Abstract
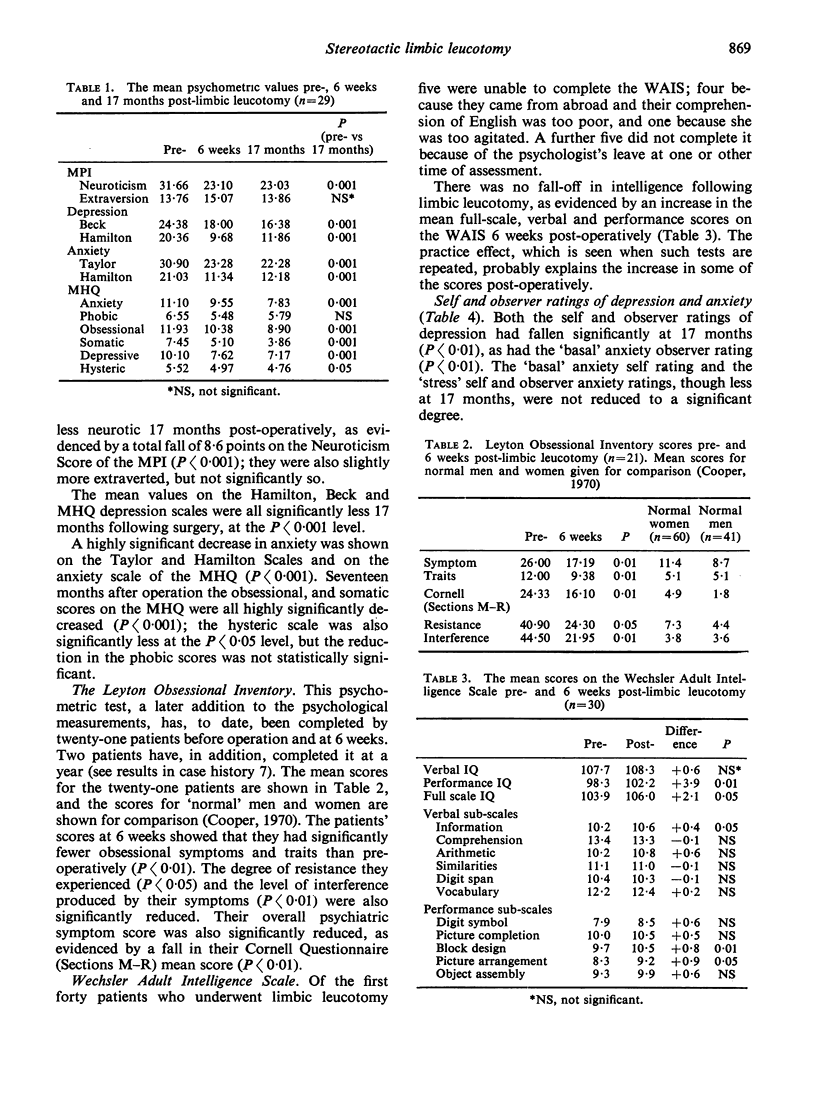
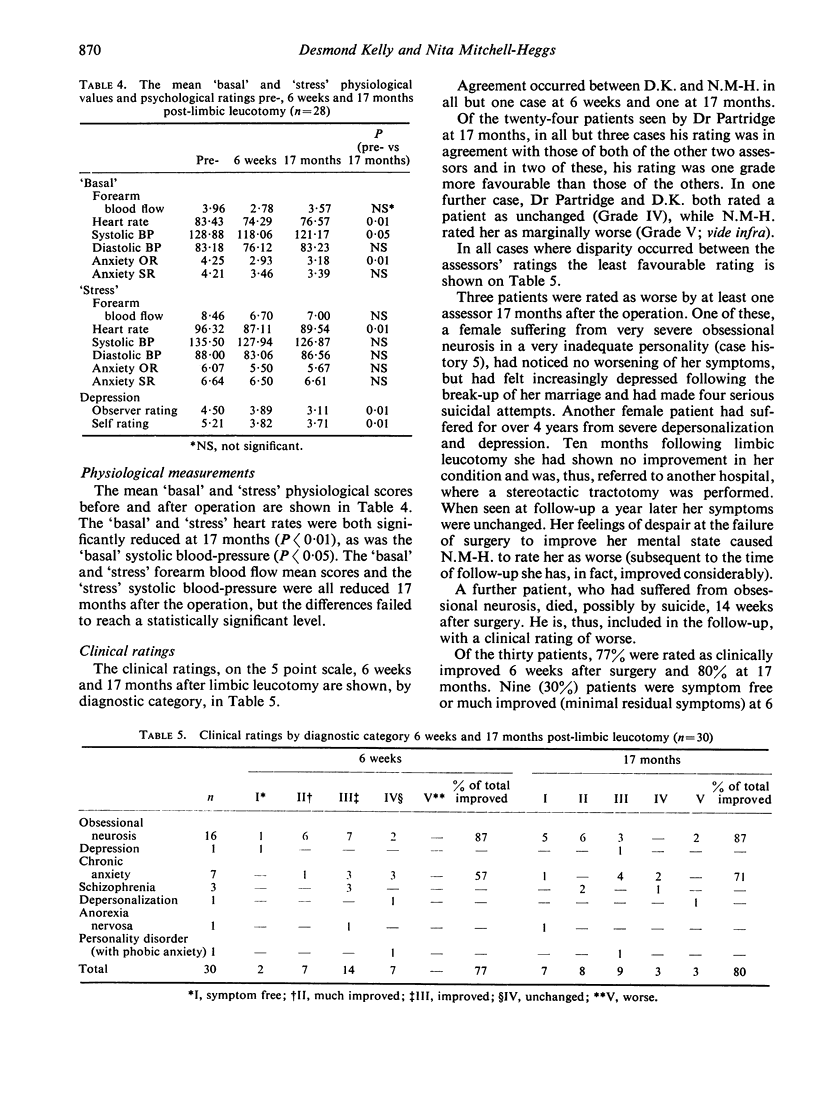
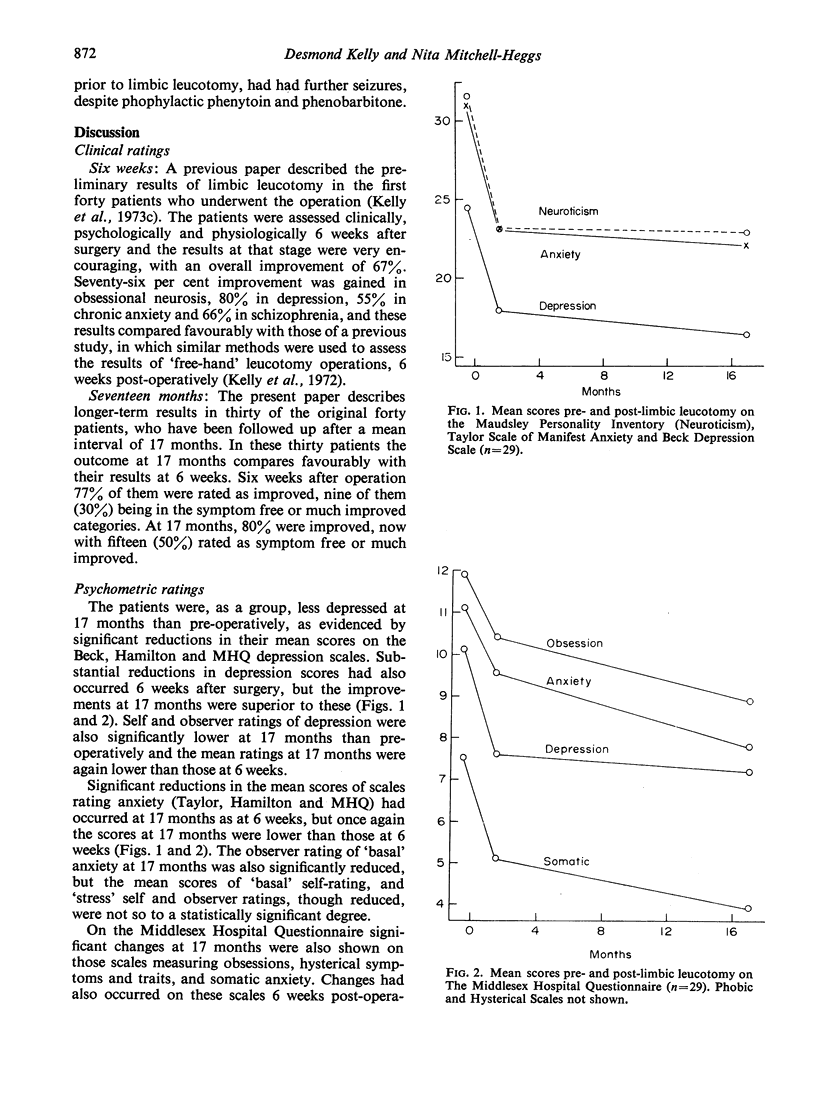
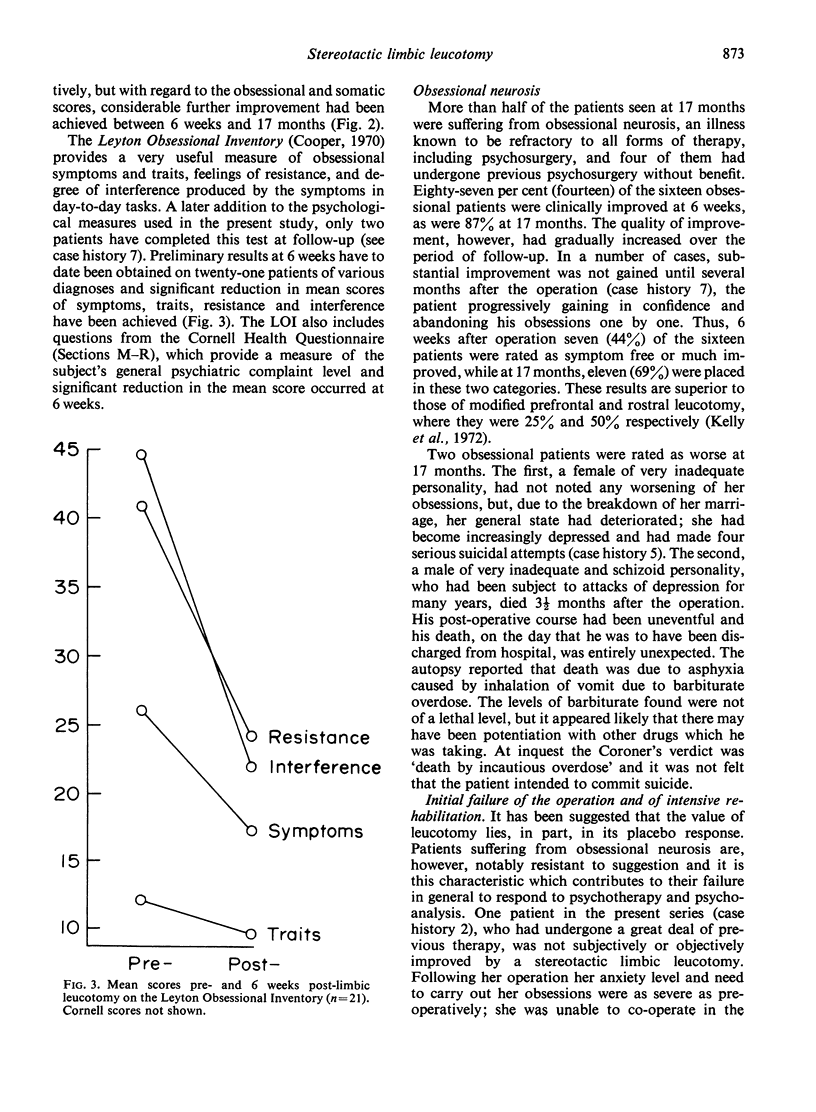
This prospective study reports the results of stereotactic limbic leucotomy at a mean of 17 months following surgery. Clinical improvement had occurred in twenty-four (80%) of the patients, fifteen (50%) of them being symptom free or much improved. Fourteen of sixteen patients suffering from obsessional neurosis were improved, as were five of seven with chronic anxiety and the degree of improvement at 17 months was superior to that at 6 weeks. Psychometric scores of anxiety, obsessions and neuroticism were all significantly reduced at 17 months. The mean depression scores were also significantly reduced and this result was superior to that reported in a previous study of ‘free-hand’ operations.
