Abstract
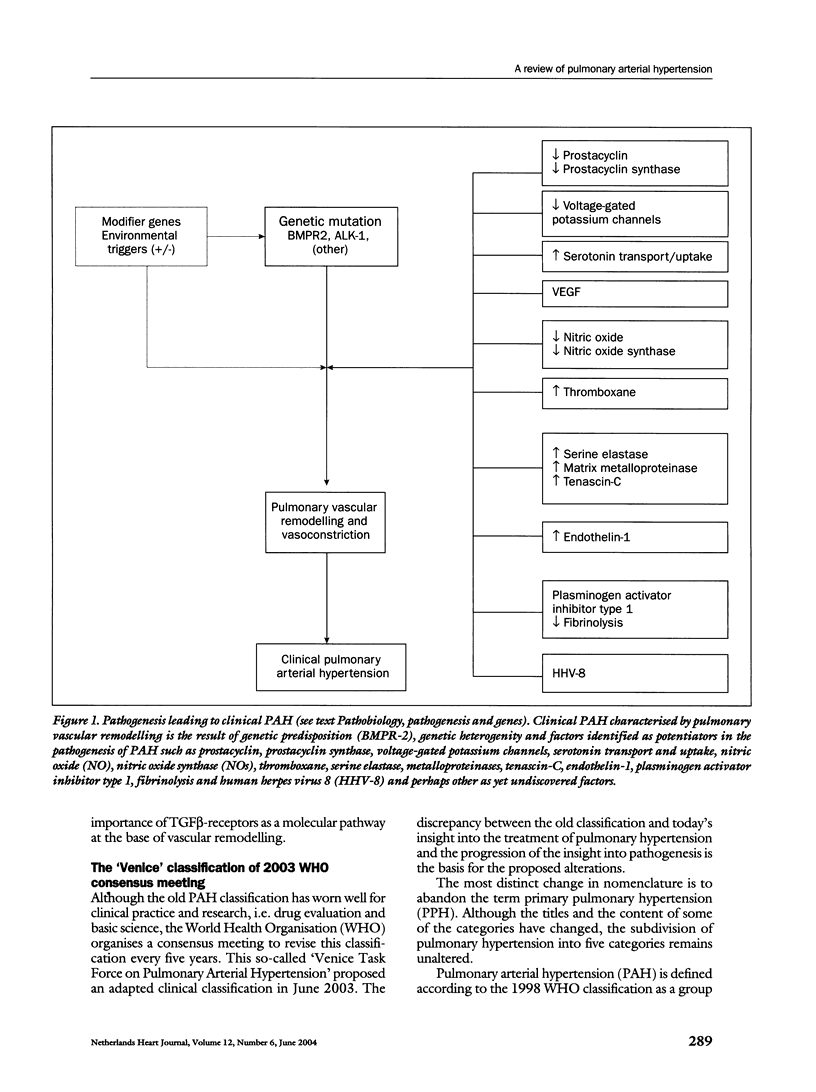
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a disease characterised by an increased pulmonary artery pressure. The precapillary pulmonary arteries show distinct pathobiological changes, i.e. medial hypertrophy, intimal fibrosis, microthrombi and plexiform lesions. Although the pathogenesis is not completely understood, pulmonary vascular proliferation and remodelling, due to a variety of mediators, is believed to play the pathogenetic key role. Genetic research reveals molecular deformities and gene mutations associated with phenotypic PAH.
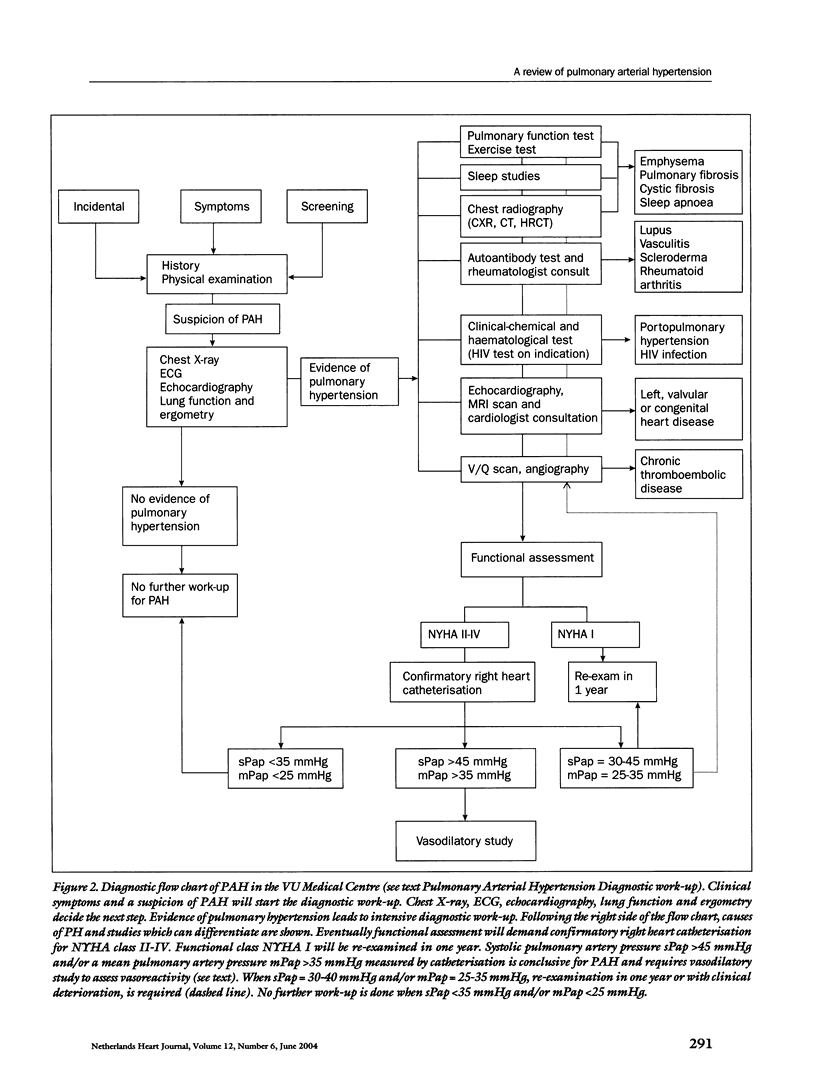
This article covers novel insights into pathobiology, pathogenesis and genes of PAH, which led to a novel classification system and a diagnostic work-up, emanated from the World Health Organisation Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension in Venice in June 2003.
