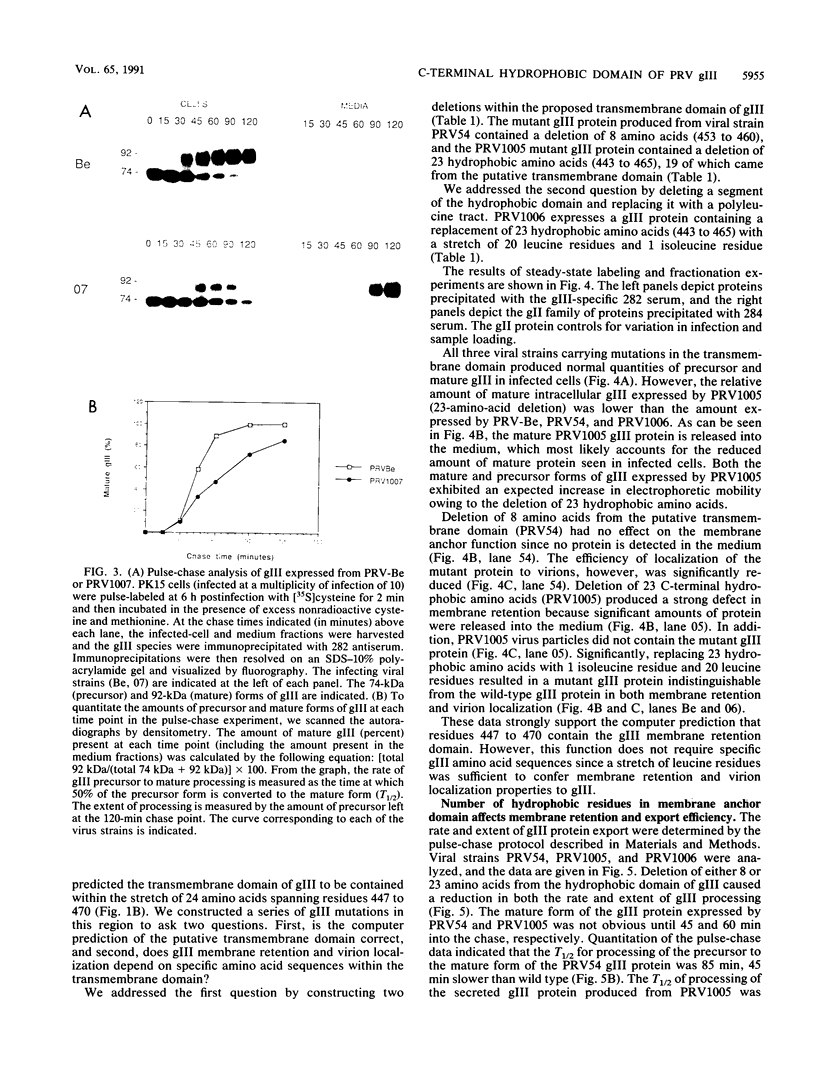
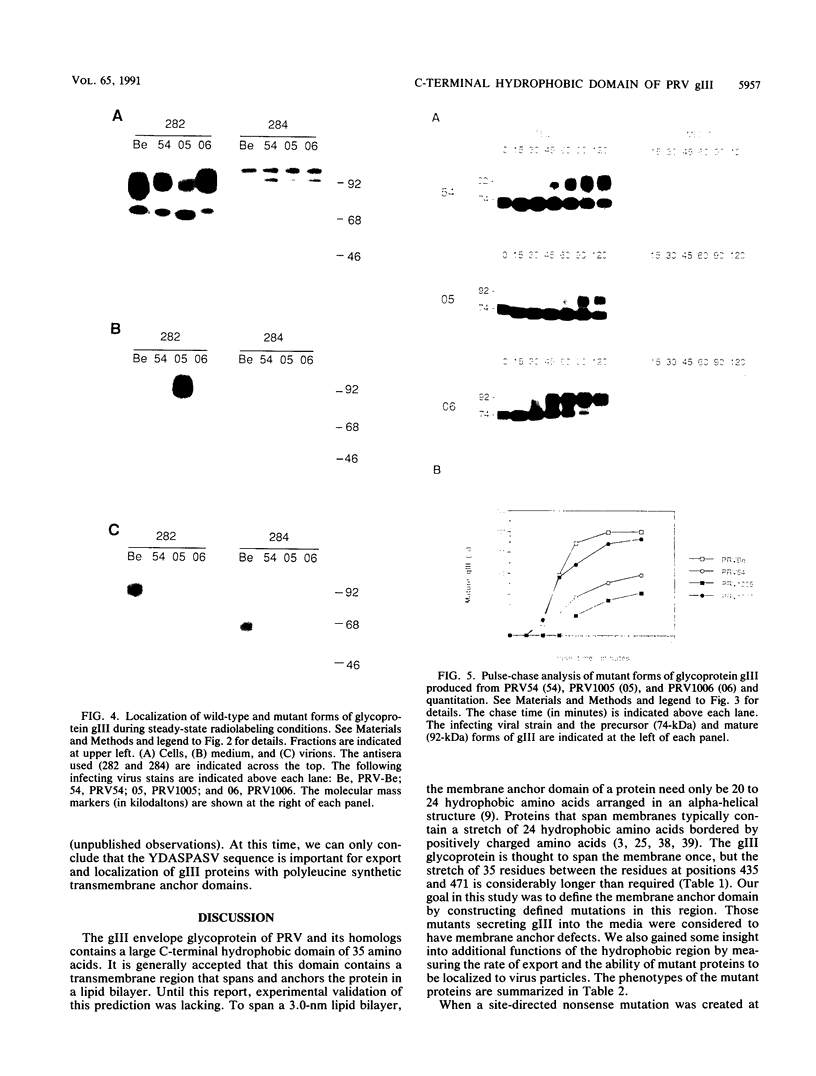
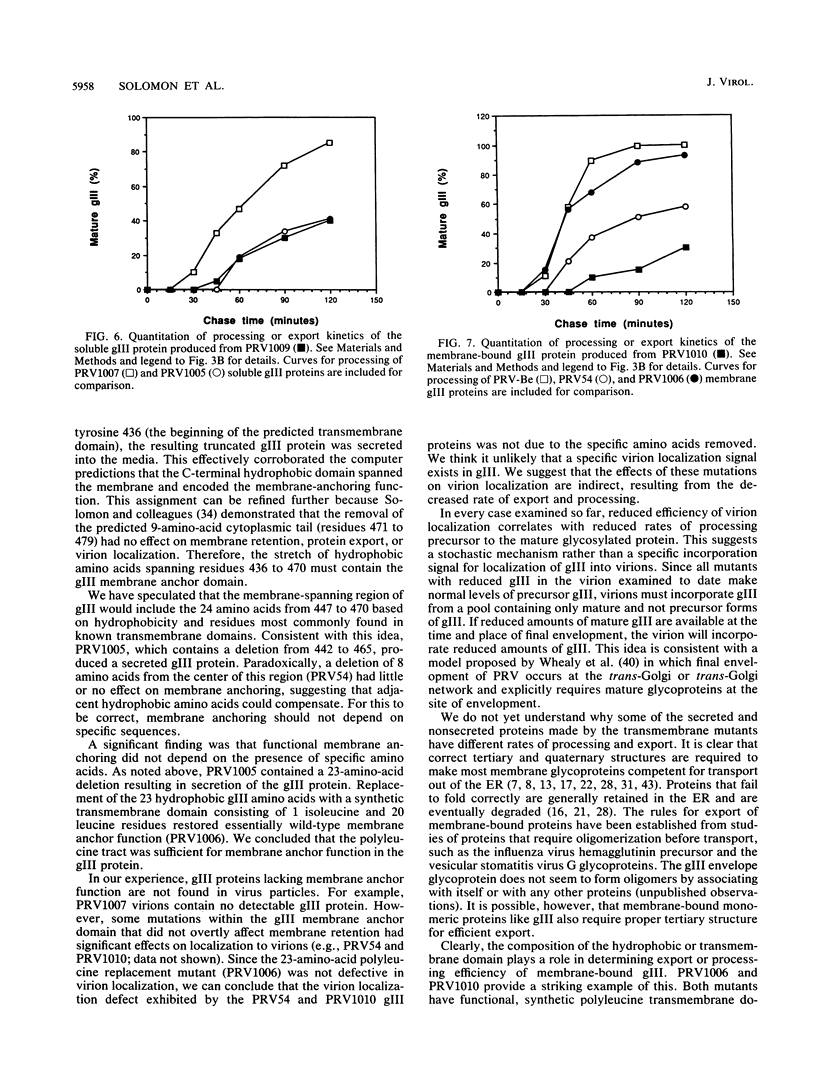
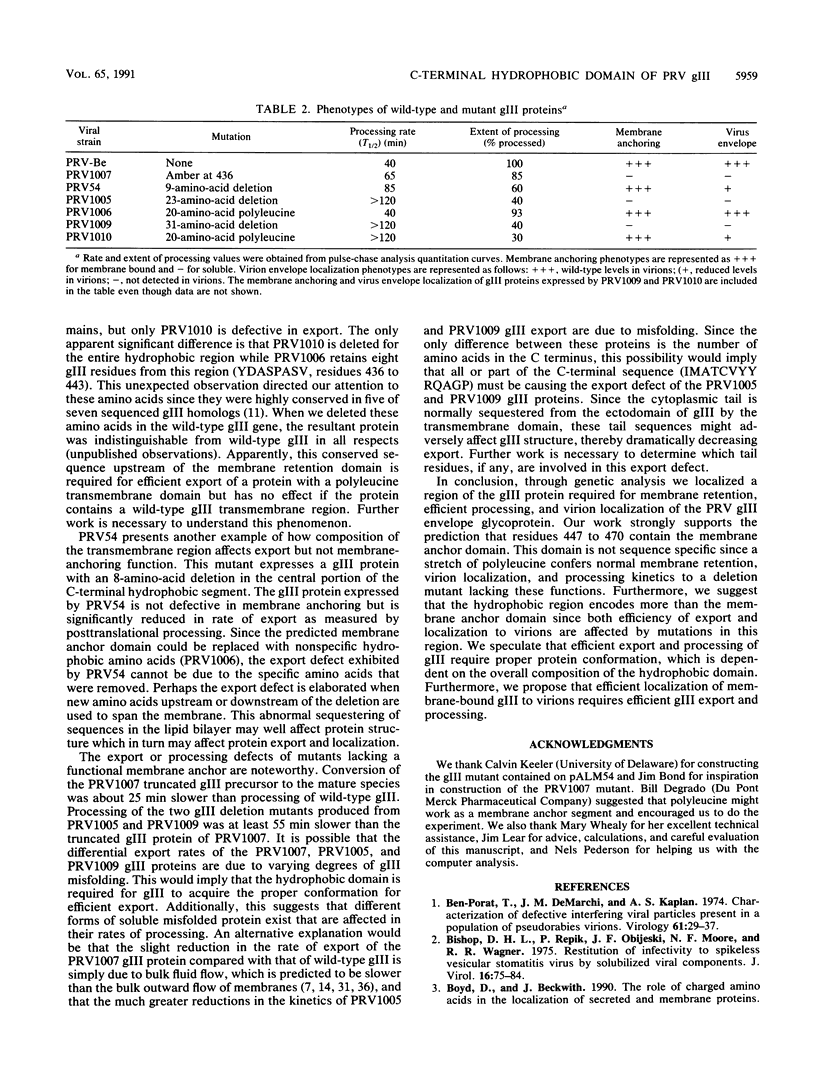
Abstract
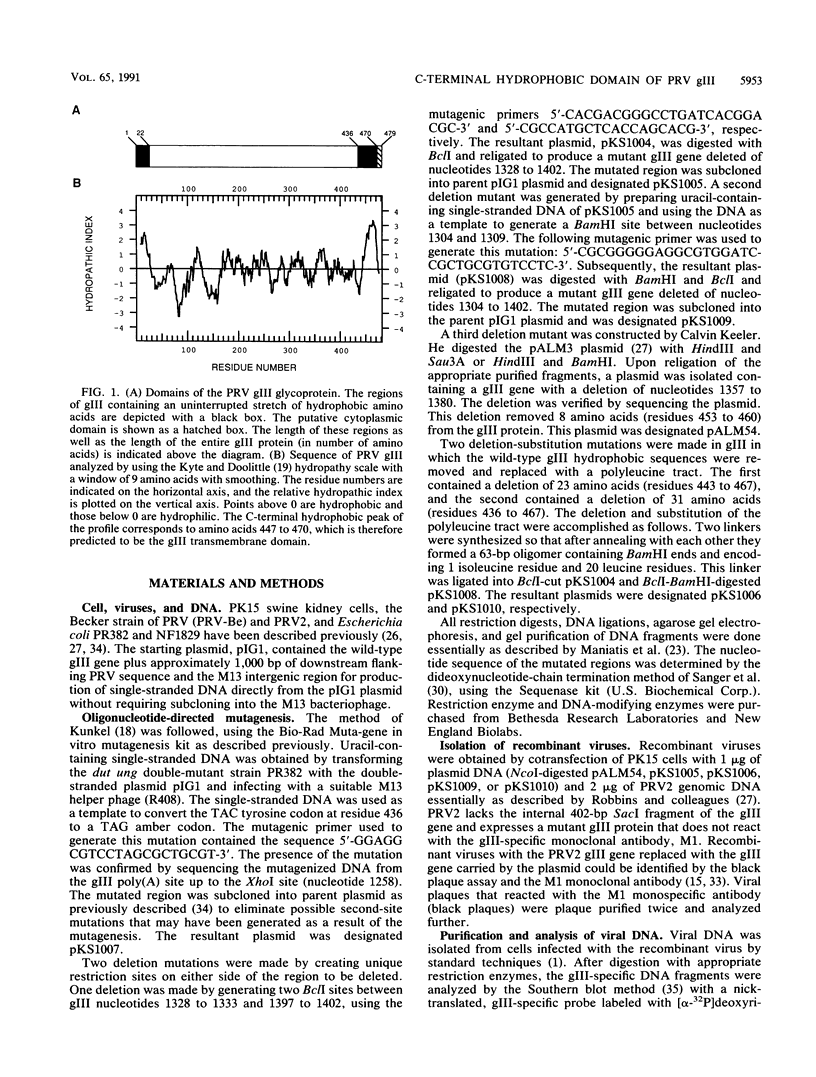
The transmembrane and anchor region of pseudorabies virus gIII is postulated to be in the 35 hydrophobic amino acids (residues 436 to 470) found near the carboxy terminus of the 479-amino-acid envelope protein. In this study, we used a genetic approach to localize the functional gIII membrane anchor between amino acids 443 and 466. Mutant gIII proteins lacking the membrane anchor were not associated with virus particles, indicating that membrane retention is a prerequisite for virion localization. Unexpectedly, the specific hydrophobic gIII sequence defined by these deletions was not required for membrane anchor function since the entire region could be replaced with leucine residues without affecting gIII membrane retention, export, or virion localization. The hydrophobic region appears to encode more than the membrane anchor domain since both efficiency of posttranslational processing and localization to virions are affected by mutations in this region. We speculate that the composition of the hydrophobic domain influences the overall conformation of gIII, which in turn effects the efficiency of gIII export and processing. The virion localization phenotype is probably indirect and reflects the efficiency of protein processing. This conclusion provides insight into the mechanism of glycoprotein incorporation into virions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Demarchi J. M., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of defective interfering viral particles present in a population of pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Repik P., Obijeski J. F., Moore N. F., Wagner R. R. Restitution of infectivity to spikeless vesicular stomatitis virus by solubilized viral components. