Abstract
In these studies very high doses (up to 4800 CCA units in adults) of formalin inactivated influenza vaccine purified by density gradient centrifugation were given safely to more than 5000 volunteers drawn from adolescent, middle aged and elderly populations. The relative paucity of reactions, compared with those groups receiving much lower doses of formalin-inactivated vaccine produced by Sharples centrifugation, suggests that reactions are due to non-viral substances rather than to toxic properties of the viruses, and that these substances are removable.
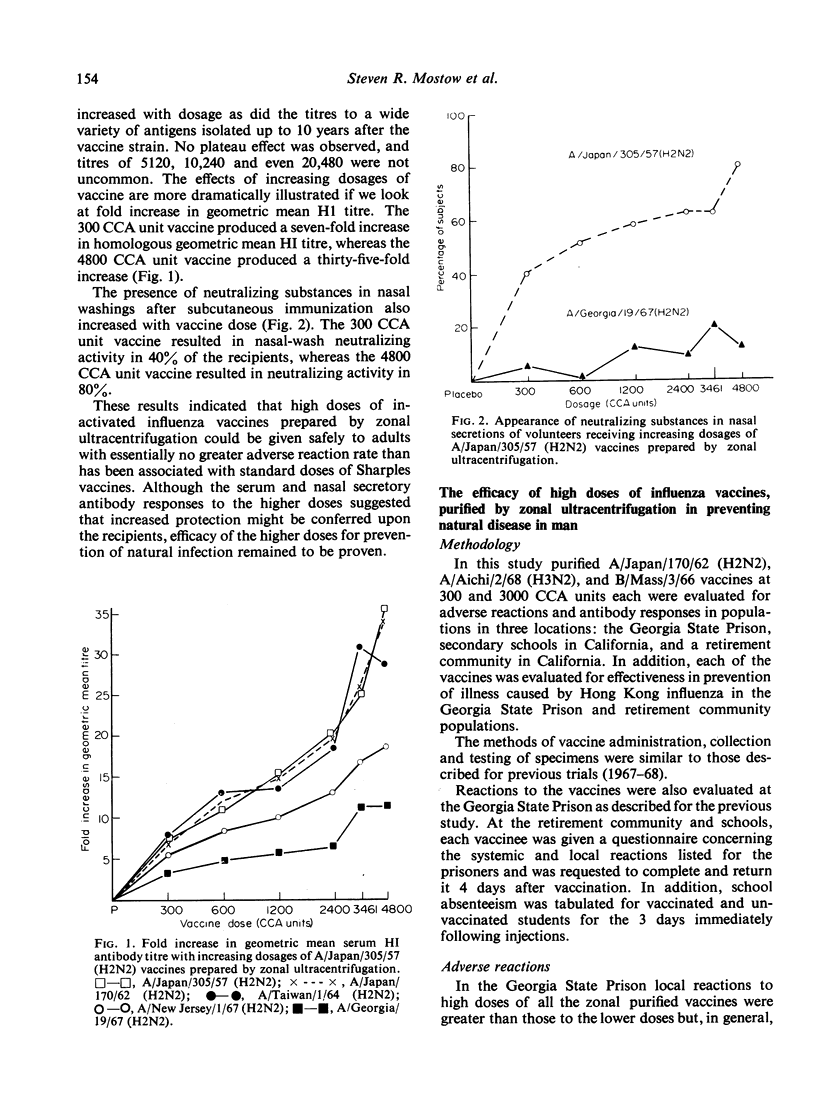
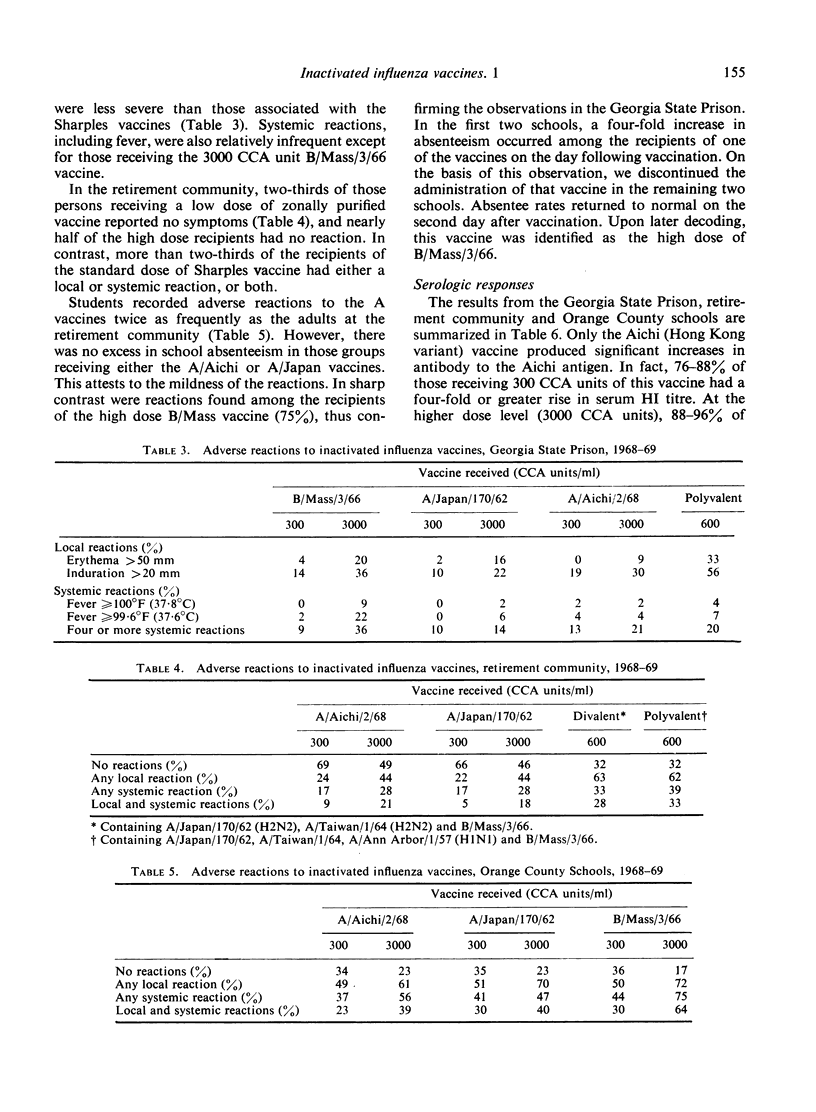
Homologous serum HI antibody responses increased with increasing vaccine dosage and there was no plateau effect at the higher dose level. In those groups studied, the appearance of neutralizing activity in post-vaccination nasal washings correlated closely with the higher vaccine doses and higher HI antibody titres.
