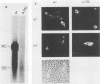
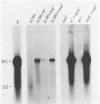
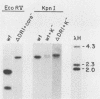
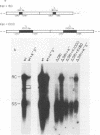
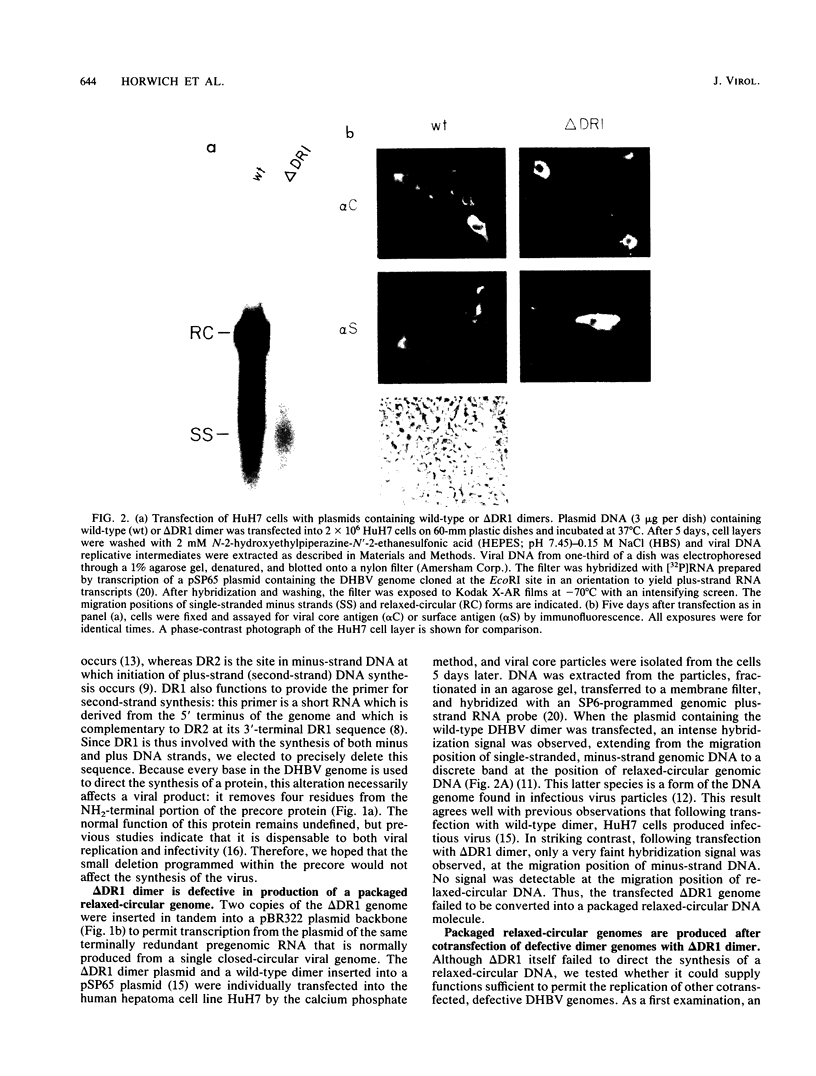
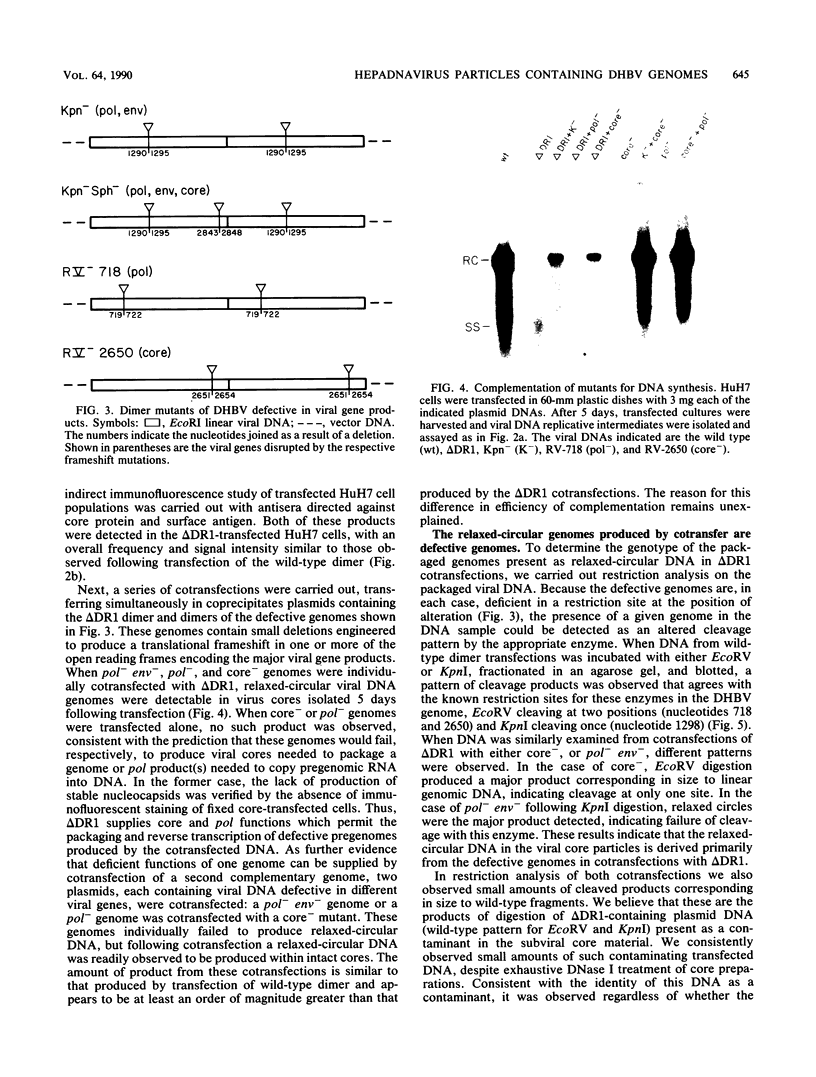
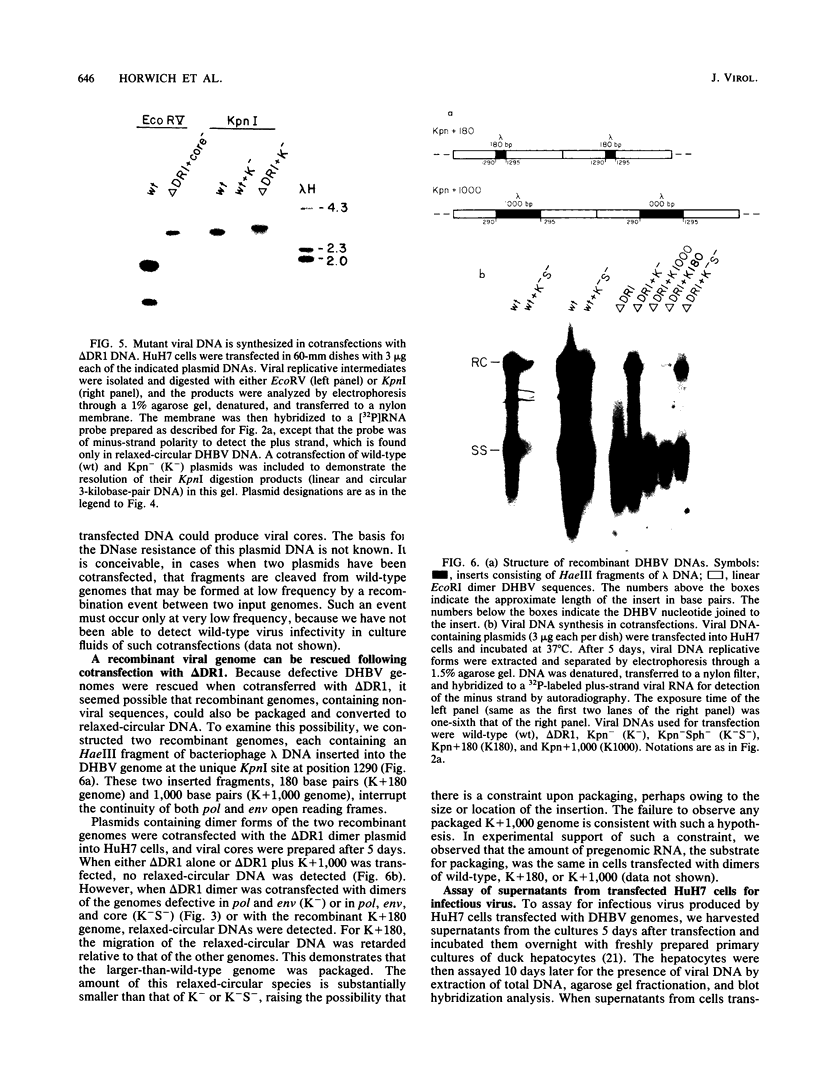
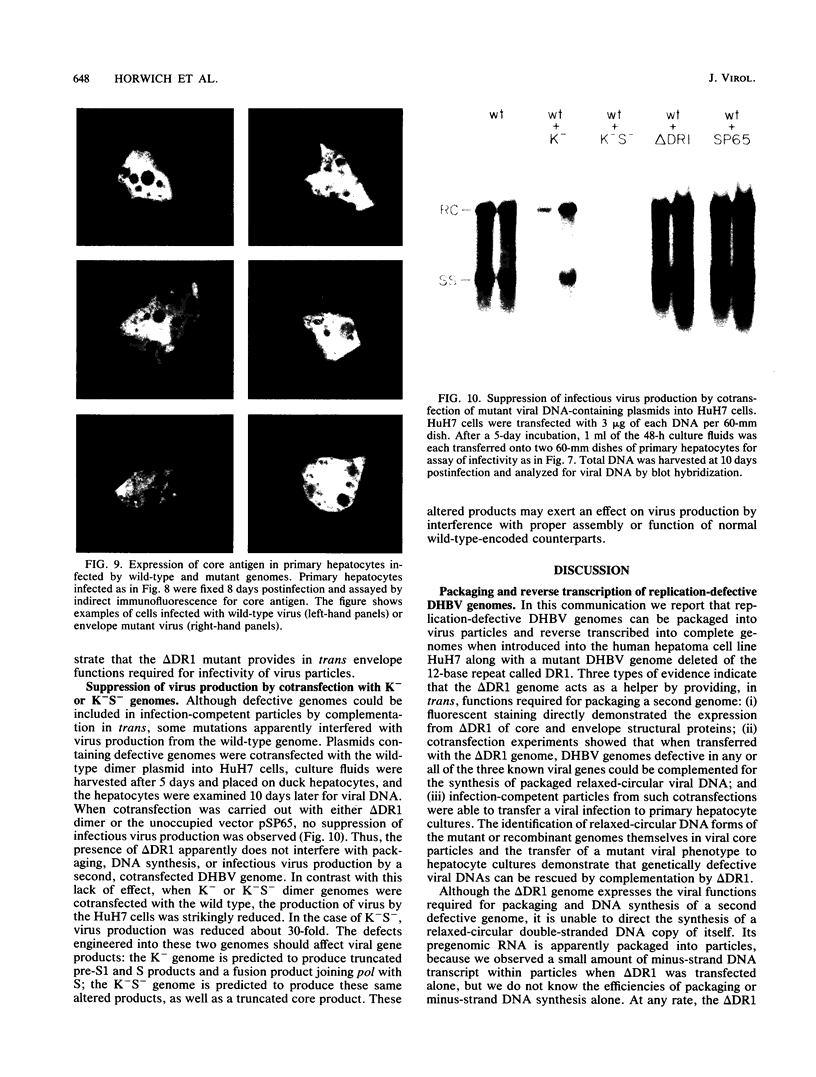
Abstract
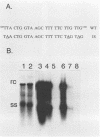
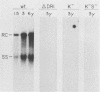
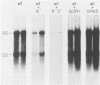
To evaluate the possibility of producing transducible replication-defective hepadnaviruses, cloned mutant duck hepatitis B virus genomes were tested both for virus antigen production and viral DNA synthesis following transfection into the human hepatoma cell line HuH7. Deletion of a cis-acting 12-nucleotide sequence implicated in viral DNA synthesis, direct repeat 1 (DR1), resulted in the loss of ability to synthesize both mature viral DNA and infectious virus. The delta DR1 mutant, however, produced envelope and core antigens and was shown to provide trans-acting functions required for the assembly of infection-competent particles. Thus, mutants with mutations in viral genes could be rescued as DNA-containing viral particles after cotransfection with delta DR1. The efficiency of rescue was influenced by the site of mutation. A mutant DNA encoding truncated core and envelope proteins