Abstract
Background
Endurance training is known to alter the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, a major goal when pursuing fitness. Here, we test the hypothesis that the training-associated rhythmic sensations alone, hence without the usual accompanying physical exercise, accomplish this effect.
Method
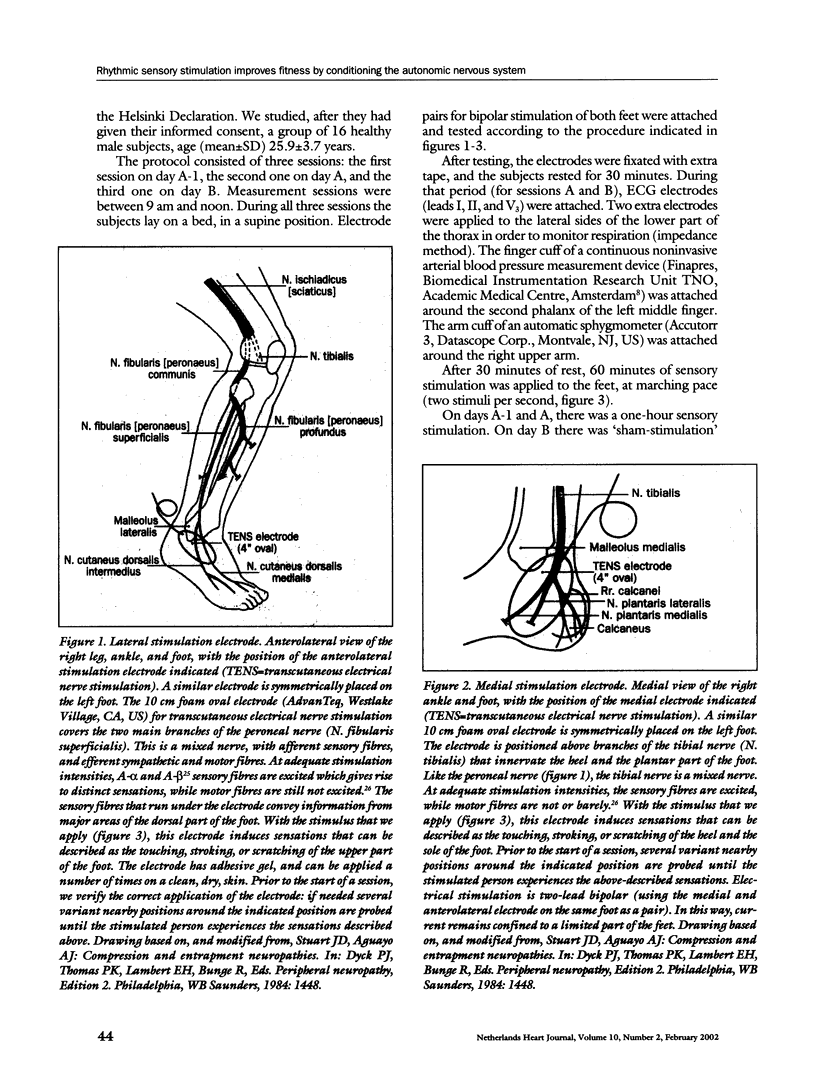
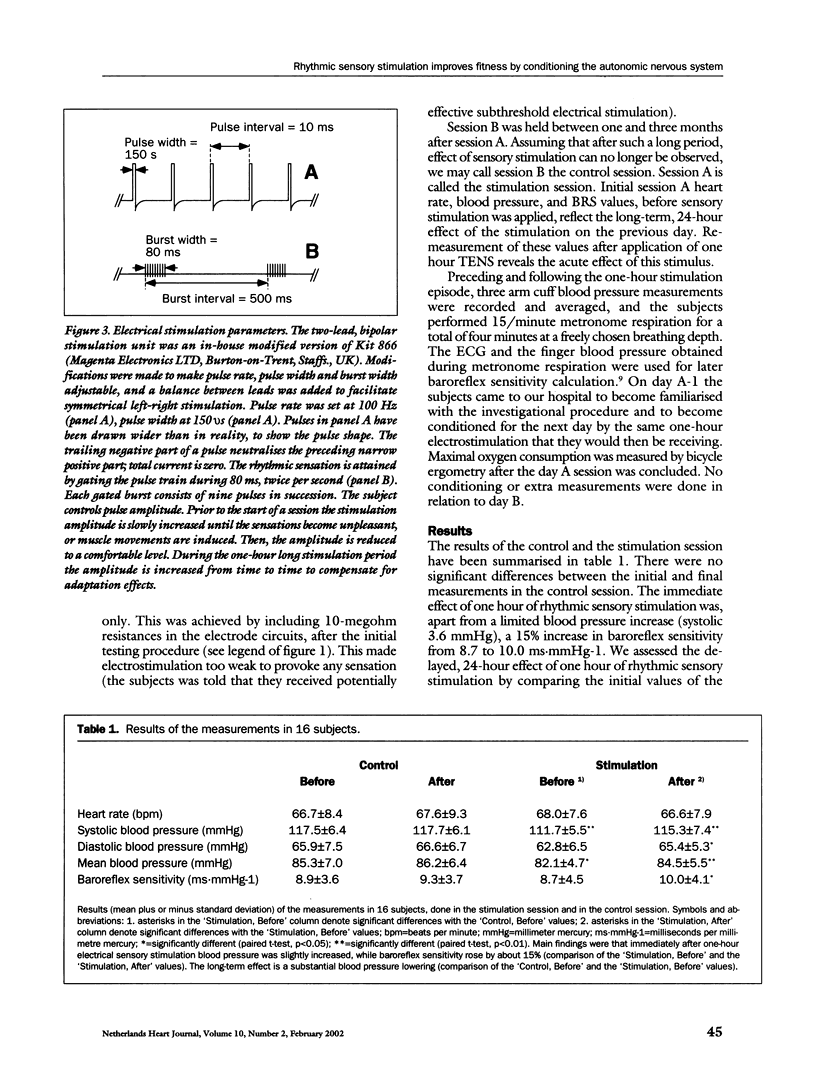
We studied sixteen resting healthy male volunteers, age (mean±SD) 25.9±3.7 years. During one hour we applied, at marching pace (2 bursts per second), bipolar transcutaneous electrical sensory nerve stimulation to both feet. The stimulation intensity was controlled in such a way that discharges of sensory fibres in the tibial and fibular nerves were induced, while motor fibres were not excited. Heart rate, blood pressure, and baroreflex sensitivity were measured before and after stimulation.
Results
Baseline baroreflex sensitivity and systolic blood pressure were 8.7±4.5 ms·mmHg-1 and 117.5±6.4 mmHg, respectively. Directly after rhythmic sensory stimulation baroreflex sensitivity had increased to 10.0±4.1 ms·mmHg-1 (p<0.05). One day later, systolic blood pressure had lowered to 111.7±5.5 mmHg (p<0.01).
Conclusions
Rhythmic sensory stimulation entails autonomic adaptations that are comparable with those of exercise. This demonstration of sensory-induced autonomic adaptations without any muscular involvement may help to design alternative, low-effort fitness programmes for specific categories of sedentary, diseased or disabled persons.
Keywords: arterial baroreflex, autonomic, blood pressure, nervous system, physical fitness, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Lundeberg T. Acupuncture--from empiricism to science: functional background to acupuncture effects in pain and disease. Med Hypotheses. 1995 Sep;45(3):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(95)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett D. R., Jr, Howley E. T. Limiting factors for maximum oxygen uptake and determinants of endurance performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000 Jan;32(1):70–84. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200001000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A. J., Clayton R. H., Murray A., Reed J. W., Subhan M. F., Ford G. A. Baroreflex function in sedentary and endurance-trained elderly people. Age Ageing. 1997 Jul;26(4):289–294. doi: 10.1093/ageing/26.4.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convertino V. A., Adams W. C., Shea J. D., Thompson C. A., Hoffler G. W. Impairment of carotid-cardiac vagal baroreflex in wheelchair-dependent quadriplegics. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):R576–R580. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.260.3.R576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ferrari G. M., Vanoli E., Stramba-Badiale M., Hull S. S., Jr, Foreman R. D., Schwartz P. J. Vagal reflexes and survival during acute myocardial ischemia in conscious dogs with healed myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):H63–H69. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.1.H63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke K. A., Doerr D. F., Convertino V. A. A single bout of exhaustive exercise affects integrated baroreflex function after 16 days of head-down tilt. Am J Physiol. 1995 Sep;269(3 Pt 2):R614–R620. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1995.269.3.R614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiks J., Swenne C. A., Bruschke A. V., van der Velde E. T., Maan A. C., TenVoorde B. J., Vanrooijen M. G., Mosterd W. L., Schiereck P. Correlated neurocardiologic and fitness changes in athletes interrupting training. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000 Mar;32(3):571–575. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200003000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiks J., Swenne C. A., TenVoorde B. J., Honzíková N., Levert J. V., Maan A. C., Schalij M. J., Bruschke A. V. The importance of high-frequency paced breathing in spectral baroreflex sensitivity assessment. J Hypertens. 2000 Nov;18(11):1635–1644. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018110-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedbäck B., Perk J., Wodlin P. Long-term reduction of cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction: 10-year results of a comprehensive rehabilitation programme. Eur Heart J. 1993 Jun;14(6):831–835. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/14.6.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imholz B. P., Wieling W., van Montfrans G. A., Wesseling K. H. Fifteen years experience with finger arterial pressure monitoring: assessment of the technology. Cardiovasc Res. 1998 Jun;38(3):605–616. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(98)00067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaada B., Flatheim E., Woie L. Low-frequency transcutaneous nerve stimulation in mild/moderate hypertension. Clin Physiol. 1991 Mar;11(2):161–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1991.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer A. F., Hahn S., Cohen N. J., Banich M. T., McAuley E., Harrison C. R., Chason J., Vakil E., Bardell L., Boileau R. A. Ageing, fitness and neurocognitive function. Nature. 1999 Jul 29;400(6743):418–419. doi: 10.1038/22682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rovere M. T., Bigger J. T., Jr, Marcus F. I., Mortara A., Schwartz P. J. Baroreflex sensitivity and heart-rate variability in prediction of total cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction. ATRAMI (Autonomic Tone and Reflexes After Myocardial Infarction) Investigators. Lancet. 1998 Feb 14;351(9101):478–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(97)11144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakka T. A., Venäläinen J. M., Rauramaa R., Salonen R., Tuomilehto J., Salonen J. T. Relation of leisure-time physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness to the risk of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 2;330(22):1549–1554. