Abstract
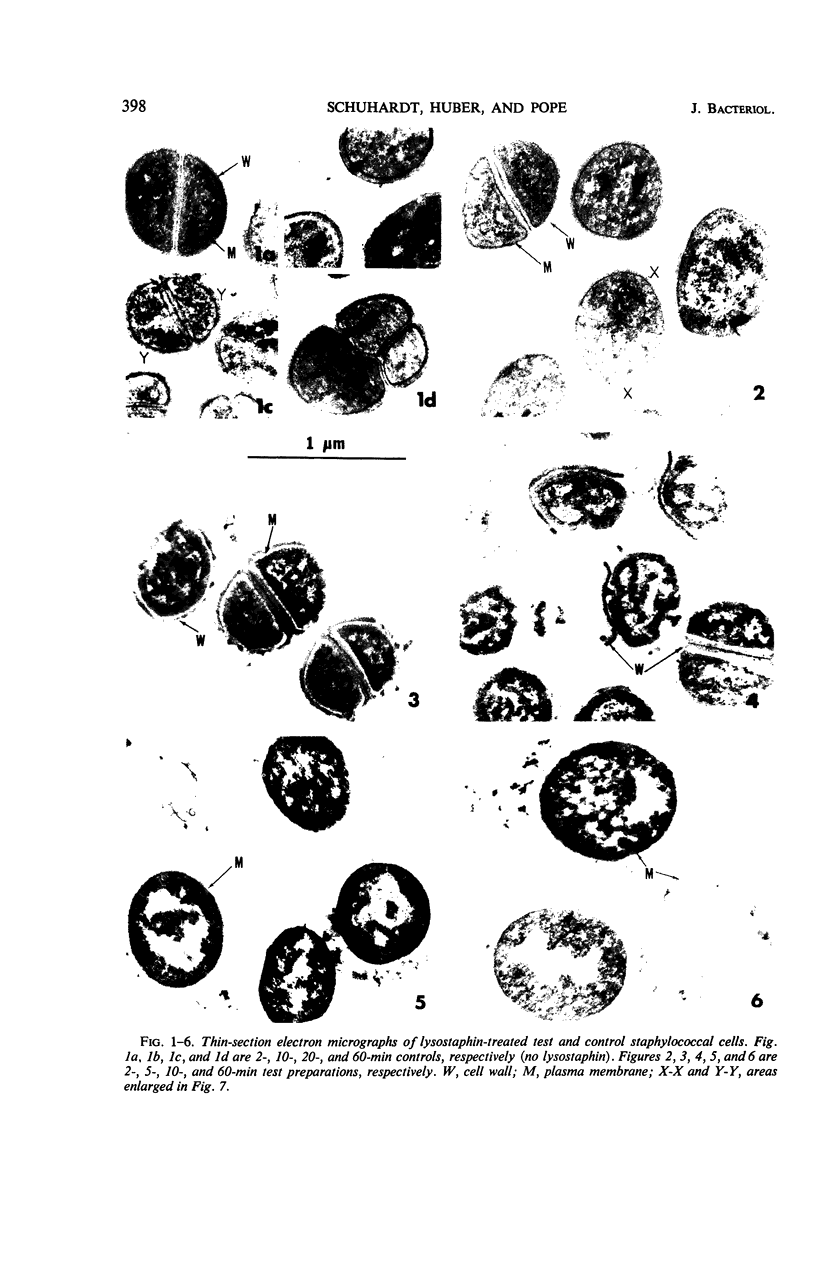
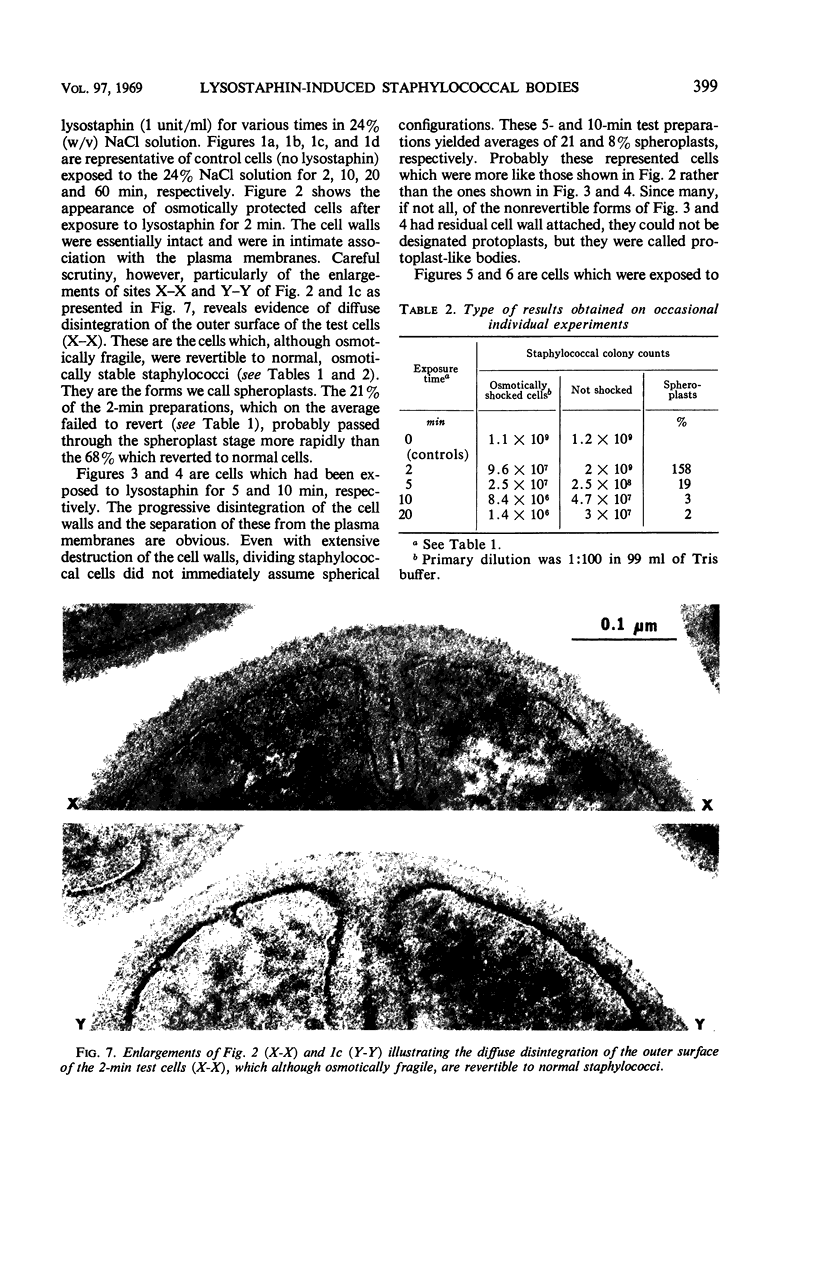
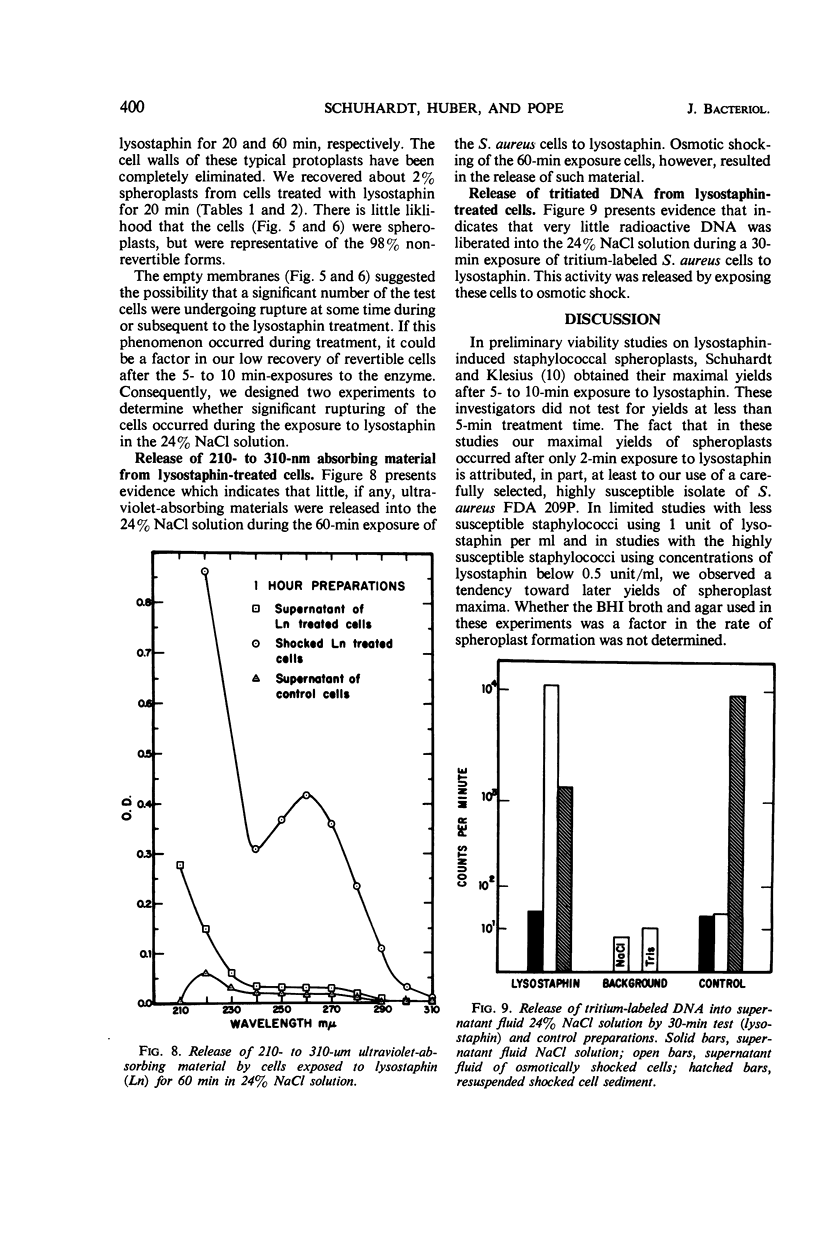
The cell walls of a selected isolate of Staphylococcus aureus FDA 209P were observed undergoing progressive disintegration when exposed to lysostaphin (1 unit/ml) in 24% NaCl solution. Electron micrographs of ultrathin sections of test cells after exposure to lysostaphin for 2 min showed only superficial evidence of lytic damage. However, an average of 89% of these cells were osmotically fragile, and 21% were damaged beyond their capacity to regenerate cell walls and to grow as normal staphylococci. The 68% (average) of the osmotically fragile cells which retained the capacity to revert to normal staphylococci were designated spheroplasts. Neither perforations of the cell walls nor separation of the cell walls from the plasma membranes were observed in the micrographs of these 2-min spheroplasts. Thus, it appears that the osmotic fragility of these and possibly all lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts results from the hydrolysis of a critical number of the pentapeptide cross-linkages of the murein of the cell wall. Electron micrographs of cells exposed to lysostaphin for 5 to 10 min showed perforations and