Abstract
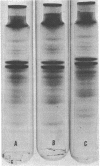
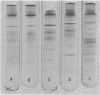
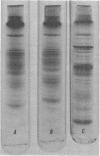
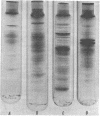
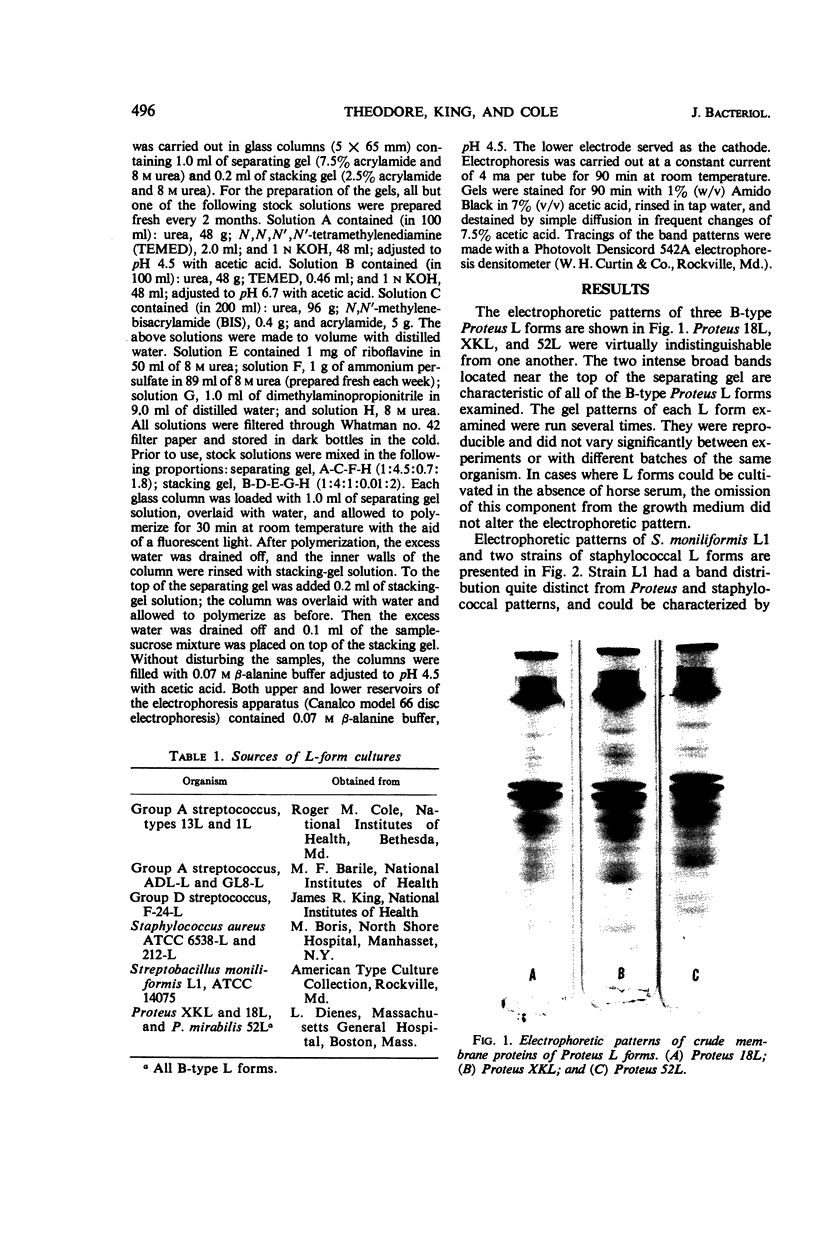
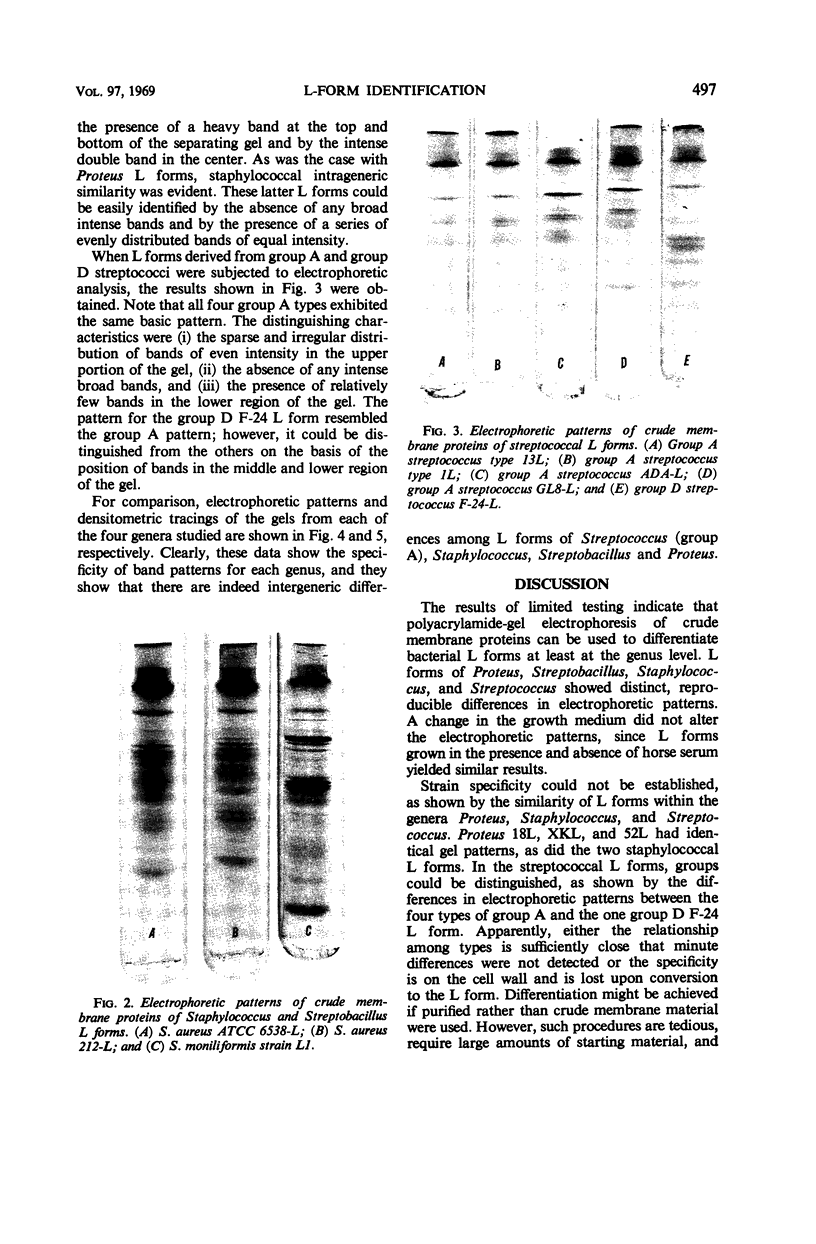
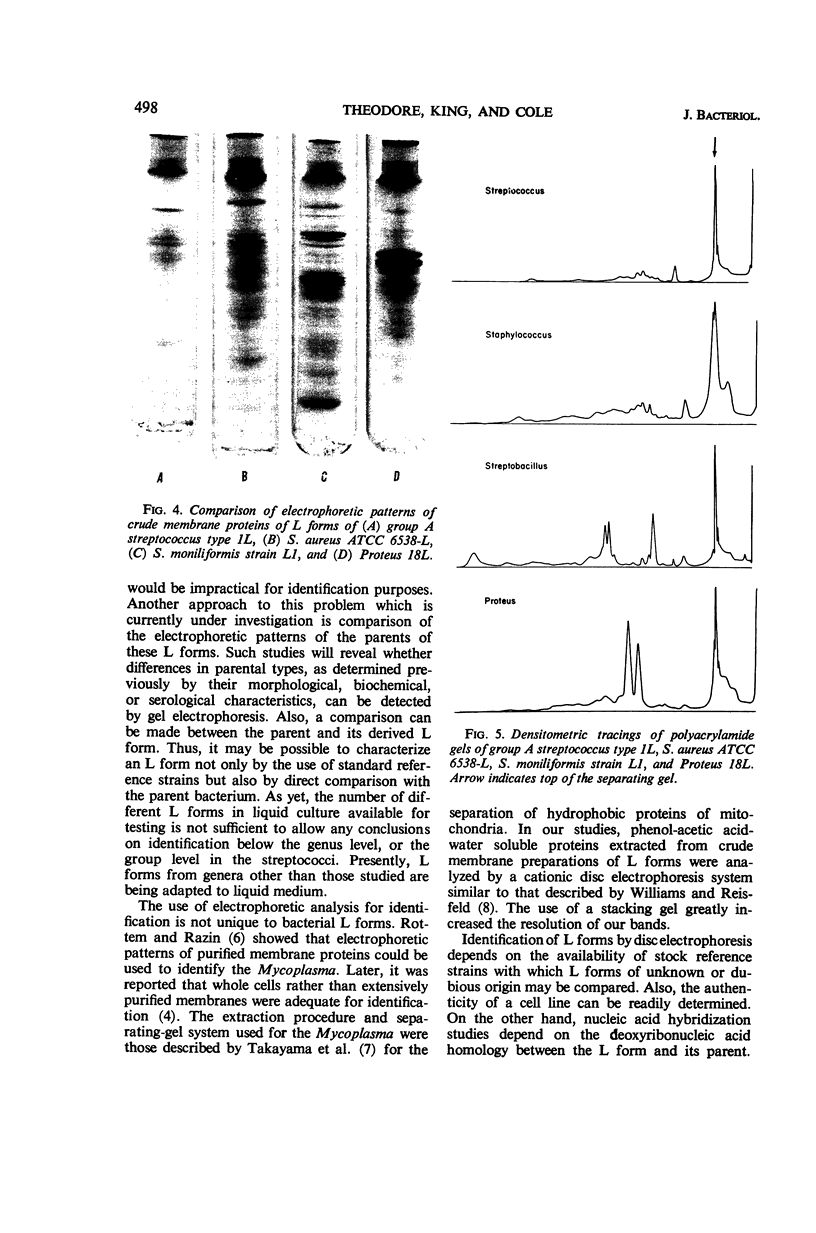
Crude membranes were obtained from L forms by allowing the cells to lyse in distilled water. The crude membranes were washed several times in distilled water, lyophilized, and extracted with phenol-acetic acid-water. The membrane proteins were separated electrophoretically in polyacrylamide gels run at pH 4.5. Electrophoretic patterns and densitometric tracings of the gels showed distinct, reproducible intergeneric differences among L forms of Proteus, Streptobacillus, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus. Differences within a genus could not be detected except between the group A streptococcal L forms and the one group D F-24 L form. This electrophoretic method offers possibilities for ready identification of L forms through the use of standard reference strains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FOWLER R. C., COBLE D. W., KRAMER N. C., BROWN T. M. STARCH GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF A FRACTION OF CERTAIN OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE GROUP OF MICROORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1145–1151. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1145-1151.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler R. C., Coble D. W., Kramer N. C., Pai R. R., Serrano B. A., Brown T. M. Immunoelectrophoretic analyses of an aqueous fraction of some Mycoplasmata and bacterial L-forms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):641–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Identification of Mycoplasma and other microorganisms by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1807-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogul M., McGee Z. A., Wittler R. G., Falkow S. Nucleic acid homologies of selected bacteria, L forms, Mycoplasma species. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1200–1204. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1200-1204.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama K., MacLennan D. H., Tzagoloff A., Stoner C. D. Studies on the electron transfer system. LXVII. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the mitochondrial electron transfer complexes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS D. E., REISFELD R. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS: EXTENSION TO NEW CONDITIONS OF PH AND BUFFER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]