Abstract
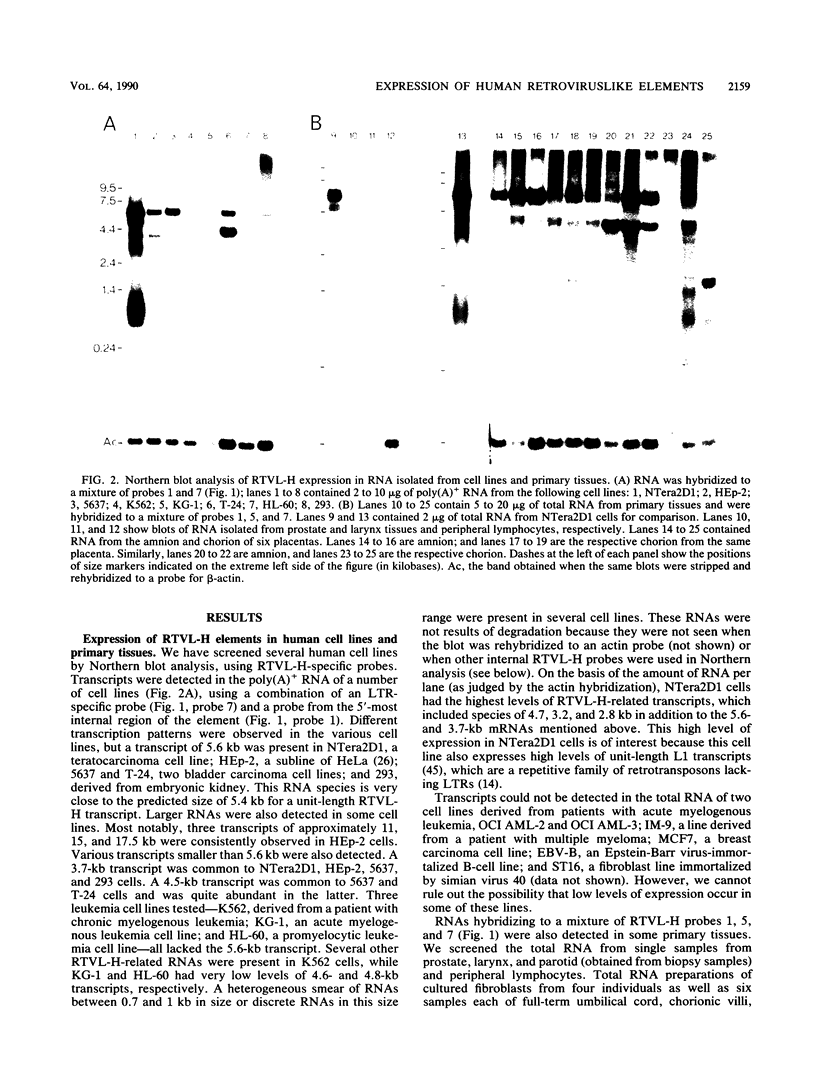
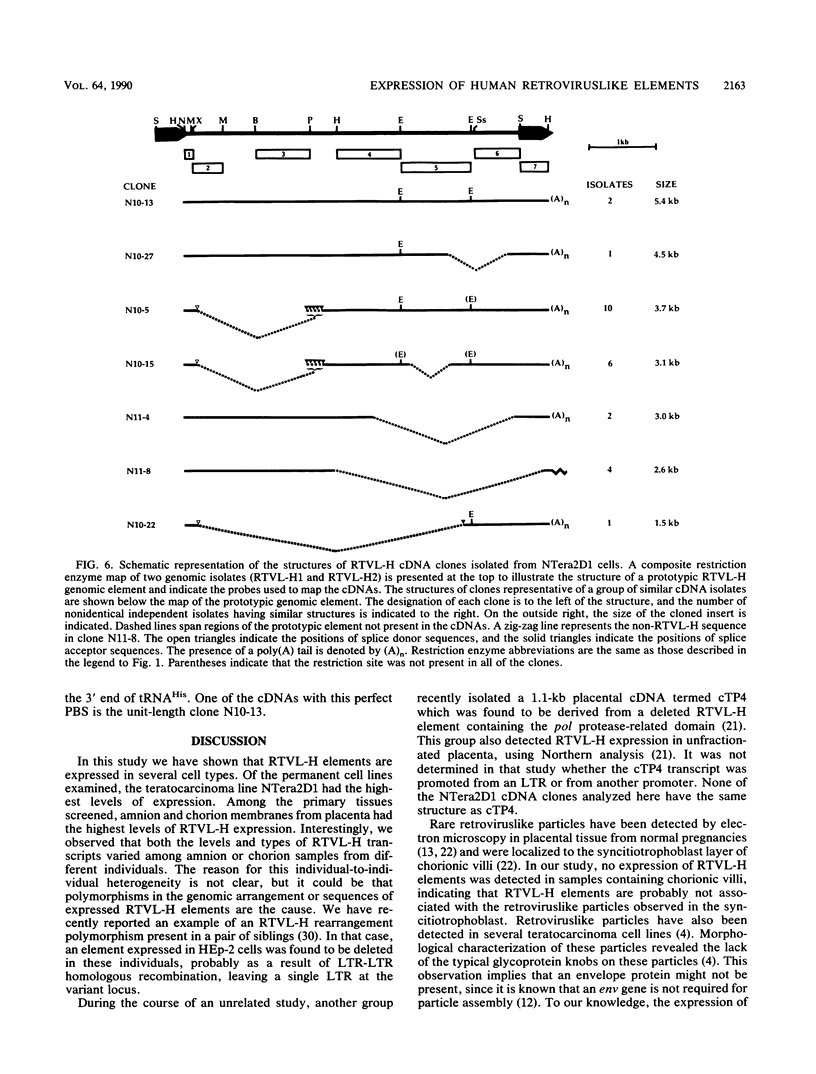
Northern (RNA) blot analysis of RNA from various human cell lines and tissues has demonstrated that elements belonging to the RTVL-H family of human endogenous retroviruslike sequences are expressed in several cell types. The highest levels of RTVL-H-related RNAs were observed in teratocarcinoma cell line NTera2D1, HeLa cells, two bladder carcinoma cell lines, and normal amniotic tissue. Expression was also observed in normal chorion and in some other cell lines. The RTVL-H transcription pattern varied among the different cell types, but several expressed a unit-length 5.6-kilobase transcript. Characterization of cDNA clones corresponding to transcripts present in NTera2D1 cells indicates that the complex transcription pattern observed in these cells is generated by the following: (i) transcription of both full-length and deleted genomic elements, which is initiated within the 5' long terminal repeat (LTR) and, in all but one case, polyadenylated in the 3' LTR; (ii) the splicing of both unit-length transcripts and transcripts from a deleted element; (iii) transcription involving solo LTR sequences; and (iv) transcription which, in one case, reads through the 3' LTR into flanking cellular sequences. Sequence data obtained from 25 cDNA clones revealed that at least 13 RTVL-H elements are expressed in NTera2D1 cells. The positions of several termination codons within the pol region are the same among nine different elements, indicating that an ancestral RTVL-H element bearing these mutations dispersed within the genome. We also found that RTVL-H expression varied among samples of amnion and chorion tissue isolated from different individuals. These findings demonstrate that regulated autonomous expression of RTVL-H sequences occurs in human cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Rathjen P. D., Stanway C. A., Fulton S. M., Malim M. H., Wilson W., Ogden J., King L., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. Complete nucleotide sequence of a mouse VL30 retro-element. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):2989–2998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boller K., Frank H., Löwer J., Löwer R., Kurth R. Structural organization of unique retrovirus-like particles budding from human teratocarcinoma cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2549–2559. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. R., Barker W. C. Nucleotide sequences of the retroviral long terminal repeats and their adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1767–1778. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Powers M., O'Connell C., Kato N. The nucleotide sequence of the env gene from the human provirus ERV3 and isolation and characterization of an ERV3-specific cDNA. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen E. R., Levy J. A. Virus-like particles in placentas from normal individuals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Oct;59(4):1187–1192. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.4.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin G. C., Chretien S., Hanson I. M., Rochefort H., May F. E., Westley B. R. Expression of human sequences related to those of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1203–1210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1203-1210.