Abstract
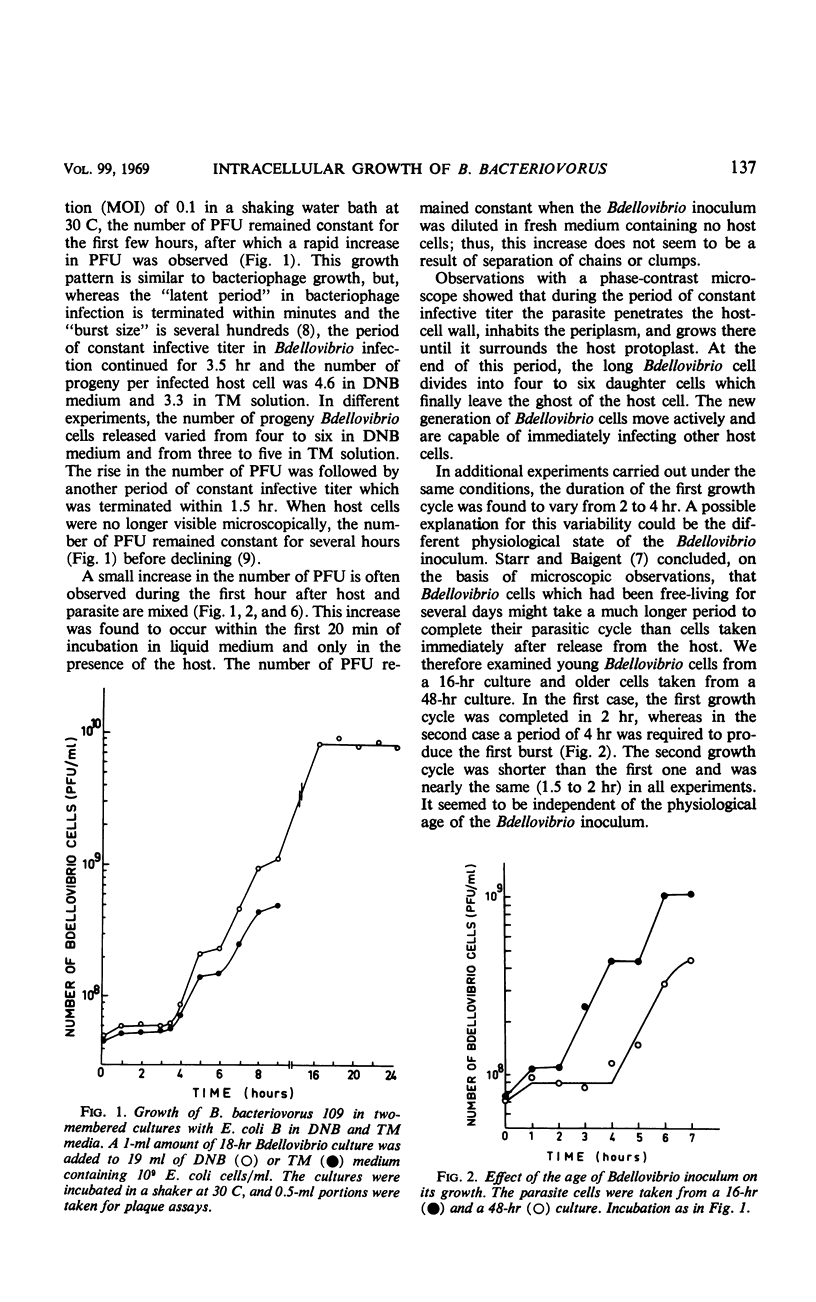
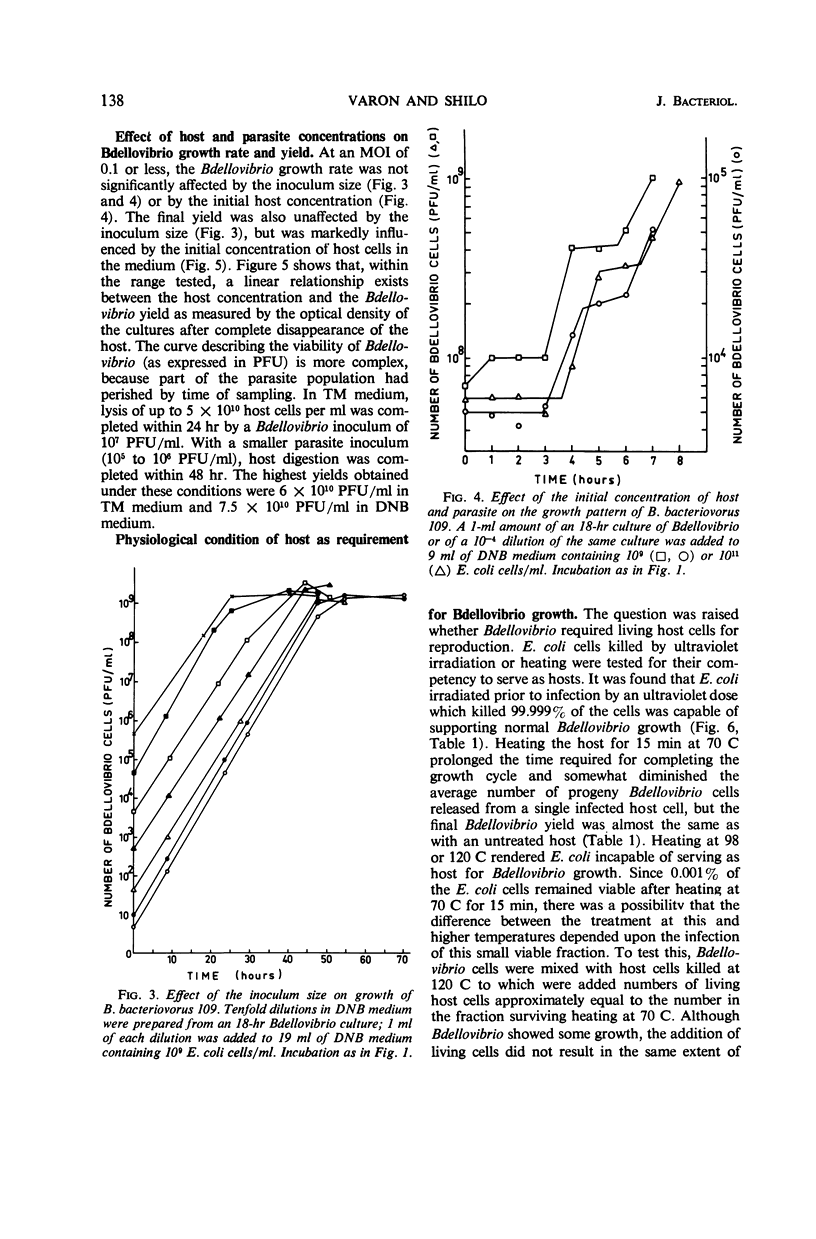
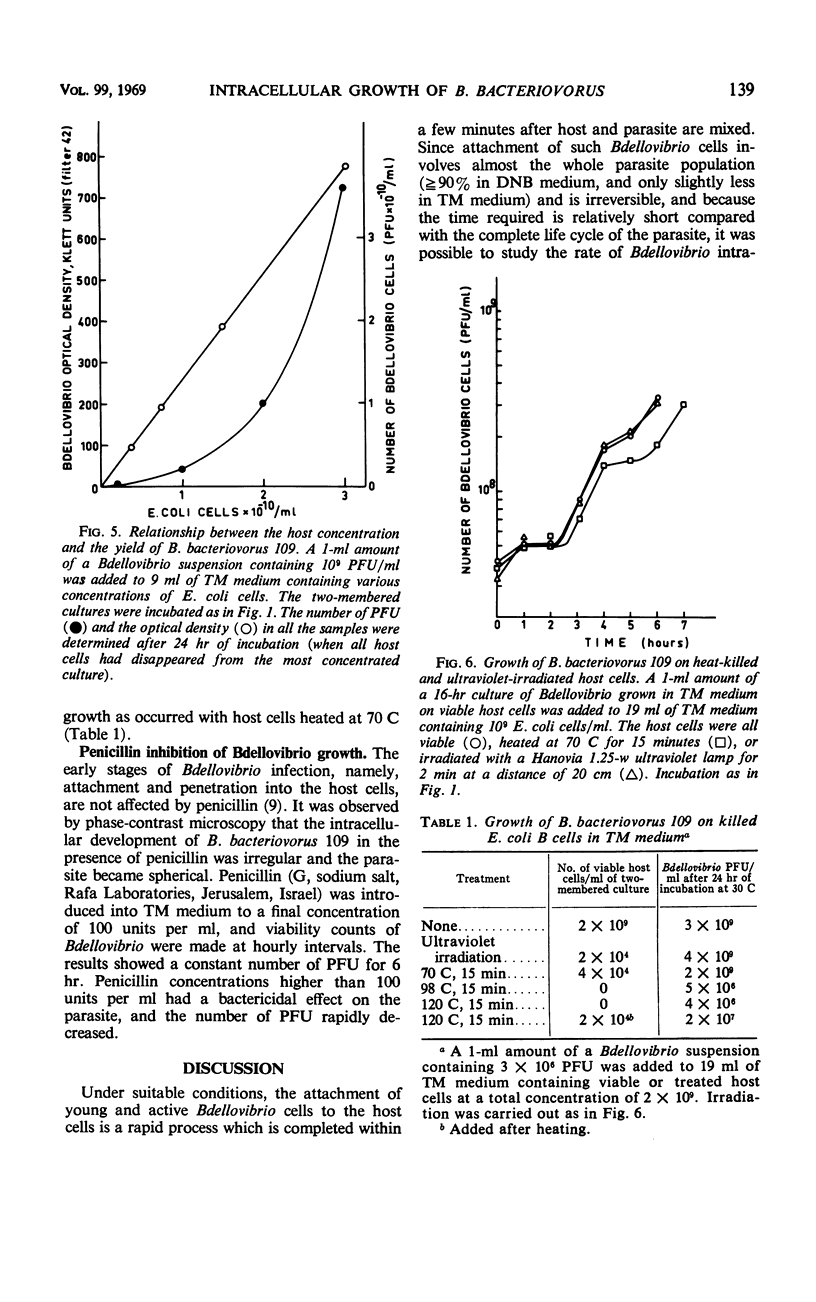
The intracellular life cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109 growing on Escherichia coli in a dilute nutrient medium exhibits a period of constant infective titer while the parasite grows and elongates inside the host cell. This period is terminated after 2 to 4 hr, and the number of the plaque-forming units in the culture rises rapidly to as much as six times the initial titer. The growth pattern of Bdellovibrio is similar with actively growing or resting host cells, or with host cells killed by ultraviolet irradiation or by heating at 70 C. The yield of B. bacteriovorus strain 109 in two-membered cultures with E. coli B depends on the host concentration and may reach 7.5 × 1010 cells per ml. Penicillin, which has no effect on the attachment and penetration of Bdellovibrio, inhibits its multiplication.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger A., Drews G., Ladwig R. Wirtskreis und Infektionscyclus eines neu isolierten Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus-Stammes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968 May 8;61(3):261–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lépine P., Guélin A., Sisman J., Lamblin D. Etude au microscope électronique de la lyse de Salmonella par Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jun 19;264(25):2957–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Factors affecting the intracellular parasitic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus developing within Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):912–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.912-923.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M., Bruff B. Lysis of Gram-negative bacteria by host-independent ectoparasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus isolates. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):317–328. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. J., Robinson J. Some energy-producing systems in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus, strain 6-5-S. Can J Biochem. 1968 Aug;46(8):865–873. doi: 10.1139/o68-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Baigent N. L. Parasitic interaction of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus with other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2006–2017. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2006-2017.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLMAN E. L., STENT G. S. Studies on activation of T4 bacteriophage by cofactor. IV. Nascent activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Nov;9(5):538–550. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