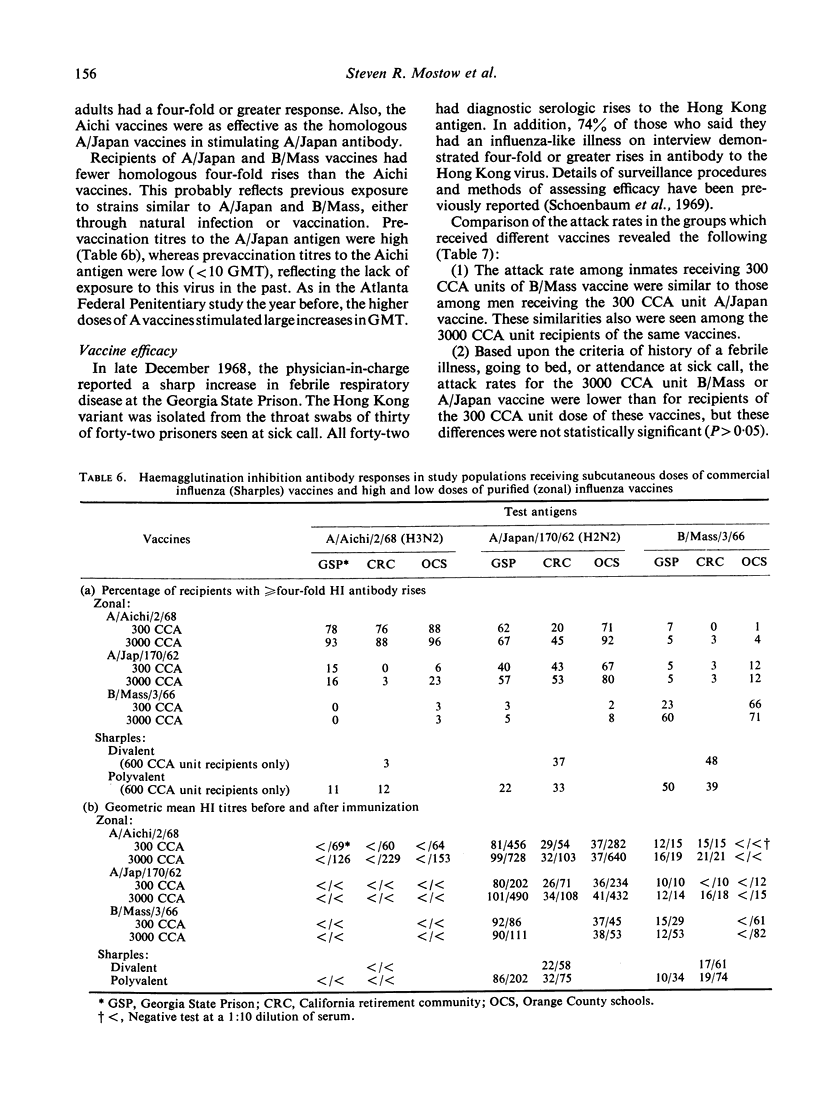
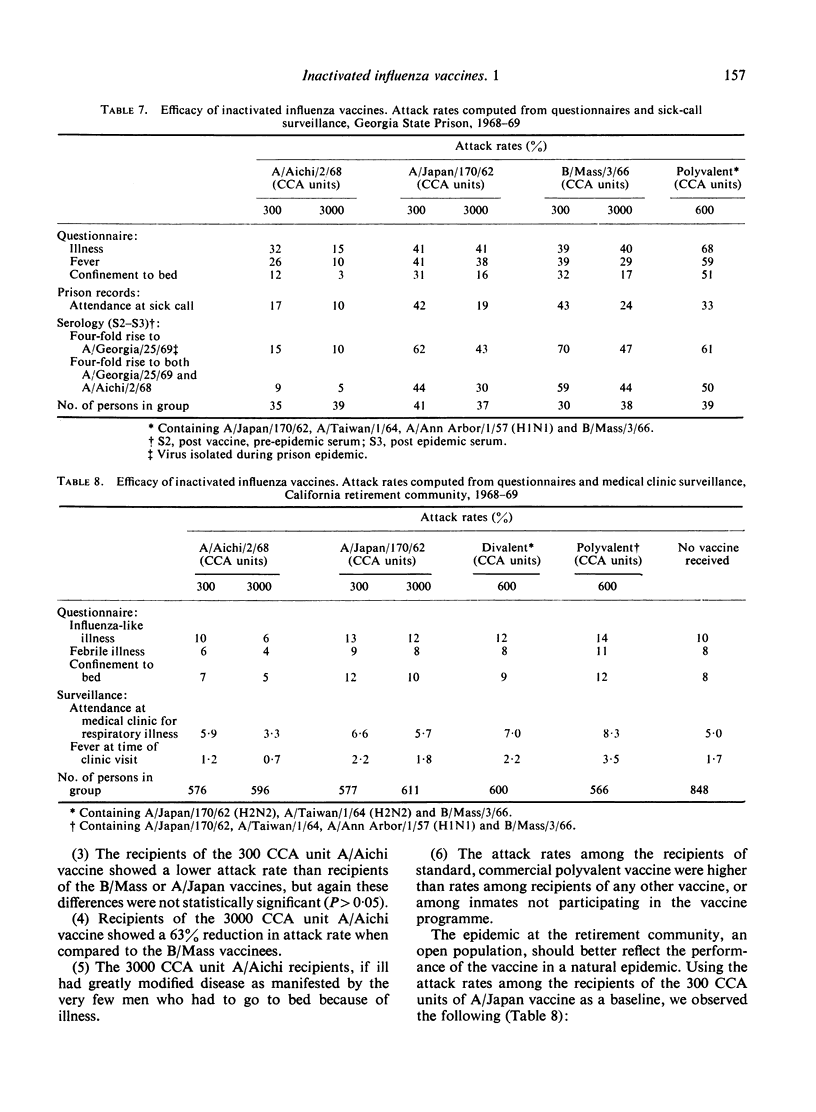
The occurrence of the ‘Hong Kong flu’ epidemic in two of the groups, including over 3000 vaccine recipients, provided a unique opportunity to study the efficacy of the various vaccines used. Only those groups receiving high doses of a Hong Kong-like antigen (A2/Aichi/2/68) enjoyed significant reduction in illness (70%). Furthermore, there was a 90% reduction in the incidence of fever in that group.
These results indicate that very large doses of purified influenza vaccine can be given safely. Significant prevention and modification of disease caused by influenza via the vaccine approach is dependent on the administration of large doses of the appropriate antigen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kaye H. S., Dowdle W. R., McQueen J. L. Studies on inactivated influenza vaccines. I. The effect of dosage on antibody response and protection against homotypic and heterotypic influenza virus challenge in mice. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Aug;90(2):162–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostow S. R., Schoenbaum S. C., Dowdle W. R., Coleman M. T., Kaye H. S., Hierholzer J. C. Studies on inactivated influenza vaccines. II. Effect of increasing dosage on antibody response and adverse reactions in man. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Oct;92(4):248–256. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck F. B., Jr Purified influenza virus vaccine. A study of viral reactivity and antigenicity. JAMA. 1968 Dec 2;206(10):2277–2282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Baker R. S., Van Frank R. M., Newlin T. E., Cline G. B., Anderson N. G. Purification of large quantities of influenza virus by density gradient centrifugation. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1207–1216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1207-1216.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