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):75–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.75-84.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F. Surface structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Keeler C. L., Jr, Robbins A. K., Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E. An amino-terminal deletion mutation of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII affects protein localization and RNA accumulation. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3565–3573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3565-3573.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Nucleotide sequence of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein gIII, a structural model for gIII as a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, and implications for the homologous glycoproteins of other herpesviruses. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Santos R. E., Spear P. G. Neutralizing antibodies specific for glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus permit viral attachment to cells but prevent penetration. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3435-3443.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D. Architectural editing: determining the fate of newly synthesized membrane proteins. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Transport of secretory and membrane glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. A rate-limiting step in protein maturation and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2107–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Influence of new glycosylation sites on expression of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5948–5954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Kern H., Ben-Porat T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.278-286.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., von Heijne G. Fine-tuning the topology of a polytopic membrane protein: role of positively and negatively charged amino acids. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90390-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh I., Doms R. W., Wagner K. R., Helenius A. Intracellular transport of soluble and membrane-bound glycoproteins: folding, assembly and secretion of anchor-free influenza hemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):631–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Kennell W. L., Lamm D. L. Visualization of minute centers of viral infection in unfixed cell cultures by an enzyme-linked antibody assay. J Immunol Methods. 1981;40(3):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon K. A., Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Enquist L. W. The putative cytoplasmic domain of the pseudorabies virus envelope protein gIII, the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C homolog, is not required for normal export and localization. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3516–3521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3516-3521.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Peet R. W., Galloway D. A. Characterization of the gene encoding herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein C and comparison with the type 1 counterpart. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):561–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.561-569.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Card J. P., Meade R. P., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Effect of brefeldin A on alphaherpesvirus membrane protein glycosylation and virus egress. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1066–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1066-1081.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. The export pathway of the pseudorabies virus gB homolog gII involves oligomer formation in the endoplasmic reticulum and protease processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1946–1955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1946-1955.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A., Gething M. J. Haemagglutinin of influenza virus expressed from a cloned gene promotes membrane fusion. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):658–659. doi: 10.1038/300658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Yellen A., Bächi T. Monoclonal antibodies localize events in the folding, assembly, and intracellular transport of the influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90426-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsak L., Mettenleiter T. C., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Release of pseudorabies virus from infected cells is controlled by several viral functions and is modulated by cellular components. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5475–5477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5475-5477.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva A. M., Balch W. E., Helenius A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: folding and misfolding of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein in cells and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):857–866. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):456–458. doi: 10.1038/341456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]