Abstract
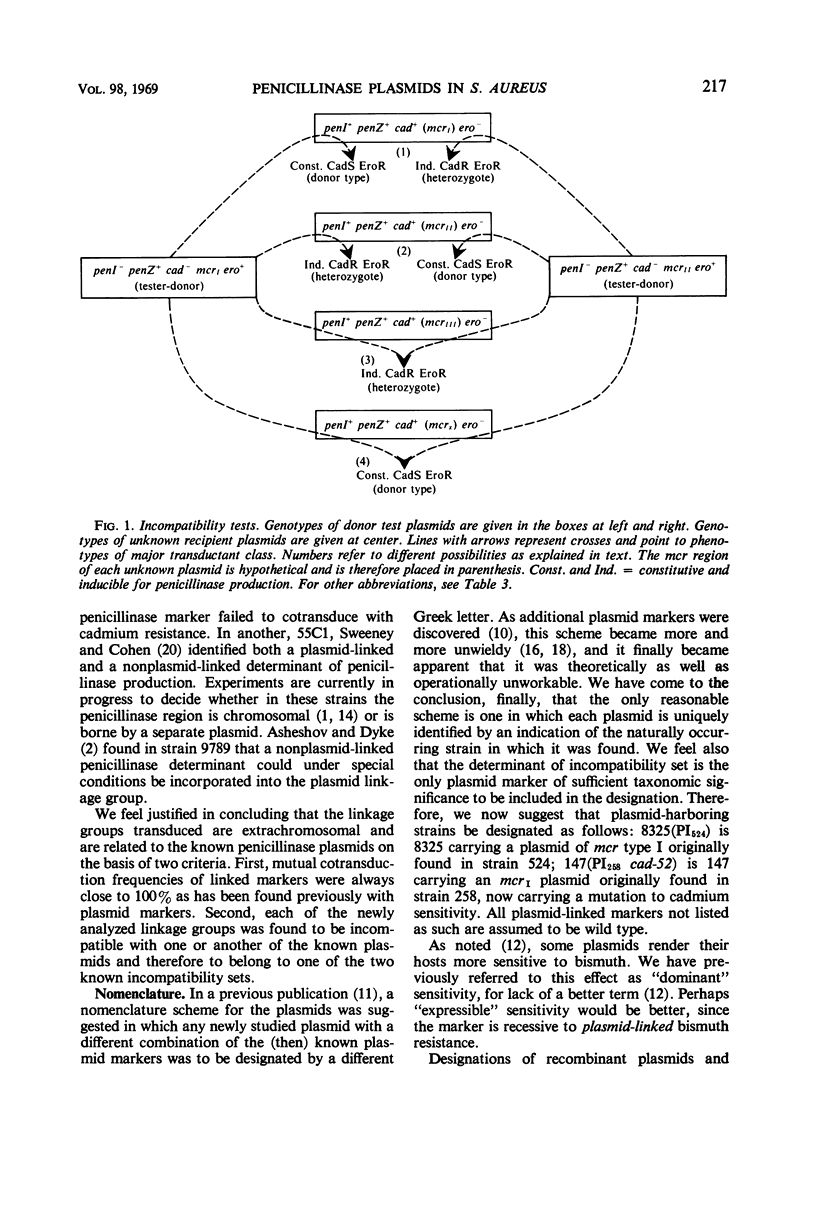
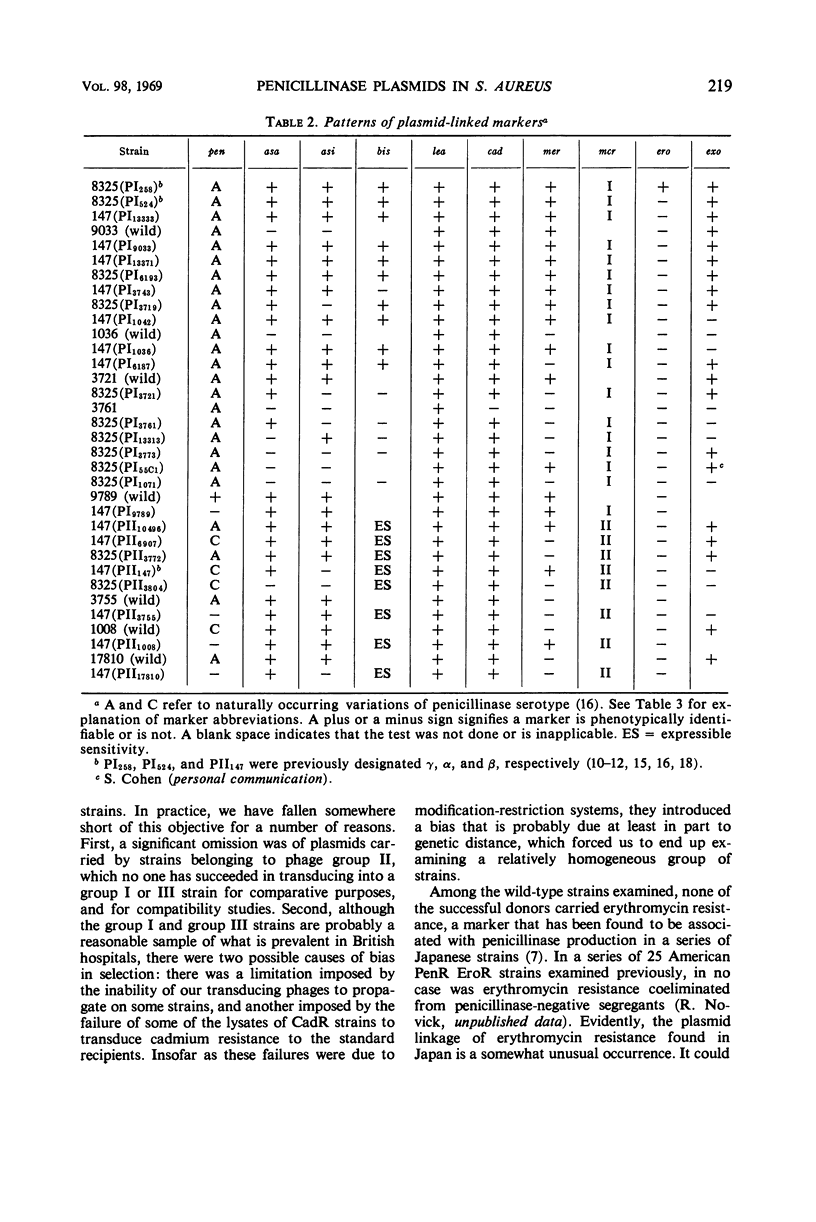
A series of plasmids harbored by naturally occurring penicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus were surveyed with a view toward exploring the variability in plasmid-linked marker patterns. Plasmids were transduced from their natural hosts to either of two plasmid-negative laboratory strains by selection for cadmium resistance, and the transductants were tested for all other markers previously found to be plasmid-linked. All of the strains that were able to serve as genetic donors to one of the two stock strains could donate cadmium and lead resistance as linked, plasmid-borne markers. Among the other plasmid markers, a wide variety of patterns was found, including four plasmids that did not carry the penicillinase determinant. Each of the 26 plasmids studied, including the latter 4, was found to belong to one of the two incompatibility sets of penicillinase plasmids previously identified. With the exception of the penicillinase-negative plasmids, which were found in both sets, all the plasmids of incompatibility set I directed the production of penicillinase type A; those belonging to set II directed either type A or type C. Those of set II without exception increased the sensitivity of their host strains to bismuth ion; those of set I carried determinants of bismuth resistance or did not affect the sensitivity of their host to this ion. No other perfect correlations between markers were encountered; in particular, there was no correlation between penicillinase serotype and the excretion of the enzyme. This finding allows the prediction that there is, in addition to all of the markers thus far identified, a plasmid-linked determinant of penicillinase excretion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asheshov E. H. Chromosomal location of the genetic elements controlling penicillinase production in a strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):804–806. doi: 10.1038/210804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asheshov E. H., Dyke K. G. Regulation of the synthesis of penicillinase in diploids of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Sweeney H. M. Constitutive penicillinase formation in Staphylococcus aureus owing to a mutation unlinked to the penicillinase plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1368–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1368-1374.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. Genetics. 1966 Jul;54(1):61–76. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke K. G., Richmond M. H. Occurrence of various types of penicillinase plasmid among 'hospital' staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jan;20(1):75–79. