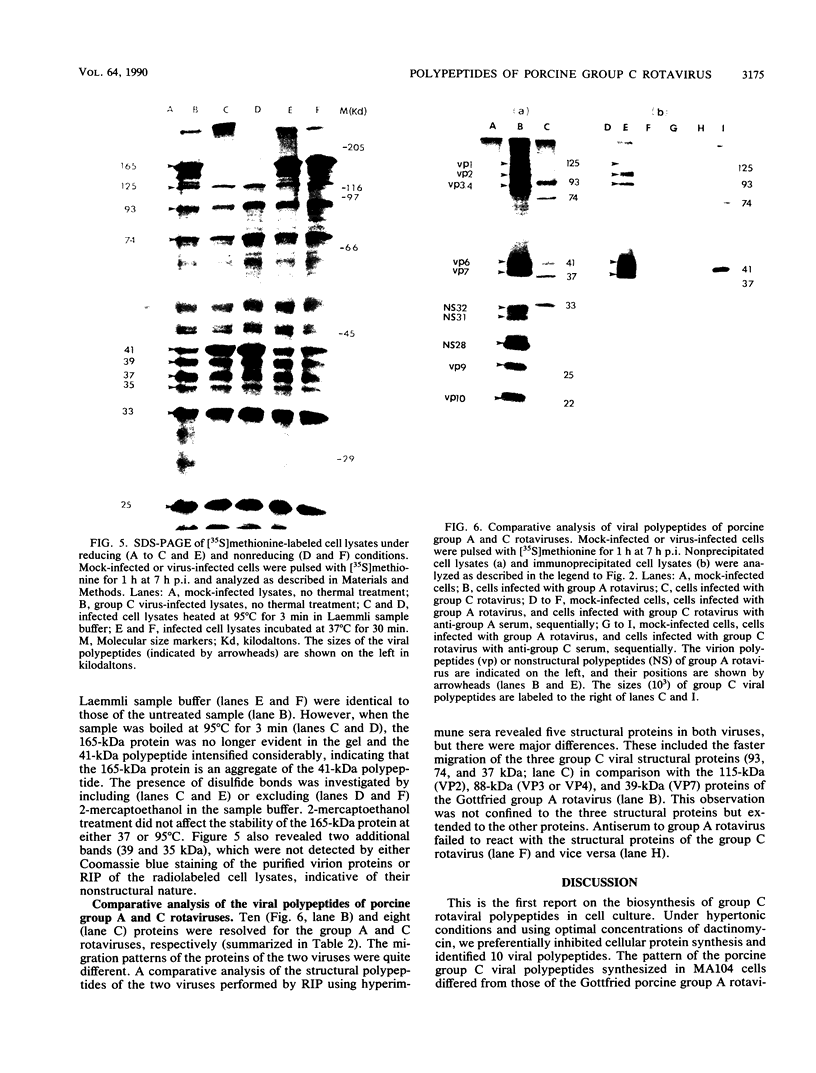
Abstract
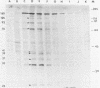
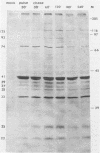
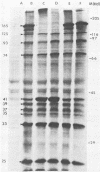
Purified virions or radiolabeled lysates of infected MA104 cells were used to characterize the structural and nonstructural polypeptides of a porcine group C rotavirus. At least six structural proteins were identified from purified group C rotavirus by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Of these, two (37,000- and 33,000-molecular-weight polypeptides) were associated with the outer shell, as demonstrated by the ability of EDTA to remove them from the purified virion. The other four polypeptides (molecular weights, 125,000, 93,000, 74,000, and 41,000) were located in the inner shell. The structural or nonstructural nature of a 25,000-molecular-weight protein identified in our studies was unclear. Glycosylation inhibition studies with tunicamycin in infected cells demonstrated that the 37,000- and 25,000-molecular-weight proteins were glycosylated and contained mannose-rich oligosaccharides identified by radiolabeling of the infected cells with [3H]mannose. The 37,000-molecular-weight outer shell glycoprotein was shown by pulse-chase experiments to be posttranslationally processed. The kinetics of viral polypeptide synthesis in infected cells were also studied, and maximal synthesis occurred at 6 to 9 h postinfection. The 41,000-molecular-weight inner capsid polypeptide was the most abundant and was the subunit structure of a 165,000-molecular-weight protein aggregate. Two polypeptides (molecular weights, 39,000 and 35,000) appeared to be nonstructural, as determined by comparison of the protein pattern of radiolabeled infected cell lysates with that of purified virions. Radioimmunoprecipitation was used to examine the serologic cross-reactions between the viral polypeptides of a group C rotavirus with those of a group A rotavirus. No serologic cross-reactivities were detected. The polypeptides of group A and C rotaviruses are compared and discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au K. S., Chan W. K., Burns J. W., Estes M. K. Receptor activity of rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4553–4562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4553-4562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastardo J. W., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Sonza S., Mercer L. D., Holmes I. H. Preparation and characterization of antisera to electrophoretically purified SA11 virus polypeptides. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):641–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.641-647.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremont M., Cohen J., McCrae M. A. Analysis of the structural polypeptides of a porcine group C rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2183–2185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2183-2185.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Novel rotaviruses in animals and man. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;128:5–23. doi: 10.1002/9780470513460.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Au K. S., Estes M. K. Topography of the simian rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein (NS28) in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90557-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson B. L., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B., Estes M. K. Identification, synthesis, and modifications of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):825–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.825-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Puerto F., Soler C., González N. Characterization of a human pararotavirus. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):112–116. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.112-116.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Conner M. E., Gilger M. A., Graham D. Y. Molecular biology and immunology of rotavirus infections. Immunol Invest. 1989 Jan-May;18(1-4):571–581. doi: 10.3109/08820138909112264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F. Rotaviruses: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:123–184. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang Z. Y., Glass R. I., Penaranda M., Dong H., Monroe S. S., Wen L., Estes M. K., Eiden J., Yolken R. H., Saif L. Purification and characterization of adult diarrhea rotavirus: identification of viral structural proteins. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2191–2197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2191-2197.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorziglia M., Larrea C., Liprandi F., Esparza J. Biochemical evidence for the oligomeric (possibly trimeric) structure of the major inner capsid polypeptide (45K) of rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1985 Sep;66(Pt 9):1889–1900. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-9-1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R. L., Birch C. J. Synthesis of human rotavirus polypeptides in cell culture. J Med Virol. 1988 May;25(1):91–103. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., McCrae M. A. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. VIII. Quantitative analysis of regulation of gene expression during virus replication. