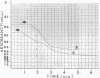
Abstract
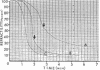
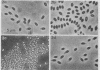
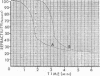
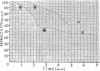
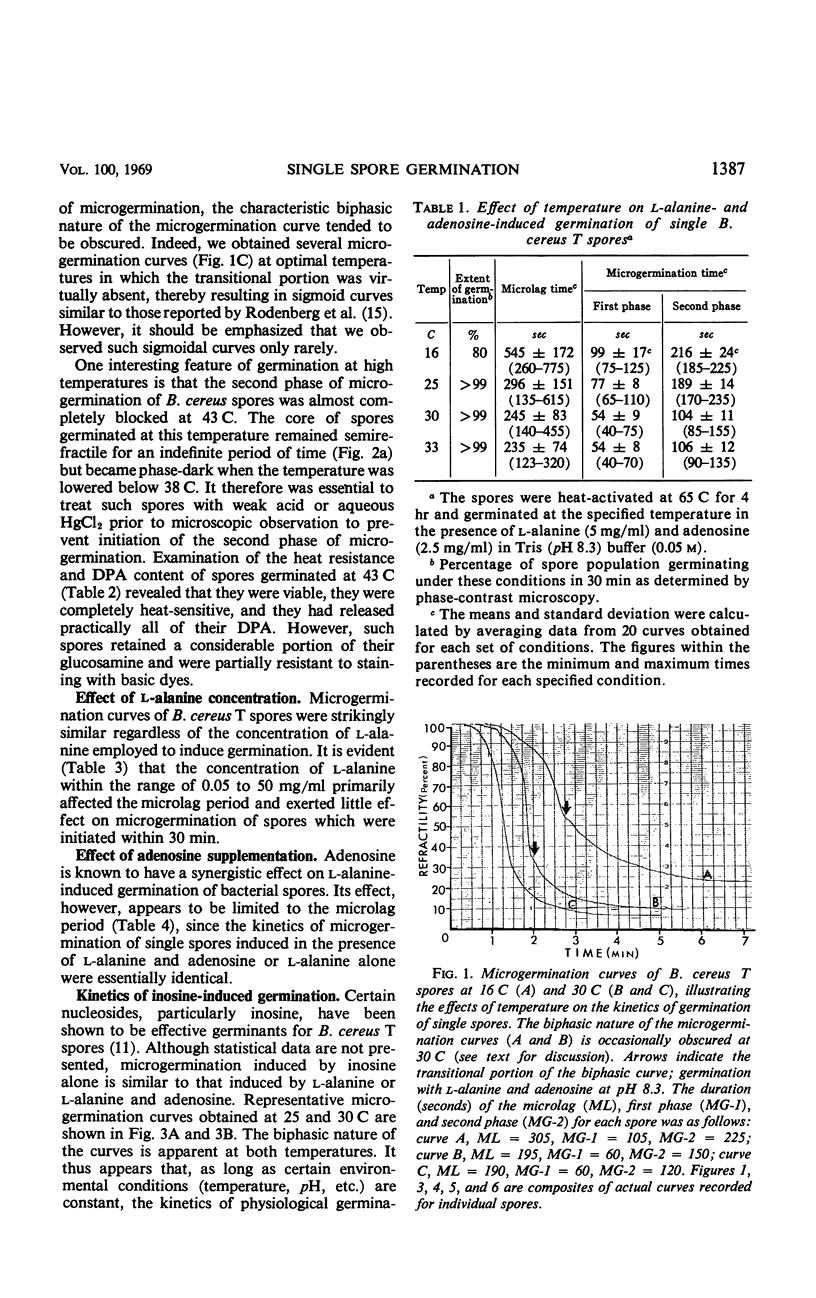
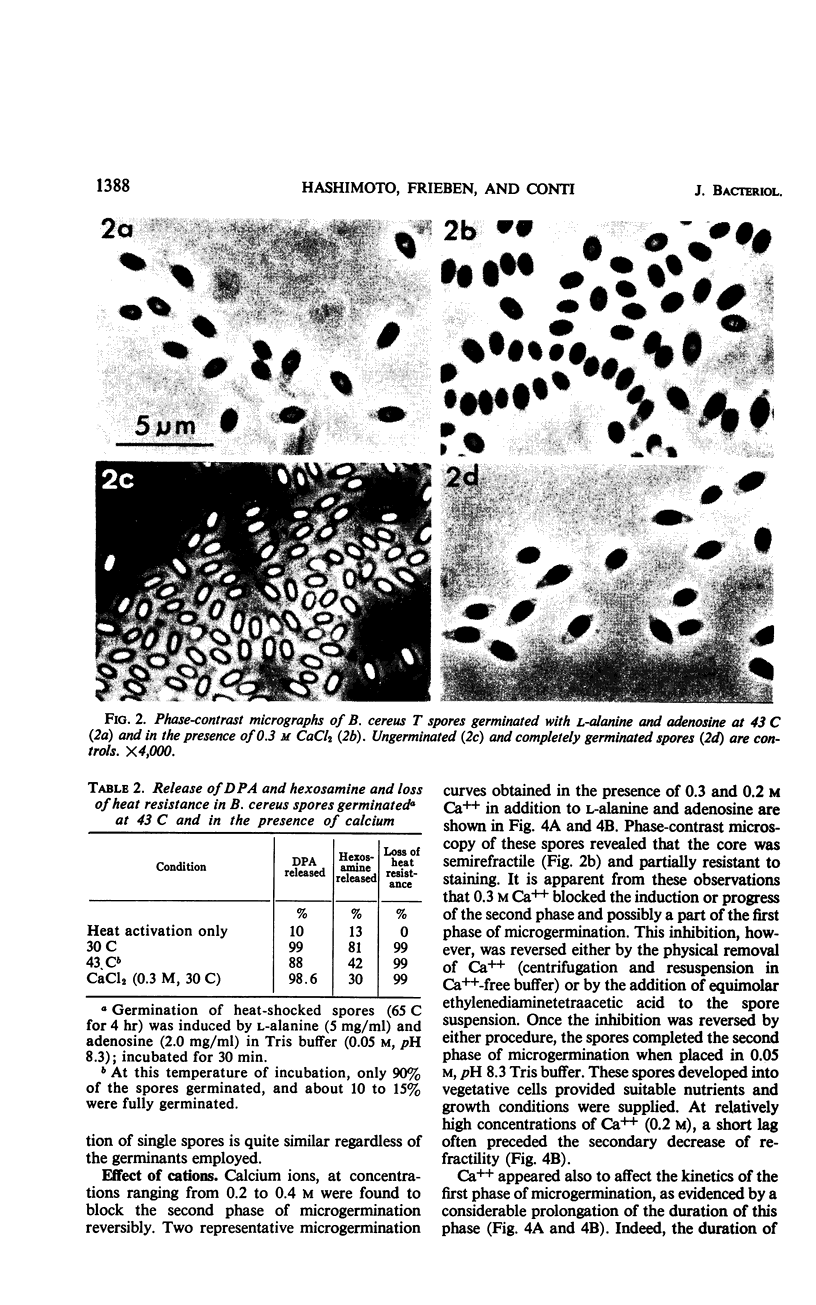
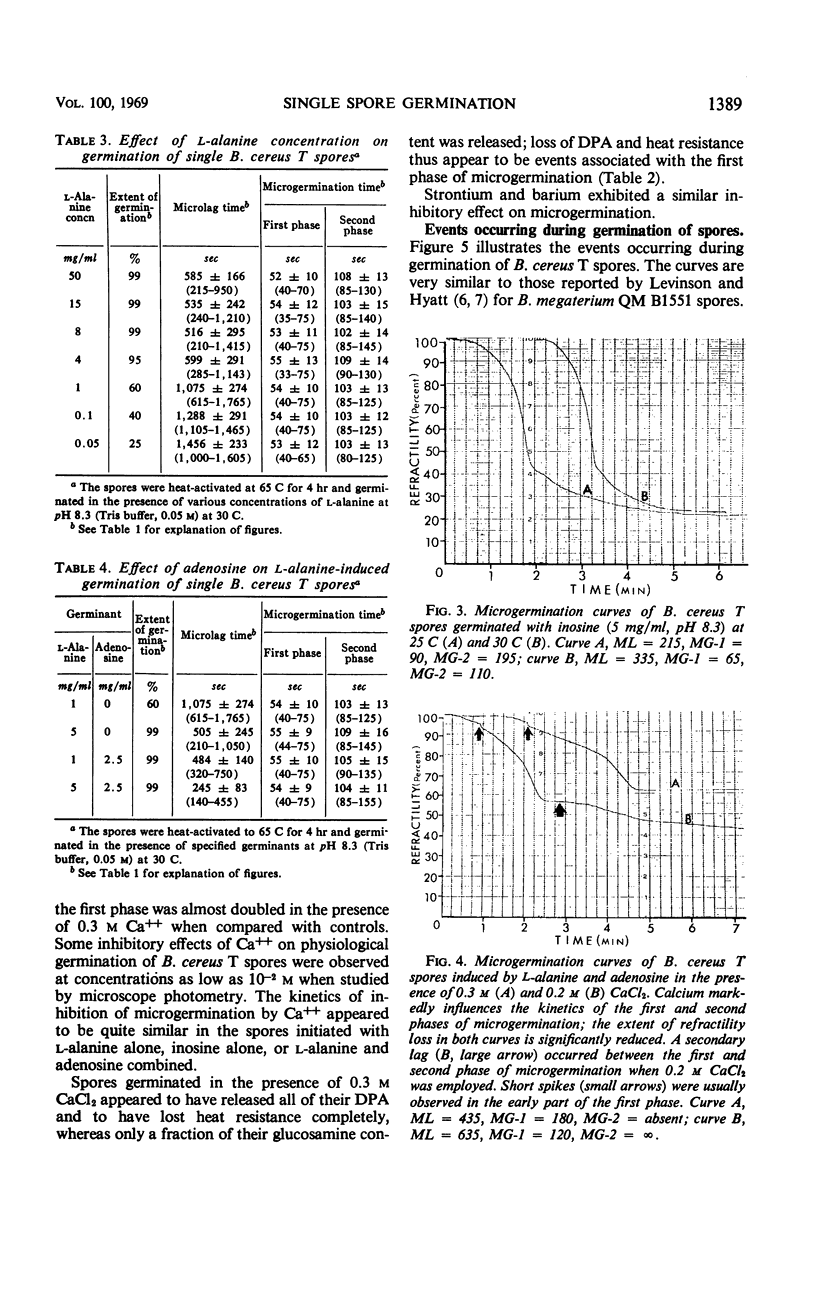
The biphasic nature of germination curves of individual Bacillus cereus T spores was further characterized by assessing the effects of temperature, concentration of germinants, and some inorganic cations on microgermination. Temperature was shown to affect both phases of microgermination as well as the microlag period, whereas the concentration of l-alanine and supplementation with adenosine exerted a significant effect only on the microlag period. The germination curves of individual spores induced by inosine were also biphasic and resembled those of spores induced by l-alanine. High concentrations (0.1 m or higher) of calcium and other inorganic cations prolonged both phases of microgermination, particularly the second phase, and had a less pronounced effect on the microlag period. The second phase of microgermination was completely inhibited when spores were germinated either in the presence of 0.3 m CaCl2 or at a temperature of 43 C; this inhibition was reversible. Observations on the germination of spore suspensions (kinetics of the release of dipicolinic acid and mucopeptides, loss of heat resistance, increase in stainability, decrease in turbidity and refractility) were interpreted on the basis of the biphasic nature of microgermination. Dye uptake by individual spores during germination appeared also to be a biphasic process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
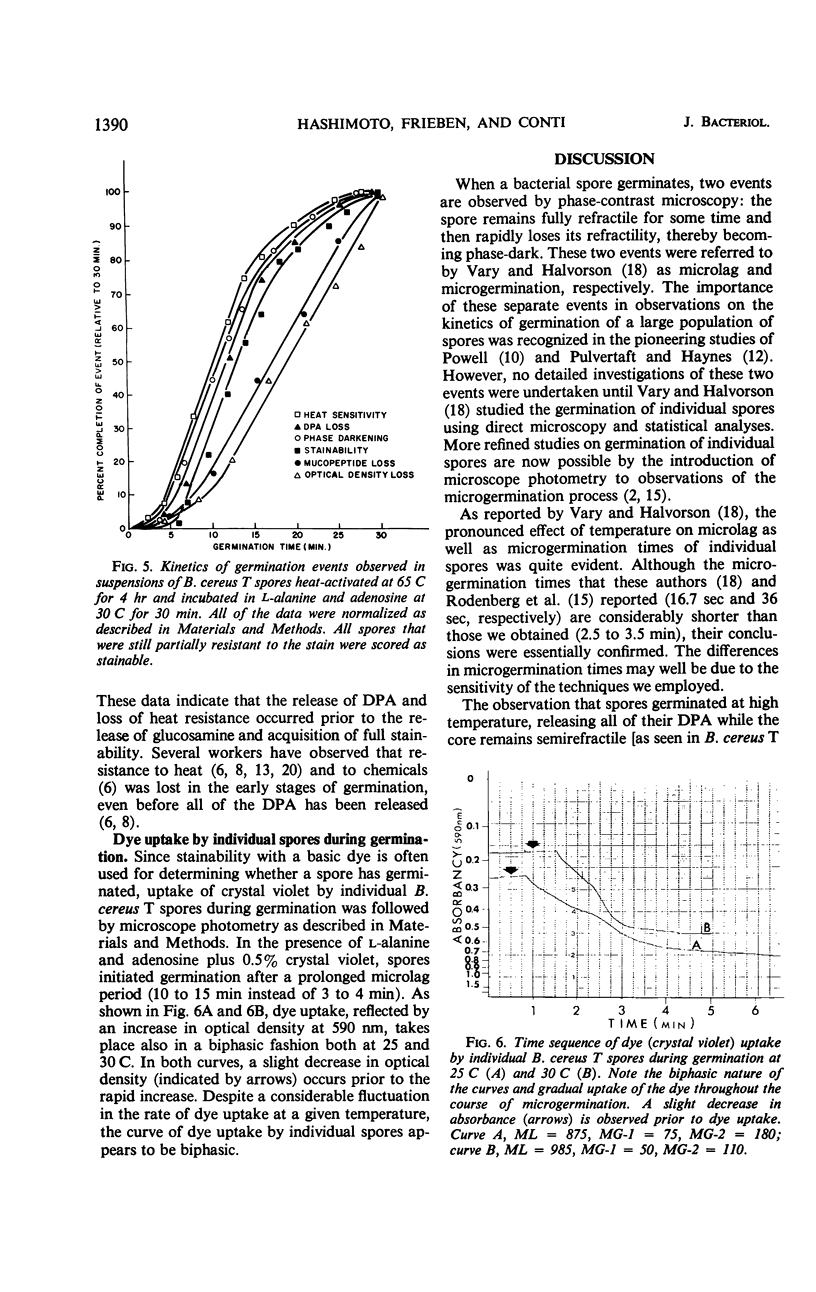
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HARRELL W. K., HALVORSON H. Studies on the role of L-alanine in the germination of spores of Bacillus terminalis. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):275–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.275-279.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Frieben W. R., Conti S. F. Germination of single bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1011–1020. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1011-1020.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNAN A., HALVORSON H. O. Calcium dipicolinic acid-induced germination of Bacillus cereus spores. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:100–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.100-105.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson H. S., Hyatt M. T., Holmes P. K. Transition of bacterial spores into vegetative cells. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Nov;30(1):81–98. