Abstract
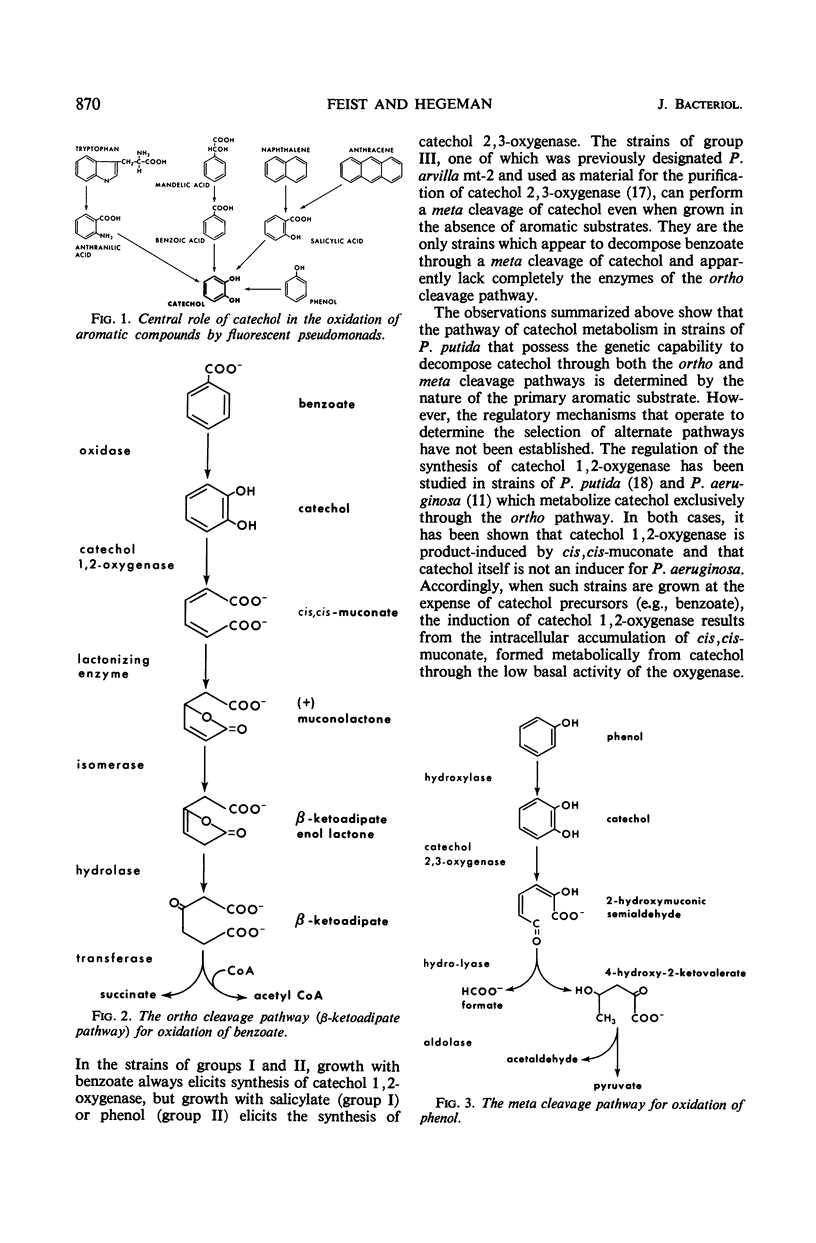
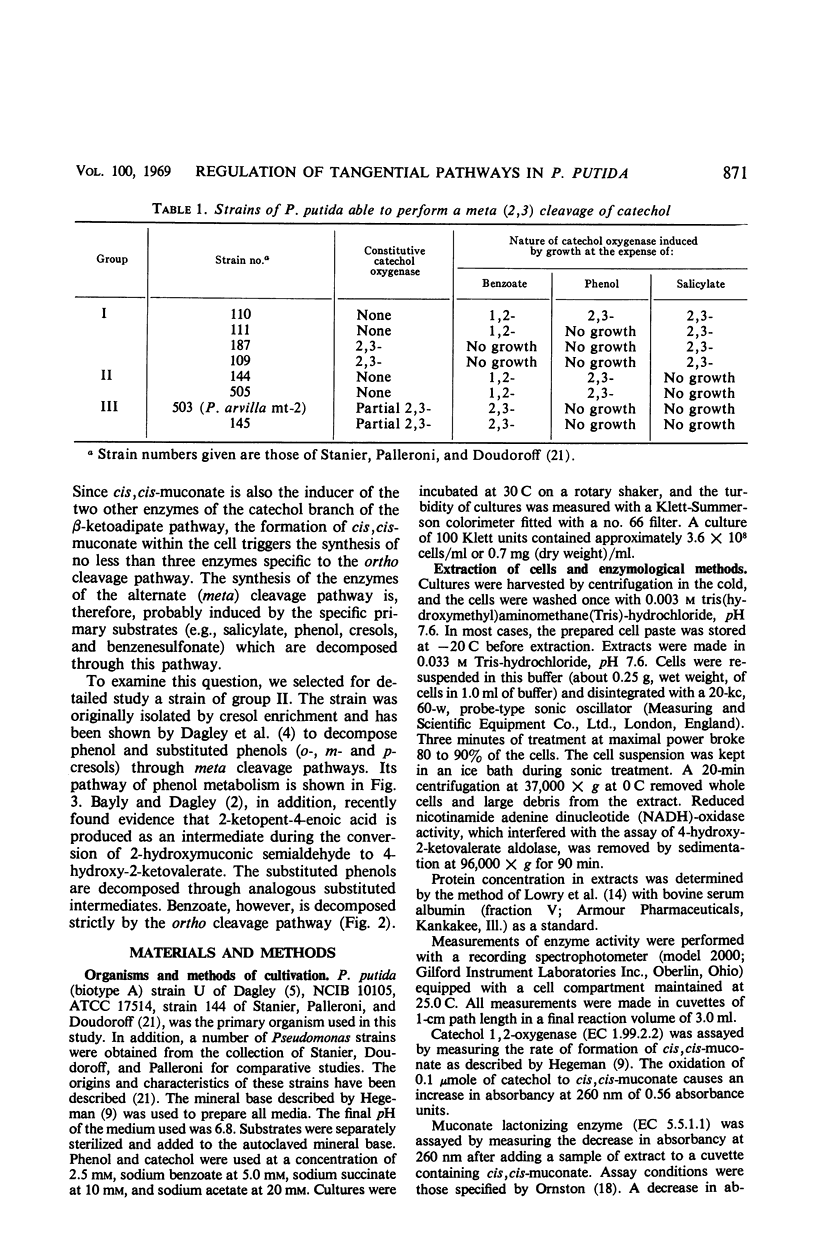
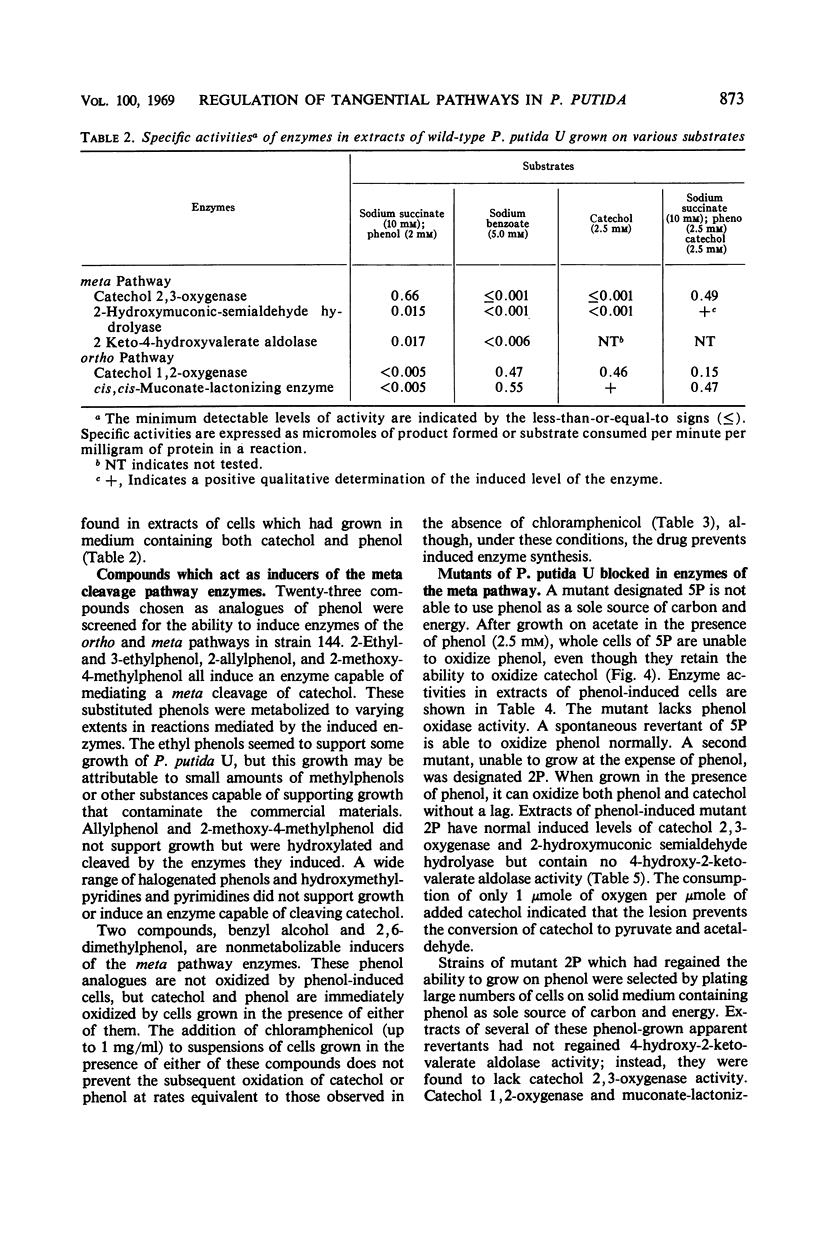
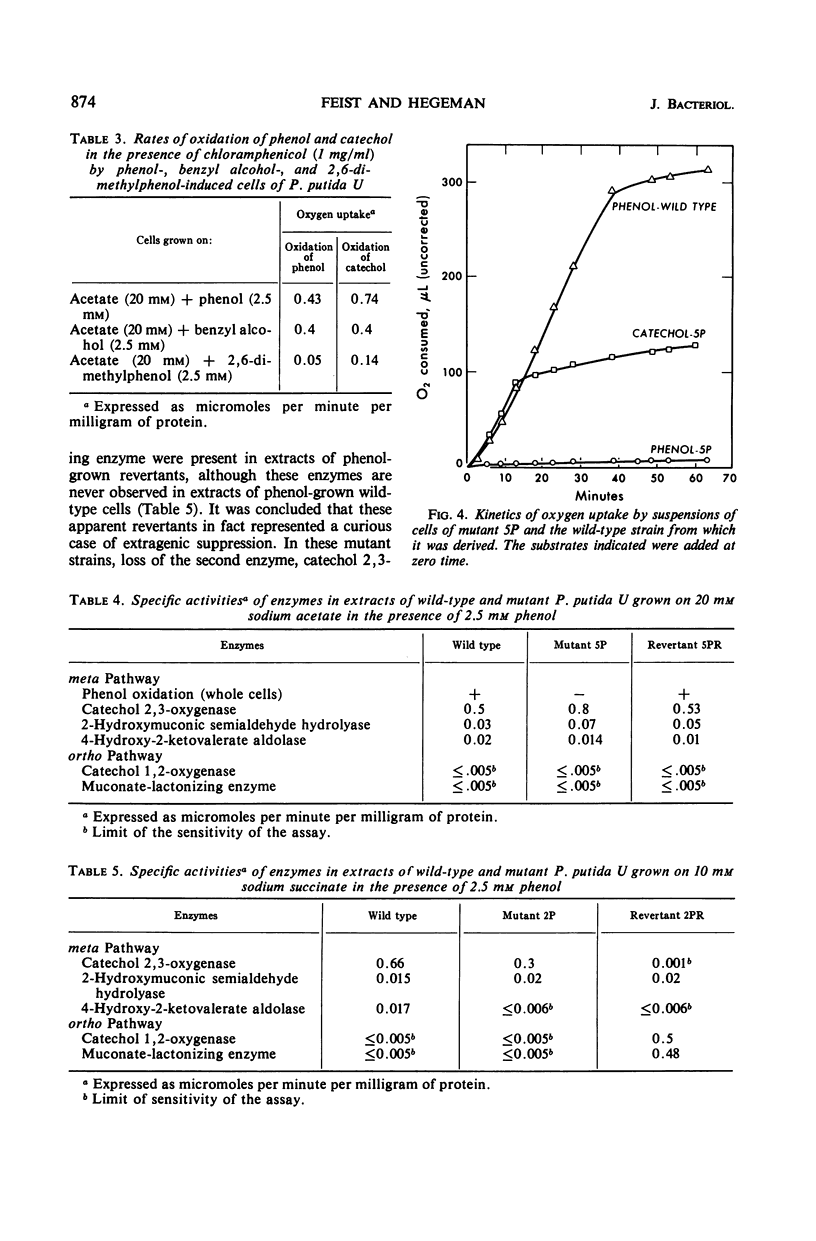
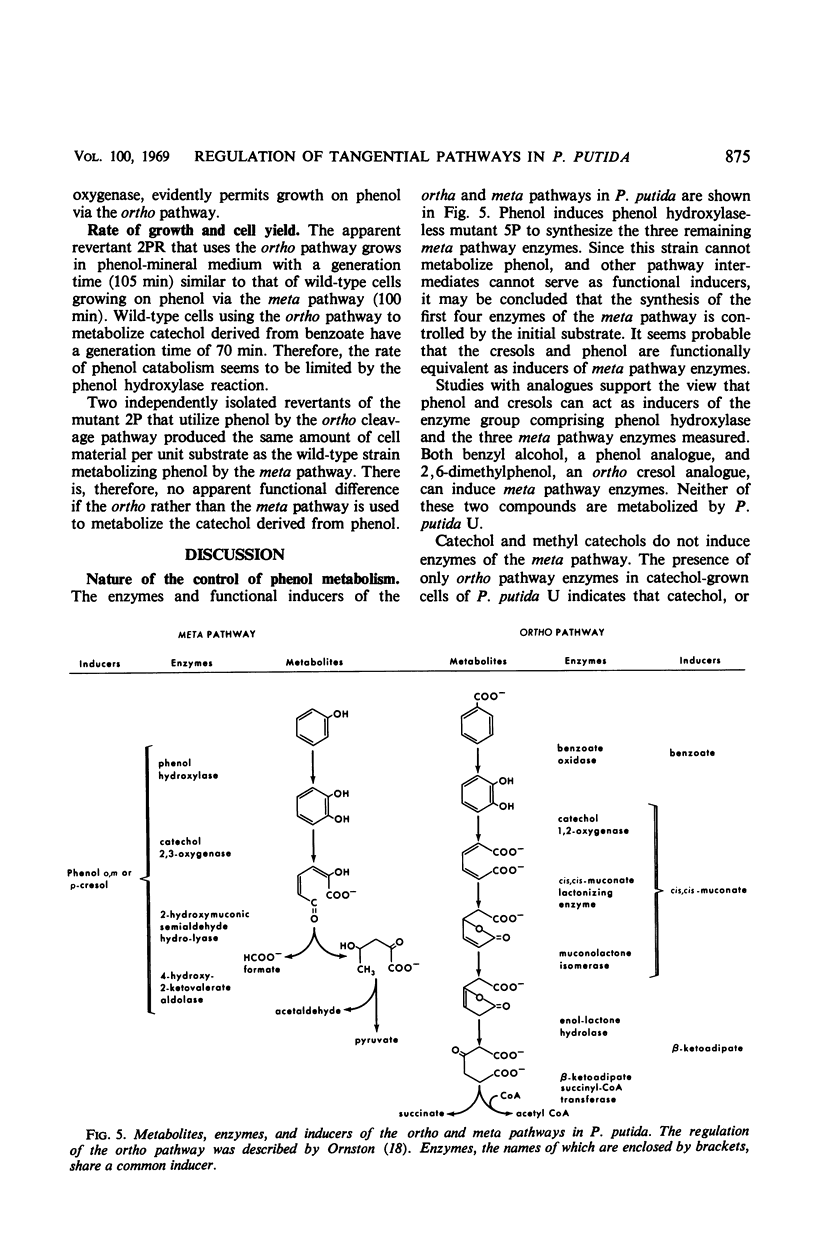
Catechol occurs as an intermediate in the metabolism of both benzoate and phenol by strains of Pseudomonas putida. During growth at the expense of benzoate, catechol is cleaved ortho (1,2-oxygenase) and metabolized via the β-ketoadipate pathway; during growth at the expense of phenol or cresols, the catechol or substituted catechols formed are metabolized by a separate pathway following meta (2,3-oxygenase) cleavage of the aromatic ring of catechol. It is possible to explain the mutually exclusive occurrence of the meta and ortho pathway enzymes in phenol- and benzoate-grown cells of P. putida on the basis of differences in the mode of regulation of these two pathways. By use of both nonmetabolizable