Abstract
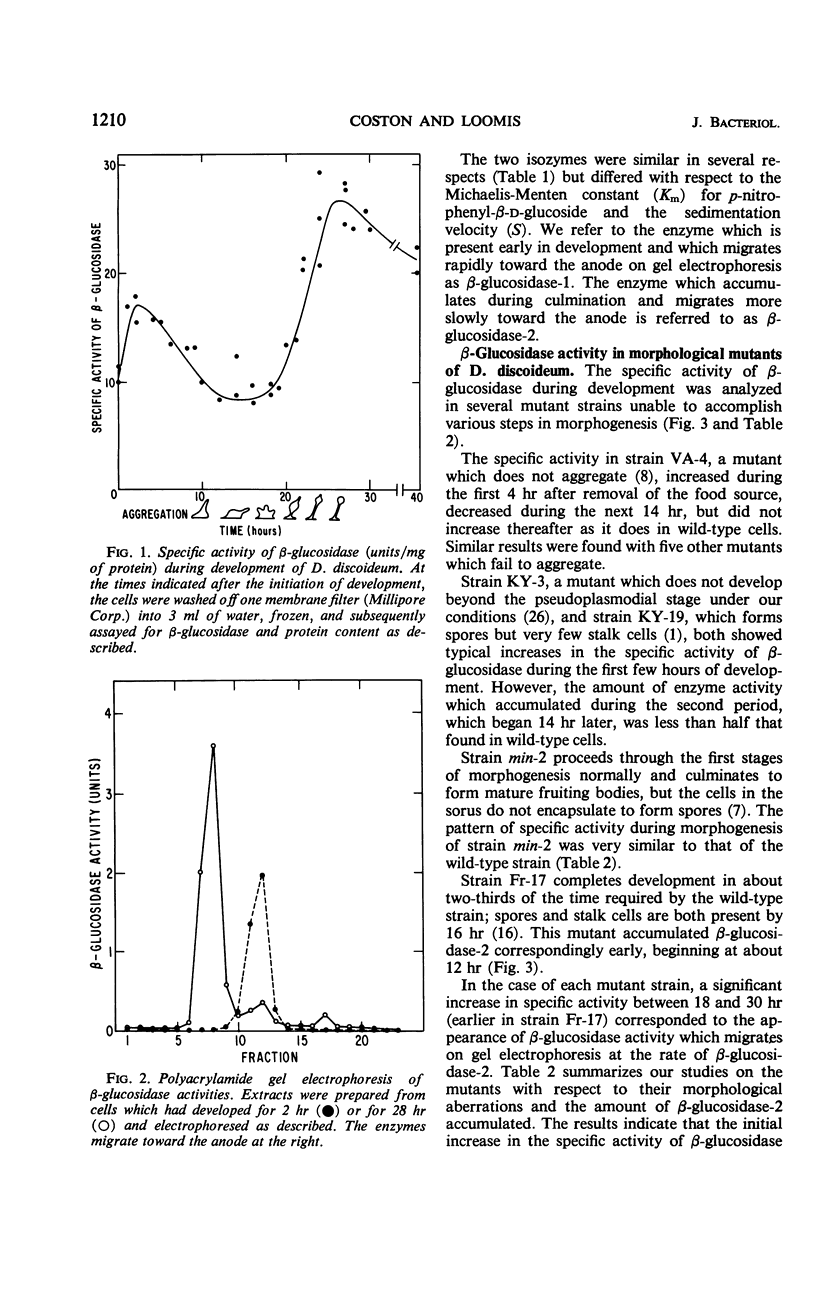
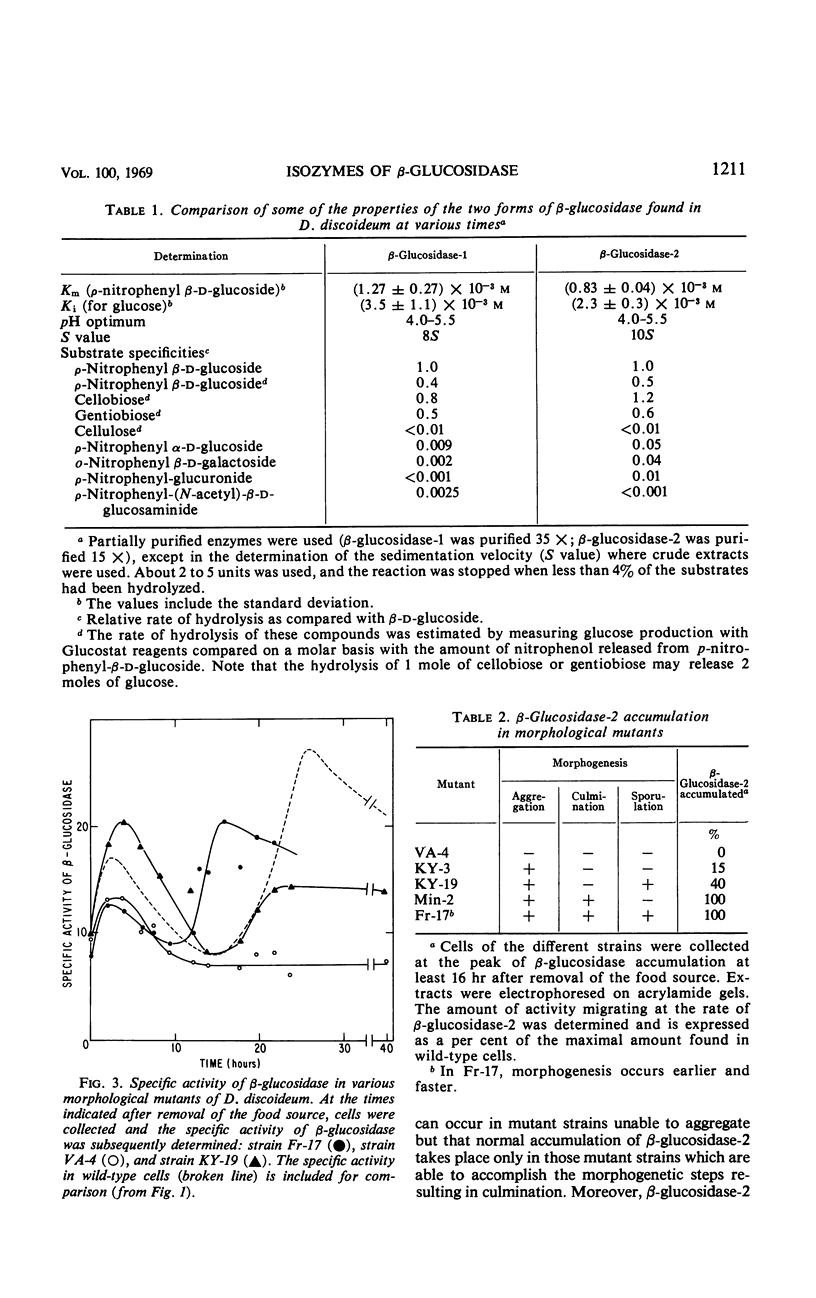
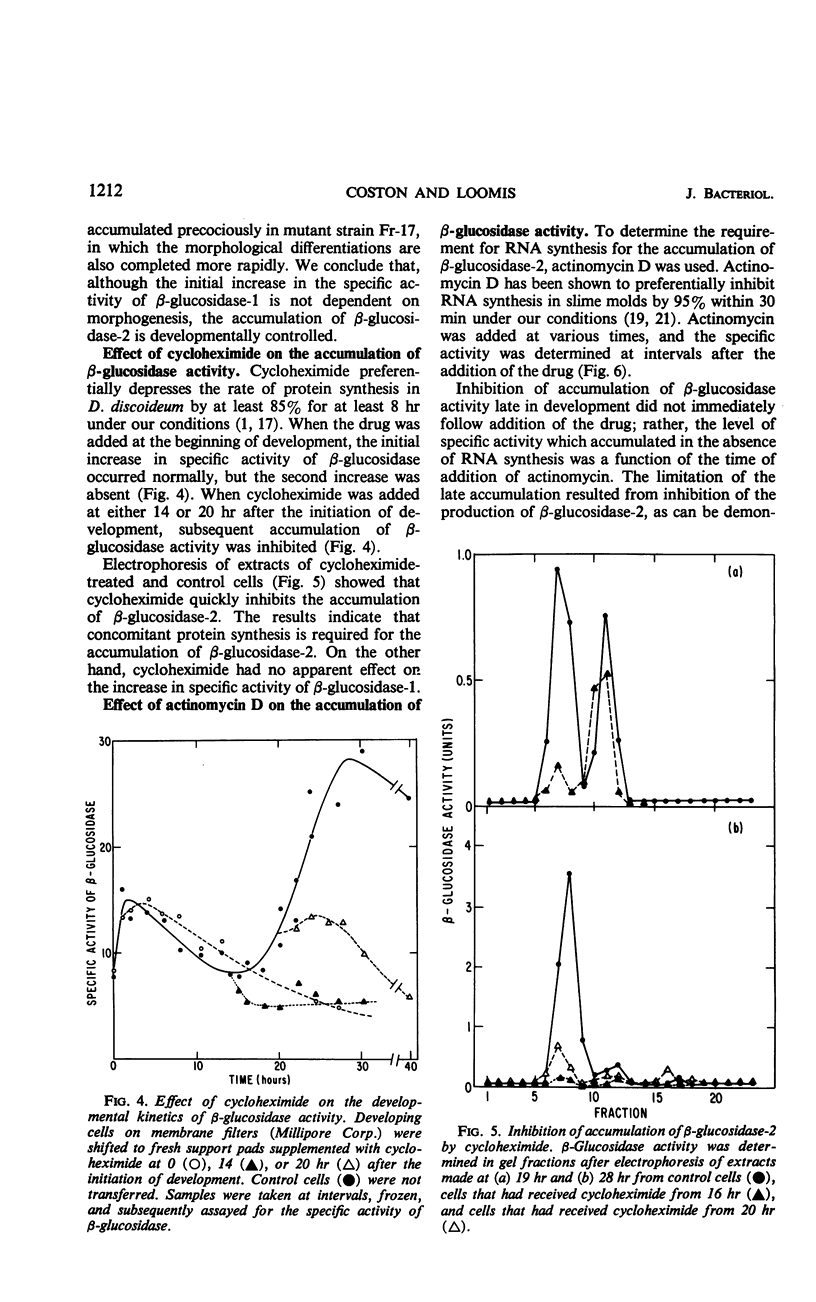
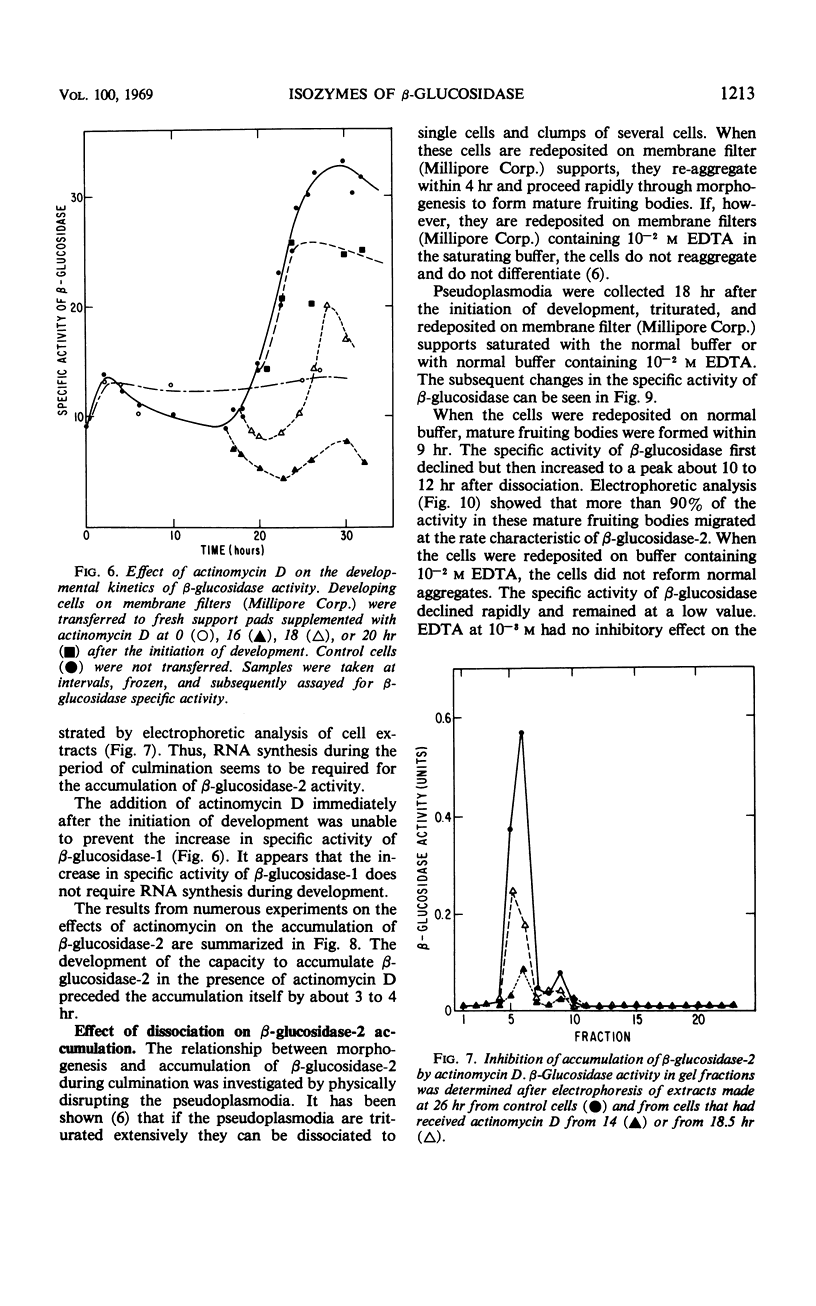
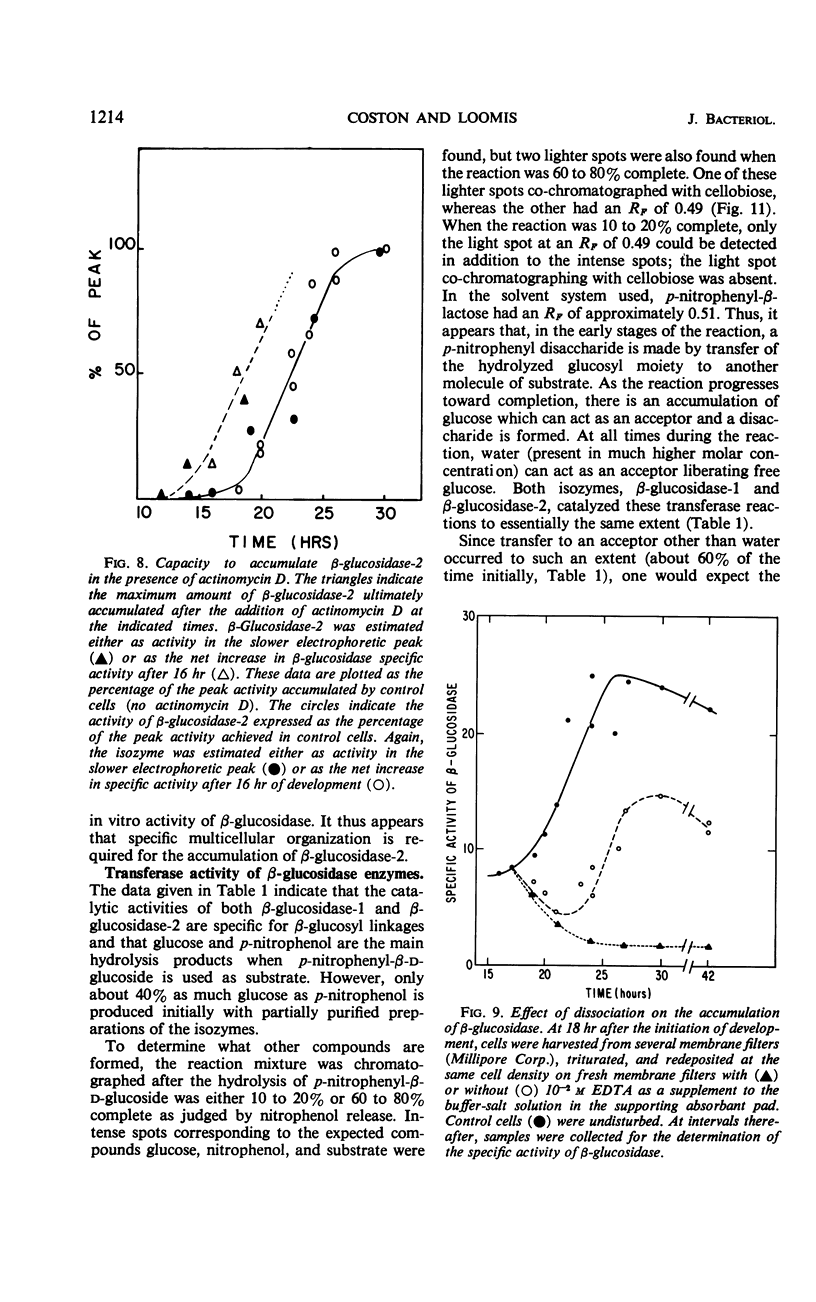
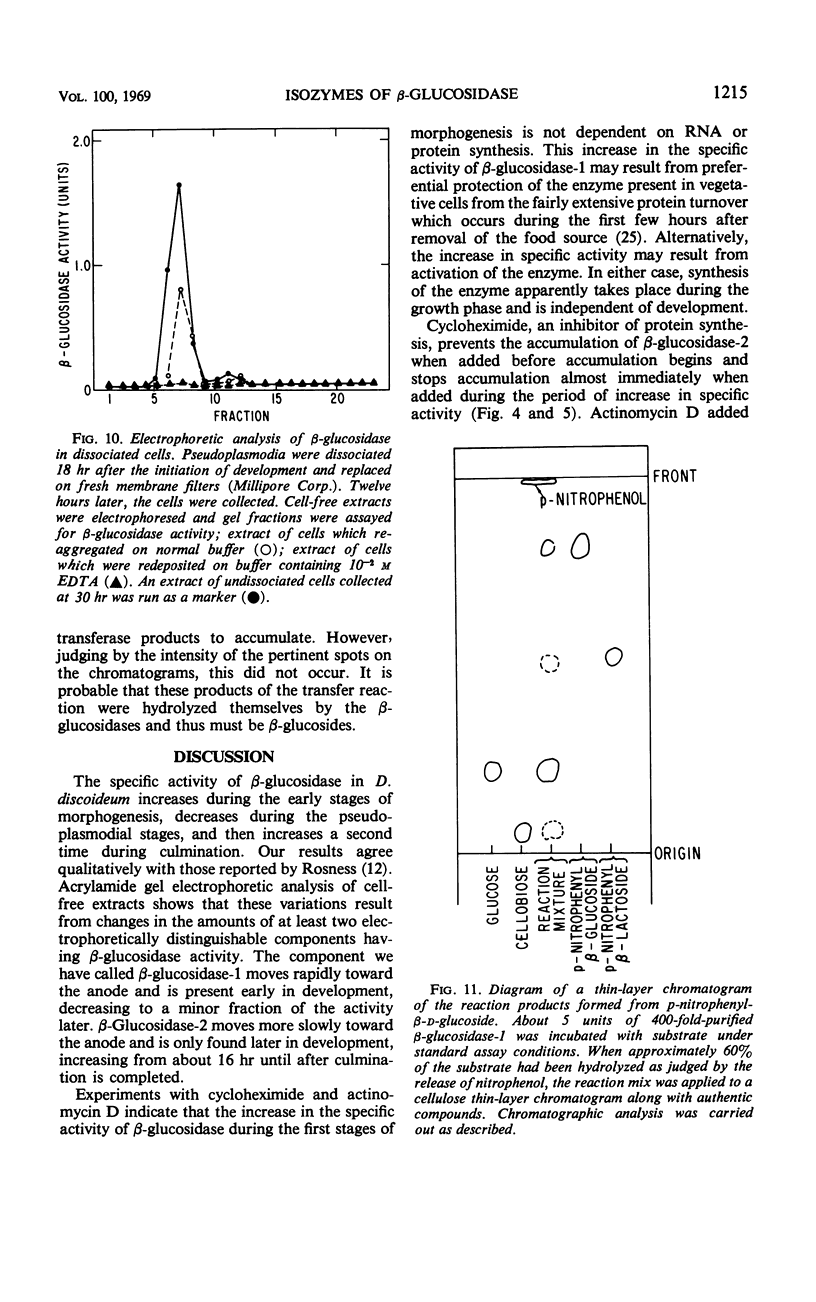
The activity of β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21) in extracts of Dictyostelium discoideum was investigated. The specific activity increased early in development, declined during pseudoplasmodium formation, and increased again during sorocarp formation. The β-glucosidase which was present in growing amoebae and during the first stages of multicellular development was electrophoretically distinct from the enzyme which accumulated during the final stages of morphogenesis. Ribonucleic acid synthesis and protein synthesis during development were required for the accumulation of the