Abstract
The accumulation and behavior of various amino acids in the pool of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 9027) were investigated. Patterns of pool formation and maintenance varied with different amino acids tested and were dependent, to a considerable extent, upon the ability of the organism to catabolize the particular amino acid. The establishment of steady-state amino acid pool levels depended upon the activity of the amino acid permease involved and upon the rate of protein synthesis. The presence of a relatively large specific amino acid pool did not affect the formation of a pool of a structurally different amino acid, and a preformed steady-state pool was not displaced by structurally unrelated amino acids. Steady-state amino acid pools decreased rapidly in the presence of inhibitors of energy metabolism and at 0 C. Steady-state internal amino acid pools were found to be in equilibrium with the corresponding external amino acid, present at low levels. A multiplicity of proline pools was demonstrated.
Full text
PDF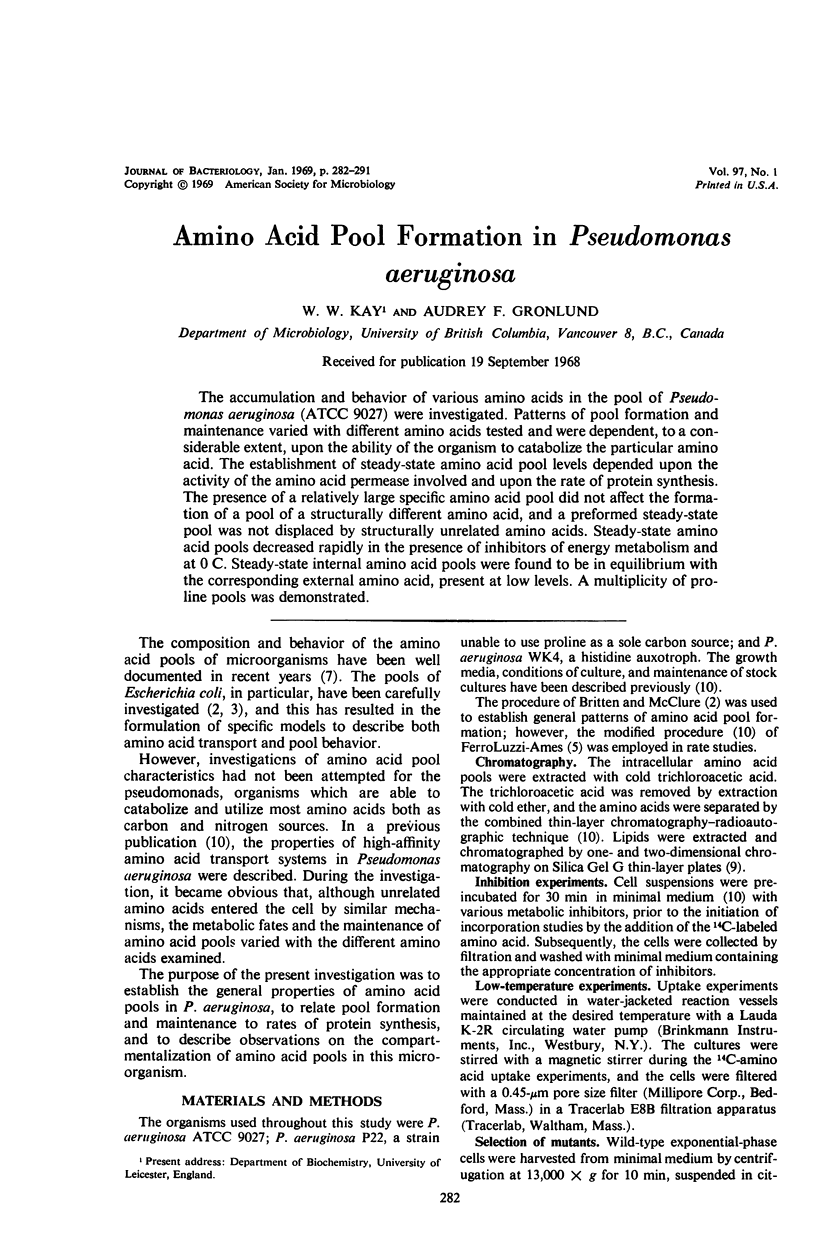


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behki R. M. Metabolism of amino acids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. 3. Uptake of L-pro- line. Can J Biochem. 1967 Dec;45(12):1819–1830. doi: 10.1139/o67-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MONOD J. Bacterial permeases. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):169–194. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.169-194.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J., Rose A. H. Cold shock in a mesophilic and a psychrophilic pseudomonad. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):429–439. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON J. B., HODGES T. K. UNCOUPLING ACTION OF CHLORAMPHENICOL AS A BASIS FOR THE INHIBITION OF ION ACCUMULATION. Nature. 1963 Dec 7;200:1009–1009. doi: 10.1038/2001009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. Transport of proline in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Feb 12;57:32–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. THE ROLE OF PERMEASE IN TRANSPORT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:177–200. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Stadtman E. R. Glycine uptake in Escherichia coli. II. Glycine uptake, exchange, and metabolism by an isolated membrane preparation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1390–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Stadtman E. R. Proline uptake by an isolated cytoplasmic membrane preparation of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):920–927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Gronlund A. F. Amino acid transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.273-281.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKelvie R. M., Gronlund A. F., Campbell J. J. Influence of cold-shock on the endogenous metabolism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jun;14(6):633–638. doi: 10.1139/m68-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