not only was poorly rescued but also was able to suppress the production from a wild-type DNA of infectious virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büscher M., Reiser W., Will H., Schaller H. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle P. R., Schlicht H. J., Fischer M., Schaller H. Production of infectious duck hepatitis B virus in a human hepatoma cell line. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1736–1740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1736-1740.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledley F. D., Darlington G. J., Hahn T., Woo S. L. Retroviral gene transfer into primary hepatocytes: implications for genetic therapy of liver-specific functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5335–5339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Evidence that a capped oligoribonucleotide is the primer for duck hepatitis B virus plus-strand DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.229-236.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Initiation and termination of duck hepatitis B virus DNA synthesis during virus maturation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3832–3840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3832-3840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Aldrich C., Summers J., Taylor J. M. Asymmetric replication of duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver cells: Free minus-strand DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K. L., Summers J. W., Mason W. S. Mapping of the cohesive overlap of duck hepatitis B virus DNA and of the site of initiation of reverse transcription. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):181–191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.181-191.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Yaginuma K., Koike K., Summers J. Duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) particles produced by transient expression of DHBV DNA in a human hepatoma cell line are infectious in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3513–3516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3513-3516.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pourcel C., Summers J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Jefferson D. M., Chowdhury J. R., Novikoff P. M., Johnston D. E., Mulligan R. C. Retrovirus-mediated transduction of adult hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. A., Yee J. K., Skelly H. F., Moores J. C., Respess J. G., Friedmann T., Leffert H. Expression of retrovirally transduced genes in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3344–3348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]