later isozyme. Analysis of β-glucosidase activity in a number of morphological mutants suggests that the enzyme which accumulates late in morphogenesis is developmentally controlled.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashworth J. M., Sussman M. The appearance and disappearance of uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity during differntiation of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1696–1700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN C., COHN M., KEPES A., MONOD J. R OLE DU LACTOSE ET DE SES PRODUITS M'ETABOLIQUES DANS L'INDUCTION DE L'OP'ERON LACTOSE CHEZ ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Apr 19;95:634–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERISCH G. [Cell functions and change in cell function in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. V. Stagespecific cell contact formation and its quantitative evaluation]. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Dec;25:535–554. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr Acetylglucosaminidase, an early enzyme in the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1149–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1149-1154.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Jr The relation between cytodifferentiation and inactivation of a developmentally controlled enzyme in Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Oct;53(1):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Sussman M. Commitment to the synthesis of a specific enzyme during cellular slime mold development. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):401–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosness A. Cellulolytic enzymes during morphogenesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):639–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.639-645.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Ashworth J. M., Sussman M. Periods of genetic transcription required for the synthesis of three enzymes during cellular slime mold development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1235–1242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Sussman M. Trehalose 6-phosphate synthetase (uridine diphosphate glucose: d-glucose 6-phosphate 1-glucosyltransferase) and its regulation during slime mold development. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5081–5087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R., Sussman M. Trehalose synthesis in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 10;122(2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONNEBORN D. R., WHITE G. J., SUSSMAN M. A mutation affecting both rate and pattern of morphogenesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1963 Mar;6:79–93. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(63)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN M., OSBORN M. J. UDP-GALACTOSE POLYSACCHARIDE TRANSFERASE IN THE CELLULAR SLIME MOLD, DICTYOSTELIUM DISCOIDEUM: APPEARANCE AND DISAPPEARANCE OF ACTIVITY DURING CELL DIFFERENTIATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:81–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M., Loomis W. F., Jr, Ashworth J. M., Sussman R. R. The effect of actinomycin D on cellular slime mold morphogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 8;26(3):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M., Sussman R. R. The regulatory program for UDPgalactose polysaccharide transferase activity during slime mold cytodifferentiation: requirement for specific synthesis of ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):463–473. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLENFELS K., ZARNITZ M. L., LAULE G., BENDER H., KESER M. [Studies on lactic acid splitting enzyme. III. Purification, crystallization and features of beta-galctosidase of Escherichia coli ML 309]. Biochem Z. 1959;331:459–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE G. J., SUSSMAN M. Metabolism of major cell components during slime mold morphogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:285–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa K., Loomis W. F., Jr, Sussman M. Developmental regulation of the enzyme UDP-galactose polysaccharide transferase. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


