Abstract
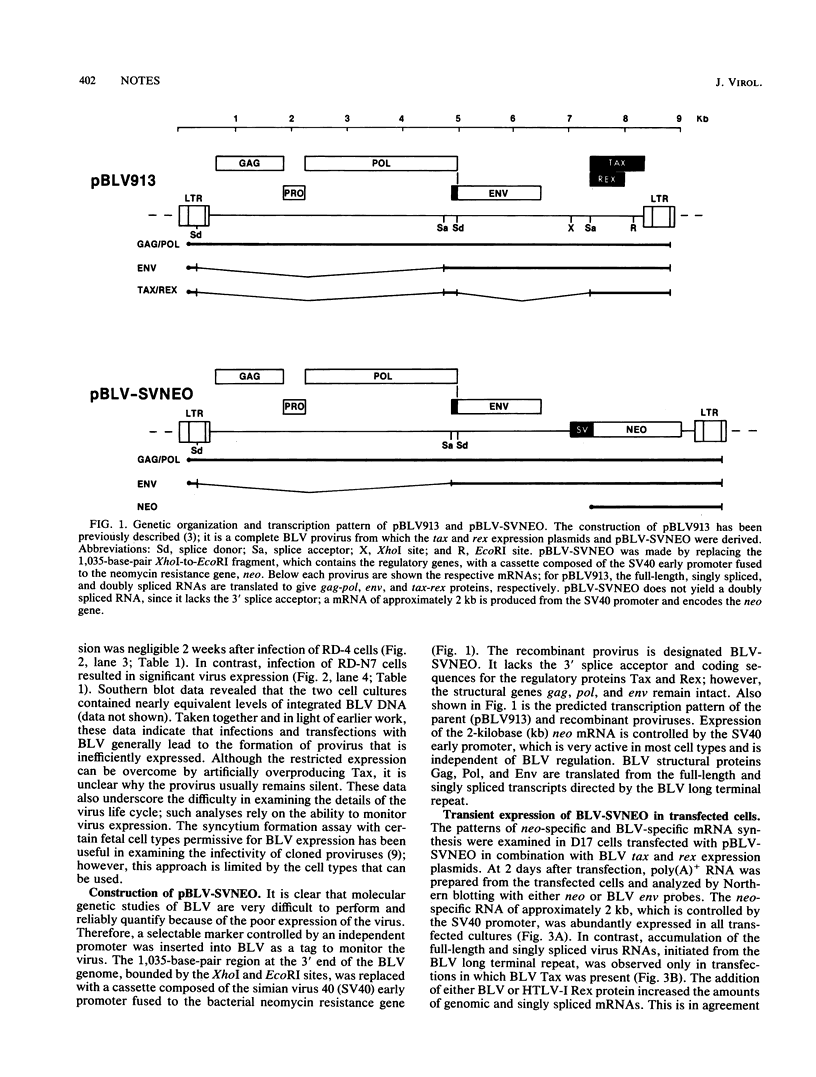
A recombinant bovine leukemia virus (BLV) was constructed in which the X region was replaced with the bacterial neomycin resistance gene controlled by the simian virus 40 early promoter. This virus, termed BLV-SVNEO, is a self-packaging, activator-dependent retroviral vector. Introduction of the plasmid pBLV-SVNEO into mammalian cells resulted in constitutive expression of the neo gene, whereas the BLV structural genes, gag, pol, and env, were expressed only in the presence of the two regulatory proteins, Tax and Rex. The production and release of recombinant virus by cells transfected with pBLV-SVNEO were proportional to the number of G418-resistant colonies that developed after susceptible cells were exposed to the filtered culture medium. BLV-SVNEO was able to infect cell lines of human, bovine, canine, feline, and murine origin. BLV-producing cell lines were resistant to superinfection with BLV-SVNEO. This cell-virus system should facilitate molecular genetic studies of BLV and will provide a rapid, quantitative measure of BLV infectivity in a variety of cell types. These studies also demonstrate the feasibility of using activator-dependent retroviral vectors such as BLV-SVNEO to deliver foreign genes into cells and eventually animals.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Derse D. Bovine leukemia virus transcription is controlled by a virus-encoded trans-acting factor and by cis-acting response elements. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2462–2471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2462-2471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1115-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djilali S., Parodi A. L., Levy D. Bovine leukemia virus replicates in sheep B lymphocytes under a T cell released factor. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Jan;23(1):81–85. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djilali S., Parodi A. L., Levy D., Cockerell G. L. Development of leukemia and lymphosarcoma induced by bovine leukemia virus in sheep: a hematopathological study. Leukemia. 1987 Nov;1(11):777–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghysdael J., Bruck C., Kettmann R., Burny A. Bovine leukemia virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;112:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69677-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., Ferrer J. F. In vitro transmission and propagation of the bovine leukemia virus in monolayer cell cultures. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 1):4152–4159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoss H. E., Olson C. Infectivity of bovine C- type (leukemia) virus for sheep and goats. Am J Vet Res. 1974 May;35(5):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itohara S., Sekikawa K. Molecular cloning of infectious proviral genomes of bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):158–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Sagata N., Ikawa Y. The bovine leukemia virus X region encodes a trans-activator of its long terminal repeat. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Feb;78(2):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Cleuter Y., Couez D., Burny A., Marbaix G. Leukemogenesis by bovine leukemia virus: proviral DNA integration and lack of RNA expression of viral long terminal repeat and 3' proximate cellular sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Marbaix G., Cleuter Y., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Burny A. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus and lack of viral RNA expression in the target cells of cattle with different responses to BLV infection. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy D., Kettmann R., Marchand P., Djilali S., Parodi A. L. Selective tropism of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) for surface immunoglobulin-bearing ovine B lymphocytes. Leukemia. 1987 May;1(5):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamoun R. Z., Astier-Gin T., Kettmann R., Deschamps J., Rebeyrotte N., Guillemain B. J. The pX region of the bovine leukemia virus is transcribed as a 2.1-kilobase mRNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):625–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.625-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nötzel U., Drescher B., Rosenthal S. Detection of bovine leukaemia virus RNA sequences in non-cultivated peripheral lymphocytes by in situ hybridization with 3H-labelled viral cDNA. Acta Virol. 1982 Jan;26(1-2):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Pomeroy K. A., Johnson D. W., Muscoplat C. C., Handwerger B. S., Soper F. F., Sorensen D. K. Evidence for the replication of bovine leukemia virus in the B lymphocytes. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jun;38(6):873–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Simek S. L., Dubois G. C., Showalter S. D., Gilden R. V., Stephens R. M. Expression of the bovine leukemia virus X region in virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1577–1585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1577-1585.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Willems L., Kettmann R., Campbell K., Zaya R., Burny A., Haseltine W. A. The 3' region of bovine leukemia virus genome encodes a trans-activator protein. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2585–2589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04538.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Nagayoshi-Aida M., Shimizu F., Imagawa K., Ikawa Y. Identification and some biochemical properties of the major XBL gene product of bovine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7879–7883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Ikawa Y. Two distinct polypeptides may be translated from a single spliced mRNA of the X genes of human T-cell leukemia and bovine leukemia viruses. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfelt M. A., Williams B. P., Clapham P. R., Solomon E., Goodfellow P. N., Weiss R. A. Human T cell leukemia viruses use a receptor determined by human chromosome 17. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.3201246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeke A., Cleuter Y., Chen G., Portetelle D., Mammerickx M., Zagury D., Fouchard M., Coulombel L., Kettmann R., Burny A. Even transcriptionally competent proviruses are silent in bovine leukemia virus-induced sheep tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9263–9267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Gegonne A., Chen G., Burny A., Kettmann R., Ghysdael J. The bovine leukemia virus p34 is a transactivator protein. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3385–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]