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser C., Humphries R. K., Mager D. L. Chromosomal distribution of the RTVL-H family of human endogenous retrovirus-like sequences. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):280–287. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni-Celli S., Kirsch K., Kalled S., Isselbacher K. J. Expression of type C-related endogenous retroviral sequences in human colon tumors and colon cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6127–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transposition of two different intracisternal A particle elements into an immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2565–2572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Holm T., Bjørklid E. Members of the RTVL-H family of human endogenous retrovirus-like elements are expressed in placenta. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalter S. S., Helmke R. J., Heberling R. L., Panigel M., Fowler A. K., Strickland J. E., Hellman A. Brief communication: C-type particles in normal human placentas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Apr;50(4):1081–1084. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Kato M., Larsson E., Rydnert J., Ohlsson R., Cohen M. Tissue-specific expression of human provirus ERV3 mRNA in human placenta: two of the three ERV3 mRNAs contain human cellular sequences. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2182–2191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2182-2191.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher C., Miyauchi J., Wong G., Clark S., Minden M. D., McCulloch E. A. Synergism between recombinant growth factors, GM-CSF and G-CSF, acting on the blast cells of acute myeloblastic leukemia. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1498–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E., Kato N., Cohen M. Human endogenous proviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;148:115–132. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74700-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavappa K. S. Survey of ATCC stocks of human cell lines for HeLa contamination. In Vitro. 1978 May;14(5):469–475. doi: 10.1007/BF02616110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwer J., Wondrak E. M., Kurth R. Genome analysis and reverse transcriptase activity of human teratocarcinoma-derived retroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2807–2815. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Freeman J. D. Human endogenous retroviruslike genome with type C pol sequences and gag sequences related to human T-cell lymphotropic viruses. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4060-4066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Goodchild N. L. Homologous recombination between the LTRs of a human retrovirus-like element causes a 5-kb deletion in two siblings. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):848–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S. Identification of a retrovirus-like repetitive element in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7510–7514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L. Polyadenylation function and sequence variability of the long terminal repeats of the human endogenous retrovirus-like family RTVL-H. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90570-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi J., Kelleher C. A., Wang C., Minkin S., McCulloch E. A. Growth factors influence the sensitivity of leukemic stem cells to cytosine arabinoside in culture. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kawakami M., Ushikubo H. Stimulation of expression of the human endogenous retrovirus genome by female steroid hormones in human breast cancer cell line T47D. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2059–2062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2059-2062.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Yasunaga T., Miyata T., Ushikubo H. Nucleotide sequence of human endogenous retrovirus genome related to the mouse mammary tumor virus genome. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):589–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.589-598.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson K. E., Matera A. G., Deka N., Schmid C. W. Transcription of a human transposon-like sequence is usually directed by other promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5199–5215. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. B., Hamagishi Y., Steele P. E., Tykocinski M., Martin M. A. Characterization of human endogenous retroviral envelope RNA transcripts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):176–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.176-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. B., Steele P. E., Garon C. F., Martin M. A. mRNA transcripts related to full-length endogenous retroviral DNA in human cells. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):604–607. doi: 10.1038/306604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske R., Steele P. E., O'Neill R. R., Rabson A. B., Martin M. A. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length human endogenous retroviral segment. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):764–772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.764-772.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Wirth T., Kröger B., Horak I. Structure and genomic organization of a new family of murine retrovirus-related DNA sequences (MuRRS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3461–3470. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih A., Misra R., Rush M. G. Detection of multiple, novel reverse transcriptase coding sequences in human nucleic acids: relation to primate retroviruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):64–75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.64-75.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. Unit-length line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1385–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Fenner S., Greenoak G. E., Moran C., Coffin J. M. Role of endogenous retroviruses as mutagens: the hairless mutation of mice. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Sanderson C. J., Hapel A. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Constitutive synthesis of interleukin-3 by leukaemia cell line WEHI-3B is due to retroviral insertion near the gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):255–258. doi: 10.1038/317255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]