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2048–2055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2048-2055.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Offit P. A., Estes M. K. Identification of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome segment 3 product. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Biochemical mapping of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):413–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.413-423.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Faulkner-Valle G. P. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. I. Characterization of basic growth parameters and pattern of macromolecular synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. C., Bergmann C. C., Bellamy A. R. Interaction of rotavirus cores with the nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):98–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Cohen J., Fortier B., Lourenco M. H., Bricout F. Isolation of a human pararotavirus. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novo E., Esparza J. Composition and topography of structural polypeptides of bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Oct;56(Pt 2):325–335. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Brown J. F., McCrae M. A. Molecular characterization of rotaviruses with distinct group antigens. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2093–2101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley S., Bridger J. C., Chasey D., McCrae M. A. Definition of two new groups of atypical rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jan;67(Pt 1):131–137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie B. L., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Effects of tunicamycin on rotavirus morphogenesis and infectivity. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):270–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.270-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tilley S. A., Bona C., Zaghouani H., Gorny M. K., Zolla-Pazner S. Oligomeric structure of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2674-2679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Bishop R. F., Holmes I. H. Detection of a rotavirus-like agent associated with diarrhea in an infant. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):724–726. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.724-726.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabara M., Ready K. F., Frenchick P. J., Babiuk L. A. Biochemical evidence for the oligomeric arrangement of bovine rotavirus nucleocapsid protein and its possible significance in the immunogenicity of this protein. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):123–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Theil K. W., Cross R. F., House J. A. Rotavirus-like, calicivirus-like, and 23-nm virus-like particles associated with diarrhea in young pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jul;12(1):105–111. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.1.105-111.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Terrett L. A., Miller K. L., Cross R. F. Serial propagation of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) in a continuous cell line and characterization of the passaged virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1277–1282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1277-1282.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Suzuki H., Kitaoka S., Konno T., Ishida N. Patterns of polypeptide synthesis in human rotavirus infected cells. Arch Virol. 1986;90(1-2):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01314142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J. Serial propagation of porcine group C rotavirus (pararotavirus) in primary porcine kidney cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jul;25(7):1316–1319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.7.1316-1319.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrett L. A., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Kohler E. M. Physicochemical characterization of porcine pararotavirus and detection of virus and viral antibodies using cell culture immunofluorescence. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Feb;25(2):268–272. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.2.268-272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquidi V., Novo E., Esparza J. Protein synthesis in cells infected with bovine rotavirus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Apr;53(Pt 2):363–369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-2-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch S. K., Crawford S. E., Estes M. K. Rotavirus SA11 genome segment 11 protein is a nonstructural phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3974–3982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3974-3982.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch S. K., Saif L. J. Monoclonal antibodies to a virulent strain of transmissible gastroenteritis virus: comparison of reactivity with virulent and attenuated virus. Arch Virol. 1988;101(3-4):221–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01311003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]