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406023302201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorst P., Schulz B. G., Seller H., Koepchen H. P. Convergence of visceral and somatic afferents on single neurones in the reticular formation of the lower brain stem in dogs. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1996 Mar 7;57(3):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(95)00132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. F., Hui-Chan C. W. Conventional and acupuncture-like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation excite similar afferent fibers. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993 Jan;74(1):54–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura Y. Basic electrical parameters for safe and effective electro-therapeutics [electro-acupuncture, TES, TENMS (or TEMS), TENS and electro-magnetic field stimulation with or without drug field] for pain, neuromuscular skeletal problems, and circulatory disturbances. Acupunct Electrother Res. 1987;12(3-4):201–225. doi: 10.3727/036012987816358788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigaudo D., Fortrat J. O., Allevard A. M., Maillet A., Cottet-Emard J. M., Vouillarmet A., Hughson R. L., Gauquelin-Koch G., Gharib C. Changes in the sympathetic nervous system induced by 42 days of head-down bed rest. Am J Physiol. 1998 Jun;274(6 Pt 2):H1875–H1884. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1998.274.6.H1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somers V. K., Conway J., Johnston J., Sleight P. Effects of endurance training on baroreflex sensitivity and blood pressure in borderline hypertension. Lancet. 1991 Jun 8;337(8754):1363–1368. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93056-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Tolbert N. S., Dengel D. R., Brown M. D., McCole S. D., Pratley R. E., Ferrell R. E., Hagberg J. M. Ambulatory blood pressure after acute exercise in older men with essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2000 Jan;13(1 Pt 1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/s0895-7061(99)00141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner M. R., Loeb J. M. Reflex regulation of atrioventricular conduction. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 2):H1077–H1085. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.6.H1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore J. H., Stanforth P. R., Gagnon J., Leon A. S., Rao D. C., Skinner J. S., Bouchard C. Endurance exercise training has a minimal effect on resting heart rate: the HERITAGE Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1996 Jul;28(7):829–835. doi: 10.1097/00005768-199607000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


