Abstract
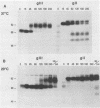
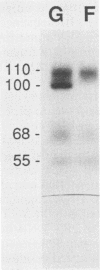
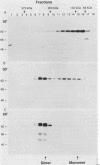
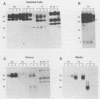
The pseudorabies virus gII gene shares significant homology with the gB gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. Unlike gB, however, gII is processed by specific protease cleavage events after the synthesis of its precursor. The processed forms are maintained in an oligomeric complex that includes disulfide linkages. In this report, we demonstrate the kinetics of modification, complex formation, and subsequent protease processing. In particular, we suggest that gII oligomer formation in the endoplasmic reticulum is an integral part of the export pathway and that protease cleavage occurs only after oligomers have formed. Furthermore, through the use of glycoprotein gene fusions between the gIII glycoprotein and the gII glycoprotein genes of pseudorabies virus, we have mapped a functional cleavage domain of gII to an 11-amino-acid segment.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Demarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of defective interfering viral particles present in a population of pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Spear P. G. Amino-terminal sequence, synthesis, and membrane insertion of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.1-7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Keller D. S., Helenius A., Balch W. E. Role for adenosine triphosphate in regulating the assembly and transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein trimers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Multimeric forms of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):348–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.348-351.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D., Hunter E. Oligomeric structure of a prototype retrovirus glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8688–8692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Keeler C. L., Jr, Robbins A. K., Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E. An amino-terminal deletion mutation of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII affects protein localization and RNA accumulation. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3565–3573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3565-3573.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Davison A. J., Lowe R. S., Bennett C. D., Ellis R. W. Identification and structure of the gene encoding gpII, a major glycoprotein of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg I., Yang H. Y., Costa E. An enkephalin-generating enzyme in bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 14;106(1):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg I., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Further characterization of an enkephalin-generating enzyme from adrenal medullary chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Mettenleiter T. C., Rziha H. J. Demonstration of three major species of pseudorabies virus glycoproteins and identification of a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):166–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.166-173.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Grossi M. P., Gualandri R., Balboni P. G., Marchini A., Rotola A., Rimessi P., Di Luca D., Cassai E., Barbanti-Brodano G. Protection from herpes simplex virus type 1 lethal and latent infections by secreted recombinant glycoprotein B constitutively expressed in human cells with a BK virus episomal vector. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):431–436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.431-436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Thiel H. J., Schreurs C., Rziha H. J. Location of the structural gene of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein complex gII. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Nelson R., Smith M. Sequence of a bovine herpesvirus type-1 glycoprotein gene that is homologous to the herpes simplex gene for the glycoprotein gB. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Biggin M. D., Barrell B., Roizman B. Epstein-Barr virus genome may encode a protein showing significant amino acid and predicted secondary structure homology with glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):807–813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.807-813.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Hunter E. Mutations within the proteolytic cleavage site of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein that block processing to gp85 and gp37. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1609-1614.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggio M. P., Cullinane A. A., Onions D. E. Identification and nucleotide sequence of the glycoprotein gB gene of equine herpesvirus 4. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1123–1133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1123-1133.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Dorney D. J., Wathen M. W., Whealy M. E., Gold C., Watson R. J., Holland L. E., Weed S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. The pseudorabies virus gII gene is closely related to the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2691–2701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2691-2701.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Weis J. H., Enquist L. W., Watson R. J. Construction of E. coli expression plasmid libraries: localization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):485–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. IV. Conformation of the virion glycoprotein designated VP7(B2). J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1159–1167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1159-1167.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sithole I., Lee L. F., Velicer L. F. Synthesis and processing of the Marek's disease herpesvirus B antigen glycoprotein complex. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4270–4279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4270-4279.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Lamm D. L. Visualization of minute centers of viral infection in unfixed cell cultures by an enzyme-linked antibody assay. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Thayer R. M., Probert W. S., Masiarz F. R., Chamberlain S. H., Rasmussen L., Merigan T. C., Pachl C. Human cytomegalovirus strain Towne glycoprotein B is processed by proteolytic cleavage. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):207–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Baumeister K., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. A herpesvirus vector for expression of glycosylated membrane antigens: fusion proteins of pseudorabies virus gIII and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4185–4194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4185-4194.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Synthesis and processing of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):401–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.401-410.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]