Abstract
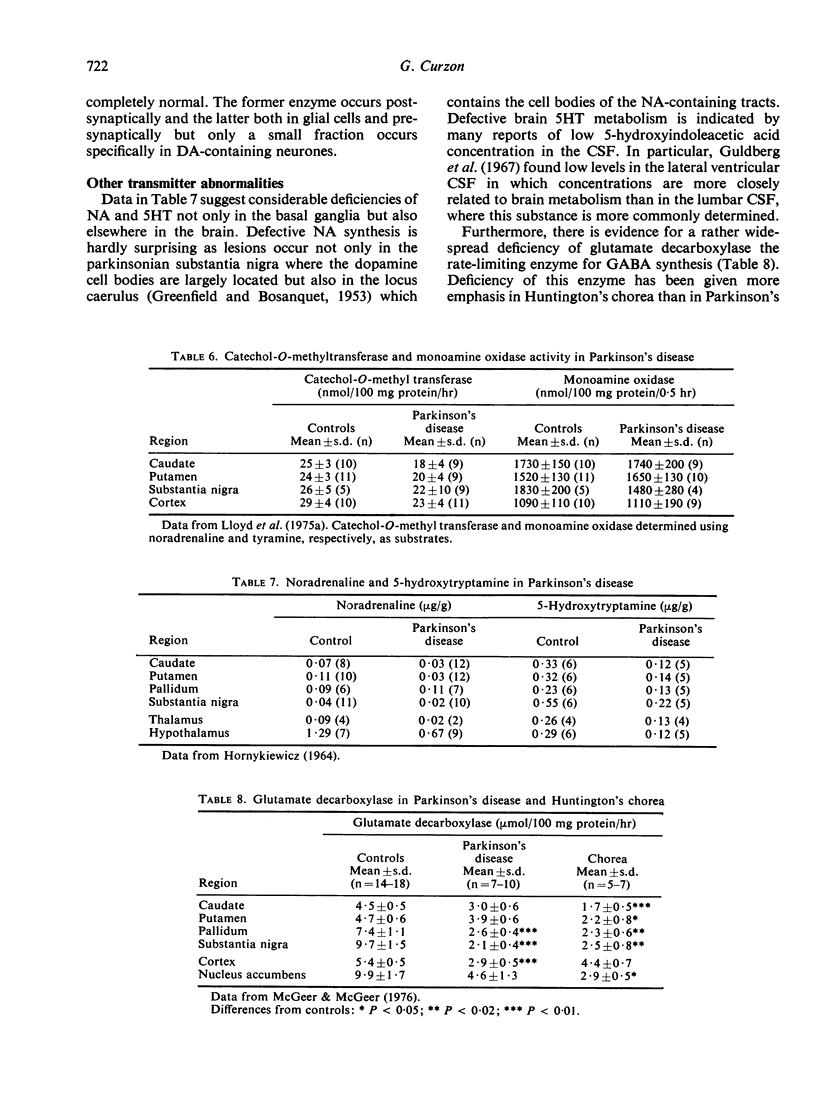
The metabolic pathways for five transmitters in the basal ganglia are briefly described; the results of determinations of their concentrations, of their rate-limiting enzymes and of their degradation products are summarized. The changes found in Parkinson's disease are described. While dopamine synthesis in the basal ganglia is defective in this condition, abnormalities of other transmitters occur, and their possible significance is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDEN N. E., CARLSSON A., DAHLSTROEM A., FUXE K., HILLARP N. A., LARSSON K. DEMONSTRATION AND MAPPING OUT OF NIGRO-NEOSTRIATAL DOPAMINE NEURONS. Life Sci. 1964 Jun;3:523–530. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agid Y., Javoy F., Glowinski J. Hyperactivity of remaining dopaminergic neurones after partial destruction of the nigro-striatal dopaminergic system in the rat. Nat New Biol. 1973 Oct 3;245(144):150–151. doi: 10.1038/newbio245150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Strömbom U., Svensson T. H. Dopamine and noradrenaline receptor stimulation: reversal of reserpine-induced suppression of motor activity. Psychopharmacologia. 1973;29(4):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00429276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER H., BIRKMAYER W., HORNYKIEWICZ O. [Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the human brain and its behavior in patients with Parkinson's syndrome]. Klin Wochenschr. 1961 Oct 15;39:1056–1059. doi: 10.1007/BF01487648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer H., Birkmayer W., Hornykiewicz O., Jellinger K., Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Dec;20(4):415–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Janssen H. J. The nucleus linearis intermedius raphe and behaviour evoked by direct and indirect stimulation of dopamine-sensitive sites within the caudate nucleus of cats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;28(2):266–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cools A. R., Van Rossum J. M. Excitation-mediating and inhibition-mediating dopamine-receptors: a new concept towards a better understanding of electrophysiological, biochemical, pharmacological, functional and clinical data. Psychopharmacologia. 1976 Feb 2;45(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00421135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman A. R., Walker R. J., Woodruff G. N. Picrotoxin antagonism of gamma-aminobutyric acid inhibitory responses and synaptic inhibition in the rat substantia nigra. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):696–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRINGER H., HORNYKIEWICZ O. [Distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the human brain and their behavior in diseases of the extrapyramidal system]. Klin Wochenschr. 1960 Dec 15;38:1236–1239. doi: 10.1007/BF01485901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD J. G., BOSANQUET F. D. The brain-stem lesions in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1953 Nov;16(4):213–226. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.16.4.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garelis E., Young S. N., Lal S., Sourkes T. L. Monoamine metabolites in lumbar CSF: the question of their origin in relation to clinical studies. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 11;79(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumpert J., Sharpe D., Curzon G. Amine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson's disease and the response to levodopa. J Neurol Sci. 1973 May;19(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Singh V. K., McGeer E. G., McGeer P. L. Immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase containing neostriatal neurons and their relationship with dopaminergic synapses. Brain Res. 1976 Jan 30;102(1):164–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornykiewicz O. Parkinson's disease: from brain homogenate to treatment. Fed Proc. 1973 Feb;32(2):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. M., Andén N. E., Dahlström A. A functional effect of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and in some other dopamine-rich parts of the rat brain. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Dec 31;45(2):139–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00429052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa I., Miyata Y., Toyokura Y., Otsuka M. The distribution of -aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the human substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:363–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. G., Davidson L., Hornykiewicz O. The neurochemistry of Parkinson's disease: effect of L-dopa therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Dec;195(3):453–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METTLER F. A. SUBSTANTIA NIGRA AND PARKINSONISM. Arch Neurol. 1964 Nov;11:529–542. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460230079007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Dolphin A., Duvoisin R. C., Jenner P., Tarsy D. Role of noradrenaline in levodopa reversal of reserpine akinesia. Brain Res. 1974 Sep 13;77(3):521–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer E. G., Fibiger H. C., McGeer P. L., Brooke S. Temporal changes in amine synthesizing enzymes of rat extrapyramidal structures after hemitransections or 6-hydroxydopamine administration. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:289–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G. Enzymes associated with the metabolism of catecholamines, acetylcholine and gaba in human controls and patients with Parkinson's disease and Huntington's chorea. J Neurochem. 1976 Jan;26(1):65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisman G., Field P. M. A quantitative investigation of the development of collateral reinnervation after partial deafferentation of the septal nuclei. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 28;50(2):241–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90729-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spehlmann R., Stahl S. M. Dopamine acetylcholine imbalance in Parkinson's disease. Possible regenerative overgrowth of cholinergic axon terminals. Lancet. 1976 Apr 3;1(7962):724–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Lloyd K. G., Gadea-Ciria M., Bartholini G. Enhanced striatal acetylcholine release by chlorpromazine and its reversal by apomorphine. Brain Res. 1973 Jun 15;55(2):476–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarsy D., Pycock C., Meldrum B., Marsden C. D. Rotational behavior induced in rats by intranigral picrotoxin. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