more extensive damage, including the separation of walls from the plasma membranes and the disintegration of large sections of the walls. Smaller numbers of spheroplasts (21 and 8%) were recovered from these 5- and 10-min preparations; those recovered probably represent cells which were attacked more slowly than the majority by the lytic enzyme. The nonrevertible, osmotically fragile cells that retained segments of cell wall were designated protoplast-like bodies. After 20-min exposure to lysostaphin, all of the cell wall was digested away from most of the cells, and true staphylococcal protoplasts were produced. These lysostaphin-induced, osmotically fragile forms appear to have different osmotic properties from the staphylococcal “protoplasts” reported by other investigators and should serve as the basis for a variety of fundamental investigations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWDER H. P., ZYGMUNT W. A., YOUNG J. R., TAVORMINA P. A. LYSOSTAPHIN: ENZYMATIC MODE OF ACTION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 23;19:383–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASH J. H., WISHNICK M., MILLER P. A. FORMATION OF "PROTOPLASTS" OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS WITH A FUNGAL N-ACETYLHEXOSAMINIDASE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:432–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.432-437.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Mosteller R. D., Hardesty B. The mechanism of sodium fluoride and cycloheximide inhibition of hemoglobin biosynthesis in the cell-free reticulocyte system. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M., HORECKER B. L. The localization of alkaline phosphatase in E. coli K12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:104–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Autolytic release and osmotic properties of protoplasts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):184–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. LYSOSTAPHIN: A NEW BACTERIOLYTIC AGENT FOR THE STAPHYLOCOCCUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:414–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF LYSOSTAPHIN--A LYTIC AGENT FOR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhardt V. T., Klesius P. H. Osmotic fragility and viability of lysostaphin-induced staphylococcal spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):734–737. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.734-737.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]