Abstract
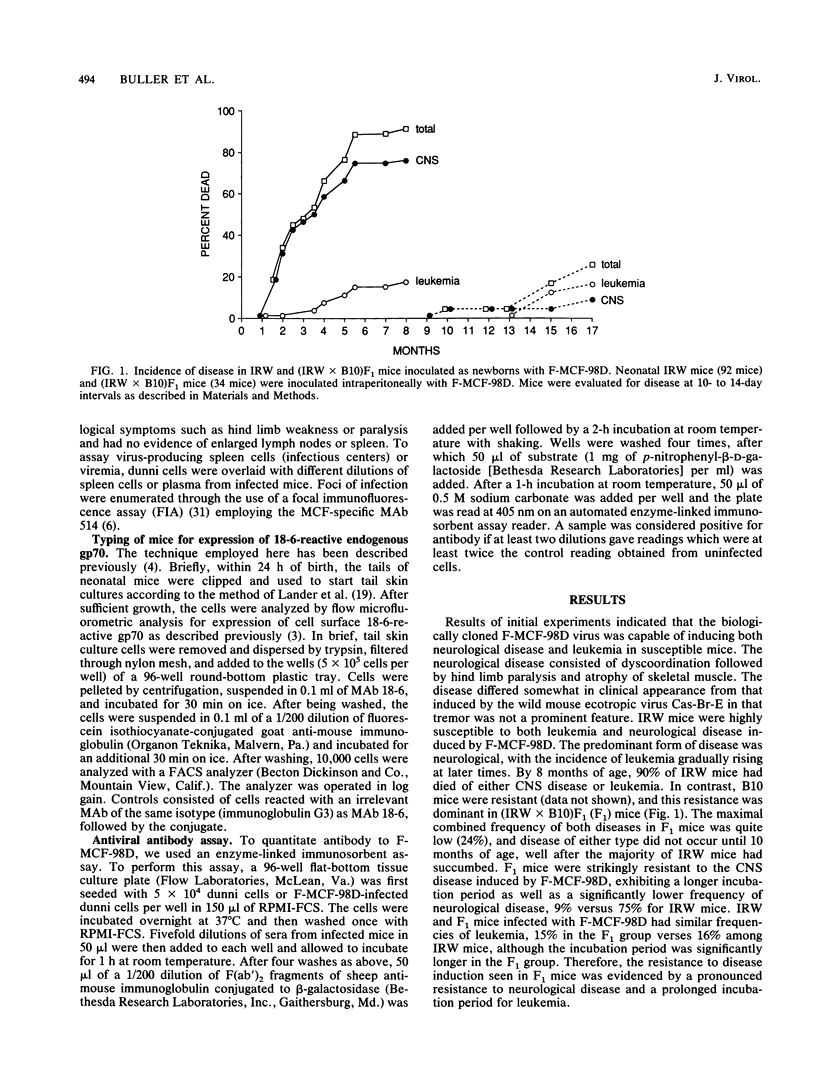
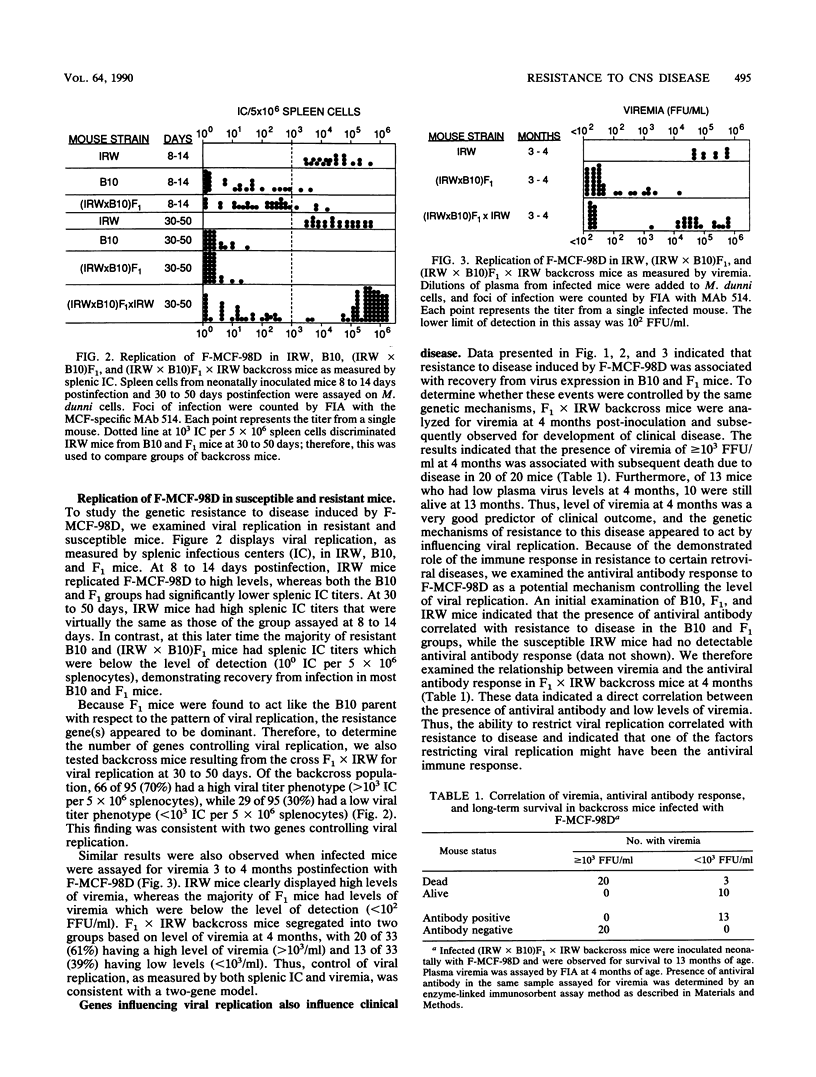
Infection of certain strains of mice with the ecotropic Friend murine leukemia virus results in the generation of recombinant polytropic mink cell focus-inducing viruses and the development of erythroleukemia. We isolated a Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus (F-MCF-98D) from a Friend murine leukemia virus-infected BALB/c mouse which caused primarily a neurological disease as well as a low incidence of leukemia in susceptible IRW mice. Through genetic studies with the resistant C57BL/10 strain, we identified two genes which correlated with restricted viral replication and resistance to the development of disease caused by F-MCF-98D. One gene correlated with the expression of an endogenous gp70 linked to the Rmcf gene and might act by viral interference. The mechanism of action of the second gene was less clear, but it appeared to be associated with development of an antiviral antibody response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Widespread natural occurrence of high titers of neutralizing antibodies to a specific class of endogenous mouse type-C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1957–1961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. S., Ahmed A., Portis J. L. Identification of two forms of an endogenous murine retroviral env gene linked to the Rmcf locus. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.29-34.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. S., Sitbon M., Portis J. L. The endogenous mink cell focus-forming (MCF) gp70 linked to the Rmcf gene restricts MCF virus replication in vivo and provides partial resistance to erythroleukemia induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1535–1546. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. S., Van Zant G., Eldridge P. W., Portis J. L. A population of murine hematopoietic progenitors expresses an endogenous retroviral gp70 linked to the Rmcf gene and associated with resistance to erythroleukemia. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):865–880. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Wehrly K., Nishio J. Effect of murine host genotype on MCF virus expression, latency, and leukemia cell type of leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia helper virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Different murine cell lines manifest unique patterns of interference to superinfection by murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Rfv-1 and Rfv-2, two H-2-associated genes that influence recovery from Friend leukemia virus-induced splenomegaly. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1081–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Genetic study of lymphoma induction by AKR mink cell focus-inducing virus in AKR x NFS crosses. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):450–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig D., Chesebro B. Anti-Friend virus antibody is associated with recovery from viremia and loss of viral leukemia cell-surface antigens in leukemic mice. Identification of Rfv-3 as a gene locus influencing antibody production. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):10–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd A mouse gene on chromosome 5 that restricts infectivity of mink cell focus-forming recombinant murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):16–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Host genetic determinants of neurological disease induced by Cas-Br-M murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):40–43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.40-43.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Robbins D. S., Morse H. C., 3rd Role of immunity in age-related resistance to paralysis after murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):734–738. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.734-738.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Yorifuji T., Tsuruta S. Rapid emergence of mink cell focus-forming (MCF) virus in various mice infected with NB-tropic friend virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):644–655. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Gromet N. J., Ikeda H., Buckler C. E. A unique sequence related to the ecotropic murine leukemia virus is associated with the Fv-4 resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):834–837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa M., Nishio J., Chesebro B. Genetic control of T cell responsiveness to the Friend murine leukemia virus envelope antigen. Identification of class II loci of the H-2 as immune response genes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1587–1605. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Brown M., Doyle T., Prentice R. L. Genetic and viral factors influencing the development of spontaneous leukemia in AKR mice. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):186–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C. Genetic control of natural immunity to ecotropic mouse leukemia viruses: immune response genes. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1098–1102. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1098-1102.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Kaehler S. L. Antibody to leukemia virus: widespread occurrence in inbred mice. Science. 1974 Sep 6;185(4154):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4154.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Kaehler S. L., Baron J. Genetic control of natural immunity to ecotropic mouse leukemia viruses: production of endogenous immunogen. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1091-1097.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. II. Role of virus and host gene products. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):180–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J., Cloyd M. W. Monoclonal antibodies to xenotropic and MCF murine leukemia viruses derived during the graft-versus-host reaction. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Feild J., Davis L., Oliff A. Factors determining the susceptibility of NIH swiss mice to erythroleukemia induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1982 Mar;117(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90475-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. Role of mink cell focus-inducing virus in leukemias induced by Friend ecotropic virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):872–877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.872-877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Axelrad A. A. Fv-2 locus controls the proportion of erythropoietic progenitor cells (BFU-E) synthesizing DNA in normal mice. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90404-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S. FV-4: a new gene affecting the splenomegaly induction by Friend leukemia virus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1975 Dec;45(6):473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Yuan E., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Scolnick E. M. Helper-independent mink cell focus-inducing strains of Friend murine type-C virus: potential relationship to the origin of replication-defective spleen focus-forming virus. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):639–653. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker HSt, Weens J., Tsichlis P., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R., Donnelly J. Influence of H-2 complex on susceptibility to infection by murine leukemia virus. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1239–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlug A., Melief C. J., de Bruyne C., Schoenmakers H., Molenaar J. L. Naturally occurring leukemia viruses in H-2 congenic C57BL mice. II. Antibody response to viral envelope antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1191–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlug A., Schoenmakers H. J., Melief C. J. Genes of the H-2 complex regulate the antibody response to murine leukemia virus. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2355–2360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