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., HASHIMOTO H., KONO M., MORIMURA M. DRUG RESISTANCE OF STAPHYLOCOCCI. II. JOINT ELIMINATION AND JOINT TRANSDUCTION OF THE DETERMINANTS OF PENICILLINASE PRODUCTION AND RESISTANCE TO MACROLIDE ANTIBIOTICS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:988–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.988-992.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P., RICHMOND M. H. NATURE AND INTERACTIONS OF THE GENETIC ELEMENTS GOVERNING PENICILLINASE SYNTHESIS IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:467–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.467-480.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Staphylococcal penicillinase and the new penicillins. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj0830229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Roth C. Plasmid-linked resistance to inorganic salts in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1335–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1335-1342.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRET C. J. Iodometric assay of penicillinase. Nature. 1954 Nov 27;174(4439):1012–1013. doi: 10.1038/1741012a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poston S. M. Cellular location of the genes controlling penicillinase production and resistance to streptomycin and tetracycline in a strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1966 May 21;210(5038):802–804. doi: 10.1038/210802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. DOMINANCE OF THE INDUCIBLE STATE IN STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS CONTAINING TWO DISTINCT PENICILLINASE PLASMIDS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:370–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.370-374.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. WILD-TYPE VARIANTS OF EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:584–593. doi: 10.1042/bj0940584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Penicillinase plasmids in Staphylococcus aureus. Br Med Bull. 1965 Sep;21(3):260–263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. M., Cohen S. Wild-type strain of Staphylococcus aureus containing two genetic linkage groups for penicillinase production. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):920–924. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.920-924.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., NISHIDA H., OGATA C., ARAI T., SATO S. EPISOME-MEDIATED TRANSFER OF DRUG RESISTANCE IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. VII. TWO TYPES OF NATURALLY OCCURRING R FACTORS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:716–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.716-726.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


