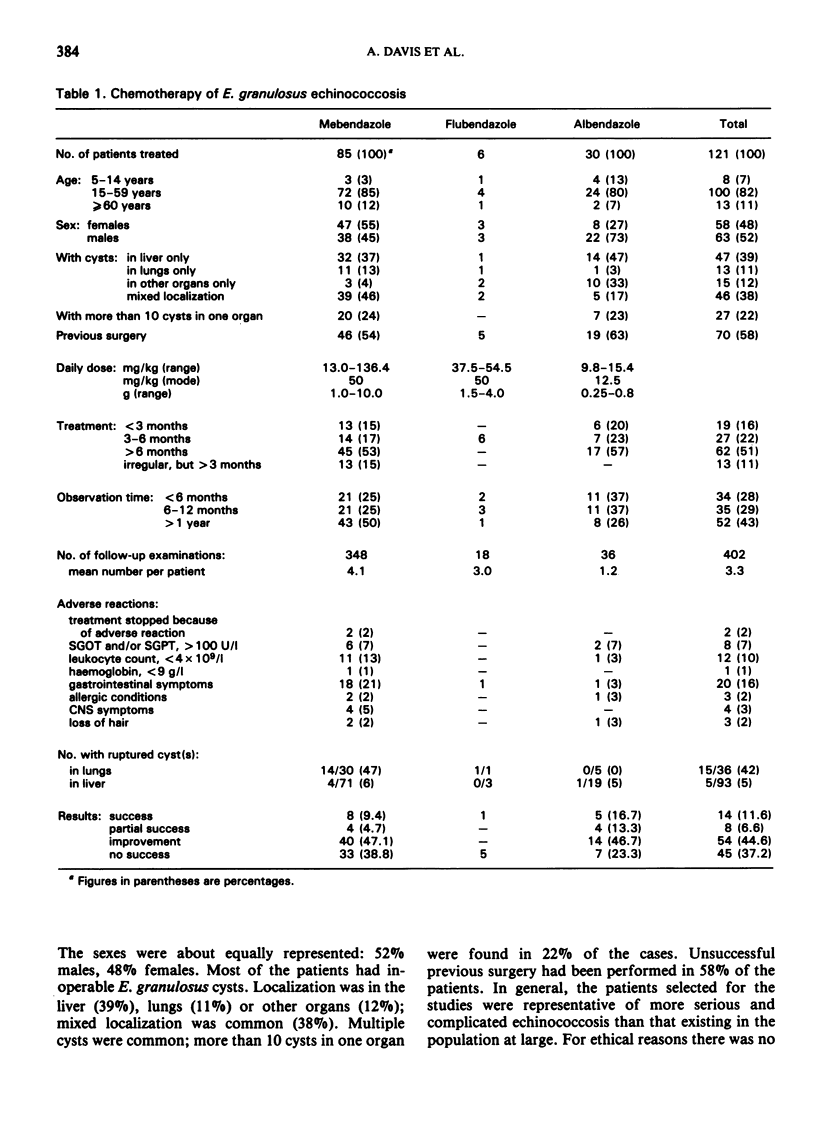
Treatment of 85 patients with mebendazole for cystic (Echinococcus granulosus) echinococcosis was successful in 8 patients and partially successful in 4 others. Flubendazole was effective in only one case of lung echinococcosis. Albendazole was successful in 5 of 30 patients treated and partially successful in 4 others. Further studies on new drugs or new formulations of existing benzimidazoles and on better forms of their application are needed. In the mean time, chemotherapy of human cystic echinococcosis should be restricted to inoperable cases.
In 54 patients with E. multilocularis echinococcosis, it was confirmed that mebendazole therapy may arrest the development of the lesions. This treatment is therefore indicated in most cases of alveolar echinococcosis with or without surgery. However, further studies are needed to clarify the optimal regimen for mebendazole treatment and to explore the effectiveness of albendazole therapy.
Full text
PDF