Abstract
A study of 150 patients examined by ultrasonography is described. It was designed specifically to diagnose and investigate abdominal aortic aneurysms. Sixty-four aneurysms were found. Ultrasonography was useful in distinguishing aneurysms from other conditions and there was a high degree of correlation between size measured by scanning and operative size. In addition to the demonstration of rupture it was possible to perform serial measurements. The technique is simple and quick and causes minimal disturbance to the patient.
Full text
PDF

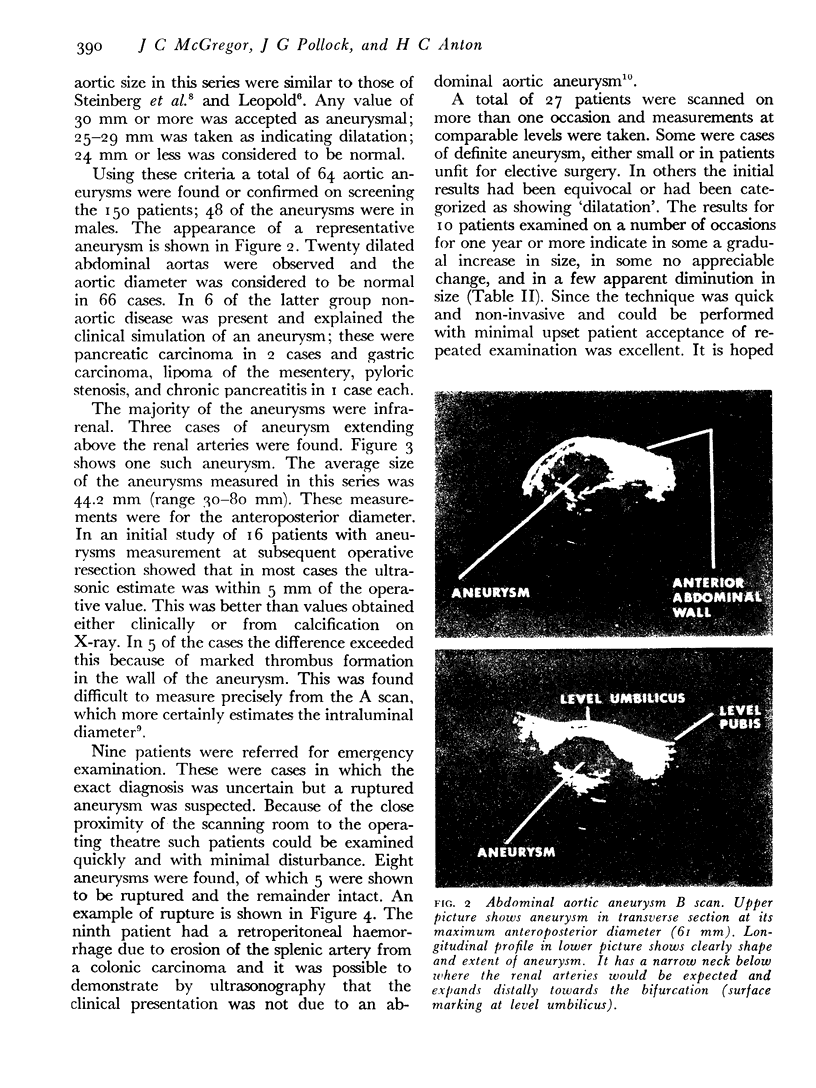
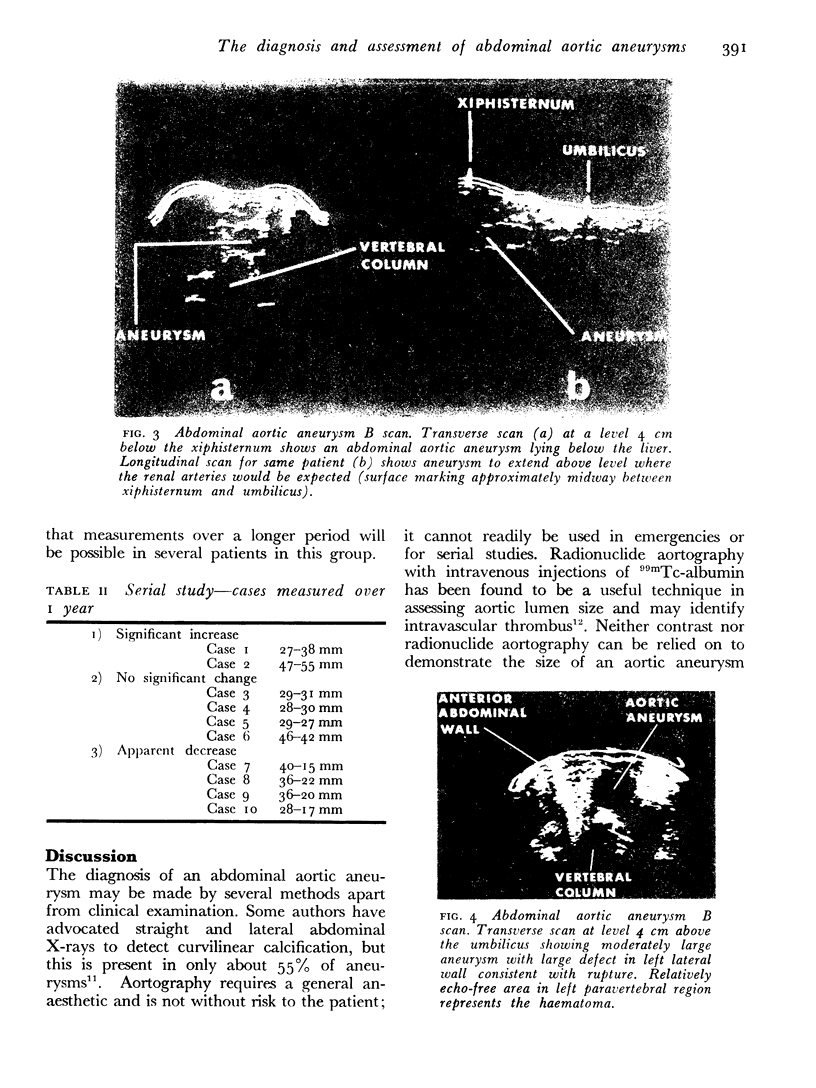

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blakemore A. H. The Clinical Behavior of Arteriosclerotic Aneurysm of the Abdominal Aorta: A Rational Surgical Therapy. Ann Surg. 1947 Aug;126(2):195–207. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194708000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE C. Arteriosclerotic aneurysm of the abdominal aorta; some pathological and clinical correlations. N Engl J Med. 1955 Dec 1;253(22):954–958. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195512012532202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling R. C. Ruptured arteriosclerotic abdominal aortic aneurysms. A pathologic and clinical study. Am J Surg. 1970 Apr;119(4):397–401. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B. B., Ostrum B. J., Isard H. J. Ultrasonic aortography. JAMA. 1966 Oct 24;198(4):353–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold G. R., Asher W. M. Deleterious effects of gastrointestinal contrast material on abdominal echography. Radiology. 1971 Mar;98(3):637–640. doi: 10.1148/98.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold G. R. Ultrasonic abdominal aortography. Radiology. 1970 Jul;96(1):9–14. doi: 10.1148/96.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. C., Pollock J. G., Anton H. C. The value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Scott Med J. 1975 May;20(3):133–137. doi: 10.1177/003693307502000313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. C., Pollock J. G., Anton H. C. Ultrasonography and possible ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 12;3(5975):78–79. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5975.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. C. Unoperated ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: a retrospective clinicopathological study over a 10-year period. Br J Surg. 1976 Feb;63(2):113–116. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor J. P. Diagnosis of ruptured aneurysm of abdominal aorta. Br Med J. 1972 Sep 23;3(5829):735–736. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5829.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg I., Stein H. L. Arteriosclerotic abdominal aneurysms. Report of 200 consecutive cases diagnosed by intravenous aortography. JAMA. 1966 Mar 21;195(12):1025–1029. doi: 10.1001/jama.195.12.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]