inducers and blocked mutants, gratuitous synthesis of some of the meta pathway enzymes was obtained. All four enzymes of the meta pathway are induced by the primary substrate, cresol or phenol, or its analogue. Three enzymes of the ortho pathway that catalyze the conversion of catechol to β-ketoadipate enol-lactone are induced by cis,cis-muconate, produced from catechol by 1,2-oxygenase-mediated cleavage. Observations on the differences in specificity of induction and function of the two pathways suggest that they are not really either tangential or redundant. The meta pathway serves as a general mechanism for catabolism of various alkyl derivatives of catechol derived from substituted phenolic compounds. The ortho pathway is more specific and serves primarily in the catabolism of precursors of catechol and catechol itself.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S. Oxoenoic acids as metabolites in the bacterial degradation of catechols. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(3):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., EVANS W. C., RIBBONS D. W. New pathways in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Nature. 1960 Nov 12;188:560–566. doi: 10.1038/188560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. I., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. The ring-fission mechanism. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):251–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0910251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Oxidation of phenol and benzoic acid by some soil bacteria. Biochem J. 1947;41(3):373–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0410373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr D. R., Cain R. B. Catechol oxygenase induction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):879–885. doi: 10.1042/bj1060879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. The metabolism of p-hydroxybenzoate by Rhodopseudomonas palustris and its regulation. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00406325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. B., Hegeman G. D. Genetic control of the beta-ketoadipate pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1488–1499. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1488-1499.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., LEDERBERG E. M. Replica plating and indirect selection of bacterial mutants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Mar;63(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.3.399-406.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVELESS A., HOWARTH S. Mutation of bacteria at high levels of survival by ethyl methane sulphonate. Nature. 1959 Dec 5;184:1780–1782. doi: 10.1038/1841780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malesset-Bras M., Azoulay E. Dégradation bactérienne du naphtalène. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Dec;109(6):894–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIZUKA Y., ICHIYAMA A., NAKAMURA S., HAYAISHI O. A new metabolic pathway of catechol. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:PC268–PC270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOZAKI M., KAGAMIYAMA H., HAYAISHI O. METAPYROCATECHASE. I. PURIFICATION, CRYSTALLIZATION AND SOME PROPERTIES. Biochem Z. 1963;338:582–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treccani V., Galli E., Catelani D., Sorlini C. Induction of 1,2- and 2,3-diphenol oxygenases in Pseudomonas desmolyticum. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(1):65–69. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630080108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