Keywords: classification system, diagnostic work-up, genes, pathobiology, pathogenesis, pulmonary arterial hypertension
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcasoy Selim M., Christie Jason D., Ferrari Victor A., Sutton Martin St John, Zisman David A., Blumenthal Nancy P., Pochettino Alberto, Kotloff Robert M. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Dec 12;167(5):735–740. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200210-1130OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroliga A. C., Dweik R. A., Kaneko F. J., Erzurum S. C. Primary pulmonary hypertension: update on pathogenesis and novel therapies. Cleve Clin J Med. 2000 Mar;67(3):175-8, 181-5, 189-90. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.67.3.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman B. W., McPherson C. D., Newman J. H., King G. A., Bernard G. R., Groves B. M., Loyd J. E. An imbalance between the excretion of thromboxane and prostacyclin metabolites in pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 9;327(2):70–75. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207093270202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool C. D., Kennedy D., Voelkel N. F., Tuder R. M. Pathogenesis and evolution of plexiform lesions in pulmonary hypertension associated with scleroderma and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Hum Pathol. 1997 Apr;28(4):434–442. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(97)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool Carlyne D., Rai Pradeep R., Yeager Michael E., Hernandez-Saavedra Daniel, Serls Amanda E., Bull Todd M., Geraci Mark W., Brown Kevin K., Routes John M., Tuder Rubin M. Expression of human herpesvirus 8 in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2003 Sep 18;349(12):1113–1122. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. N., Heilbut A., Humpl T., Lam C., Ito S., Rabinovitch M. Complete reversal of fatal pulmonary hypertension in rats by a serine elastase inhibitor. Nat Med. 2000 Jun;6(6):698–702. doi: 10.1038/76282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alonzo G. E., Barst R. J., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Kernis J. T. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Sep 1;115(5):343–349. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-5-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alonzo G. E., Bower J. S., Dantzker D. R. Differentiation of patients with primary and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1984 Apr;85(4):457–461. doi: 10.1378/chest.85.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Lingling, Sullivan Christopher C., Chu Danny, Cho Augustine J., Kido Masakuni, Wolf Paul L., Yuan Jason X-J, Deutsch Reena, Jamieson Stuart W., Thistlethwaite Patricia A. Signaling molecules in nonfamilial pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2003 Feb 6;348(6):500–509. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddahibi S., Fabre V., Boni C., Martres M. P., Raffestin B., Hamon M., Adnot S. Induction of serotonin transporter by hypoxia in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells. Relationship with the mitogenic action of serotonin. Circ Res. 1999 Feb 19;84(3):329–336. doi: 10.1161/01.res.84.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eysmann S. B., Palevsky H. I., Reichek N., Hackney K., Douglas P. S. Two-dimensional and Doppler-echocardiographic and cardiac catheterization correlates of survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1989 Aug;80(2):353–360. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaine S. P., Rubin L. J. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1998 Aug 29;352(9129):719–725. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)02111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galiè N., Manes A., Branzi A. The new clinical trials on pharmacological treatment in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2002 Oct;20(4):1037–1049. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.05542002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galiè N., Ussia G., Passarelli P., Parlangeli R., Branzi A., Magnani B. Role of pharmacologic tests in the treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1995 Jan 19;75(3):55A–62A. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaid A., Saleh D. Reduced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 27;333(4):214–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507273330403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Miyazono K., ten Dijke P. TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature. 1997 Dec 4;390(6659):465–471. doi: 10.1038/37284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervé P., Launay J. M., Scrobohaci M. L., Brenot F., Simonneau G., Petitpretz P., Poubeau P., Cerrina J., Duroux P., Drouet L. Increased plasma serotonin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Med. 1995 Sep;99(3):249–254. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)80156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderliter A. L., Willis P. W., 4th, Barst R. J., Rich S., Rubin L. J., Badesch D. B., Groves B. M., McGoon M. D., Tapson V. F., Bourge R. C. Effects of long-term infusion of prostacyclin (epoprostenol) on echocardiographic measures of right ventricular structure and function in primary pulmonary hypertension. Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. Circulation. 1997 Mar 18;95(6):1479–1486. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.6.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L. Bone morphogenetic proteins: multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes Dev. 1996 Jul 1;10(13):1580–1594. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.13.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber K., Beckmann R., Frank H., Kneussl M., Mlczoch J., Binder B. R. Fibrinogen, t-PA, and PAI-1 plasma levels in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Oct;150(4):929–933. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.4.7921465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus J. T., Vonk Noordegraaf A., De Vries P. M., Van Rossum A. C., Roseboom B., Heethaar R. M., Postmus P. E. MRI evaluation of right ventricular pressure overload in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998 Sep-Oct;8(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1002/jmri.1880080502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Nagaya N., Satoh T., Kyotani S., Sakamaki F., Fujita M., Nakanishi N., Miyatake K. Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Feb;161(2 Pt 1):487–492. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.2.9906015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes D., Loscalzo J. Pulmonary hypertension: newer concepts in diagnosis and management. Clin Cardiol. 1997 Aug;20(8):676–682. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960200804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. H., Wheeler L., Lane K. B., Loyd E., Gaddipati R., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Loyd J. E. Mutation in the gene for bone morphogenetic protein receptor II as a cause of primary pulmonary hypertension in a large kindred. N Engl J Med. 2001 Aug 2;345(5):319–324. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108023450502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietra G. G., Edwards W. D., Kay J. M., Rich S., Kernis J., Schloo B., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M. Histopathology of primary pulmonary hypertension. A qualitative and quantitative study of pulmonary blood vessels from 58 patients in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Registry. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1198–1206. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffy O., Azarian R., Brenot F., Parent F., Sitbon O., Petitpretz P., Hervé P., Duroux P., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Simonneau G. Clinical significance of the pulmonary vasodilator response during short-term infusion of prostacyclin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1996 Feb 1;93(3):484–488. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi M. J., Bossone E., Bach D. S., Armstrong W. F., Rubenfire M. Echocardiographic predictors of an adverse response to a nifedipine trial in primary pulmonary hypertension: diminished left ventricular size and leftward ventricular septal bowing. Chest. 1999 Nov;116(5):1218–1223. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.5.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Brundage B. H. High-dose calcium channel-blocking therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: evidence for long-term reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure and regression of right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 1987 Jul;76(1):135–141. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Dantzker D. R., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Koerner S. K. Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):216–223. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Pietra G. G., Kieras K., Hart K., Brundage B. H. Primary pulmonary hypertension: radiographic and scintigraphic patterns of histologic subtypes. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Oct;105(4):499–502. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-4-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeleveld Roald J., Vonk-Noordegraaf Anton, Marcus J. Tim, Bronzwaer Jean G. F., Marques Koen M. J., Postmus Pieter E., Boonstra Anco. Effects of epoprostenol on right ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation in pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2004 Feb;125(2):572–579. doi: 10.1378/chest.125.2.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runo James R., Loyd James E. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 2003 May 3;361(9368):1533–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon O., Humbert M., Jagot J. L., Taravella O., Fartoukh M., Parent F., Herve P., Simonneau G. Inhaled nitric oxide as a screening agent for safely identifying responders to oral calcium-channel blockers in primary pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 1998 Aug;12(2):265–270. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.12020265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. G., Hansen J. E., Oudiz R. J., Wasserman K. Exercise pathophysiology in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2001 Jul 24;104(4):429–435. doi: 10.1161/hc2901.093198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trembath R. C., Thomson J. R., Machado R. D., Morgan N. V., Atkinson C., Winship I., Simonneau G., Galie N., Loyd J. E., Humbert M. Clinical and molecular genetic features of pulmonary hypertension in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. N Engl J Med. 2001 Aug 2;345(5):325–334. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108023450503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuder R. M., Groves B., Badesch D. B., Voelkel N. F. Exuberant endothelial cell growth and elements of inflammation are present in plexiform lesions of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1994 Feb;144(2):275–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. X., Aldinger A. M., Juhaszova M., Wang J., Conte J. V., Jr, Gaine S. P., Orens J. B., Rubin L. J. Dysfunctional voltage-gated K+ channels in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells of patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1998 Oct 6;98(14):1400–1406. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.98.14.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X. J., Wang J., Juhaszova M., Gaine S. P., Rubin L. J. Attenuated K+ channel gene transcription in primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1998 Mar 7;351(9104):726–727. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)78495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Yidan D., Campbell Andrew I. M., Robb Malcolm, Ng Douglas, Stewart Duncan J. Protective role of angiopoietin-1 in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 2003 Apr 10;92(9):984–991. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000070587.79937.F0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