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1967.tb02454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson H. S., Hyatt M. T. Sequence of events during Bacillus megaterim spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1811–1818. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1811-1818.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORMICK N. G. KINETICS OF SPORE GERMINATION. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1180-1185.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. Factors affecting the germination of thick suspensions of bacillus subtilis spores in L-alanine solution. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):330–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT R. J. V., HAYNES J. A. Adenosine and spore germination; phase-contrast studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):657–663. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Induced release of dipicolinic acid from spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1960 May;79:650–656. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.5.650-656.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONDLE C. J., MORGAN W. T. The determination of glucosamine and galactosamine. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):586–589. doi: 10.1042/bj0610586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Influence of exchangeable ions on germinability of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1582–1588. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1582-1588.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenberg S., Steinberg W., Piper J., Nickerson K., Vary J., Epstein R., Halvorson H. O. Relationship between protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis during outgrowth of spores of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.492-500.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara M., Frank H. A. Sequence of events during germination of putrefactive anaerobe 3679 spores. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):506–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.506-511.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARY J. C., HALVORSON H. O. KINETICS OF GERMINATION OF BACILLUS SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1340–1347. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1340-1347.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLEY B. C., COLLIER R. E. CHANGES IN THERMORESISTANCE OF CLOSTRIDIUM ROSEUM AS RELATED TO THE INTRACELLULAR CONTENT OF CALCIUM AND DIPICOLINIC ACID. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:279–285. doi: 10.1139/m65-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]