Adverse effects were not a problem following limbic leucotomy. Emotional blunting, disinhibition, post-operative epilepsy and excessive weight gain were not encountered, and intelligence was unaffected by the operation. Limbic leucotomy is a much more limited and precise procedure than older ‘free-hand’ operations which we have studied, but its therapeutic effects are comparable and in obsessional neurosis, superior.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK A. T., WARD C. H., MENDELSON M., MOCK J., ERBAUGH J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961 Jun;4:561–571. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1961.01710120031004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. The Leyton obsessional inventory. Psychol Med. 1970 Nov;1(1):48–64. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700040010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisp A. H., Kalucy R. S. The effect of leucotomy in intractable adolescent weight phobia (primary anorexia nervosa). Postgrad Med J. 1973 Dec;49(578):883–893. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.49.578.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crown S., Crisp A. H. A short clinical diagnostic self-rating scale for psychoneurotic patients. The Middlesex Hospital Questionnaire (M.H.Q.). Br J Psychiatry. 1966 Sep;112(490):917–923. doi: 10.1192/bjp.112.490.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman W. Frontal lobotomy in early schizophrenia. Long follow-up in 415 cases. Br J Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;119(553):621–624. doi: 10.1192/bjp.119.553.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32(1):50–55. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1967 Dec;6(4):278–296. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1967.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri P., Hawkins D. R. Human sleep after leucotomy. A case study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972 May;26(5):469–473. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1972.01750230079015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON H. Leucotomy; a recent development. J Ment Sci. 1954 Jan;100(418):62–65. doi: 10.1192/bjp.100.418.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):32–41. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. H. The technique of forearm plethysmography for assessing anxiety. J Psychosom Res. 1967 May;10(4):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(67)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. H., Walter C. J., Sargant W. Modified leucotomy assessed by forearm blood flow and other measurements. Br J Psychiatry. 1966 Sep;112(490):871–881. doi: 10.1192/bjp.112.490.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. Physiological changes during operations on the limbic system in man. Cond Reflex. 1972 Jul-Sep;7(3):127–138. doi: 10.1007/BF03000212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Pik R., Chen C. N. A psychological and physiological evaluation of the effects of intravenous diazepam. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;122(569):419–426. doi: 10.1192/bjp.122.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. Psychosurgery and the limbic system. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Dec;49(578):825–833. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.49.578.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Richardson A., Mitchell-Heggs N., Greenup J., Chen C., Hafner R. J. Stereotactic limbic leucotomy: a preliminary report on forty patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Aug;123(573):141–148. doi: 10.1192/bjp.123.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Richardson A., Mitchell-Heggs N. Stereotactic limbic leucotomy: neurophysiological aspects and operative technique. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Aug;123(573):133–140. doi: 10.1192/bjp.123.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Walter C. J., Mitchell-Heggs N., Sargant W. Modified leucotomy assessed clinically, physiologically and psychologically at six weeks and eighteen months. Br J Psychiatry. 1972 Jan;120(554):19–29. doi: 10.1192/bjp.120.554.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koella W. P., Czicman J. Mechanism of the EEG-synchronizing action of serotonin. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):926–934. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. V. Stereotactic lesions in the knee of the corpus callosum in the treatment of emotional disorders. Lancet. 1972 Feb 26;1(7748):472–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKISSOCK W. Discussion on psychosurgery. Proc R Soc Med. 1959 Mar;52(3):206–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIPPARD J. Rostral leucotomy: a report on 240 cases personally followed up after 1 1/2 to 5 years. J Ment Sci. 1955 Oct;101(425):756–773. doi: 10.1192/bjp.101.425.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLITT J. Natural history of obsessional states; a study of 150 cases. Br Med J. 1957 Jan 26;1(5012):194–198. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5012.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. Stereotactic limbic leucotomy: surgical technique. Postgrad Med J. 1973 Dec;49(578):860–864. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.49.578.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ström-Olsen R., Carlisle S. Bi-frontal stereotactic tractotomy. A follow-up study of its effects on 210 patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1971 Feb;118(543):141–154. doi: 10.1192/bjp.118.543.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. A. A personality scale of manifest anxiety. J Abnorm Psychol. 1953 Apr;48(2):285–290. doi: 10.1037/h0056264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter C. J., Mitchell-Heggs N., Sargant W. Modified narcosis, ECT and antidepressant drugs: a review of technique and immediate outcome. Br J Psychiatry. 1972 Jun;120(559):651–662. doi: 10.1192/bjp.120.559.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


