Abstract
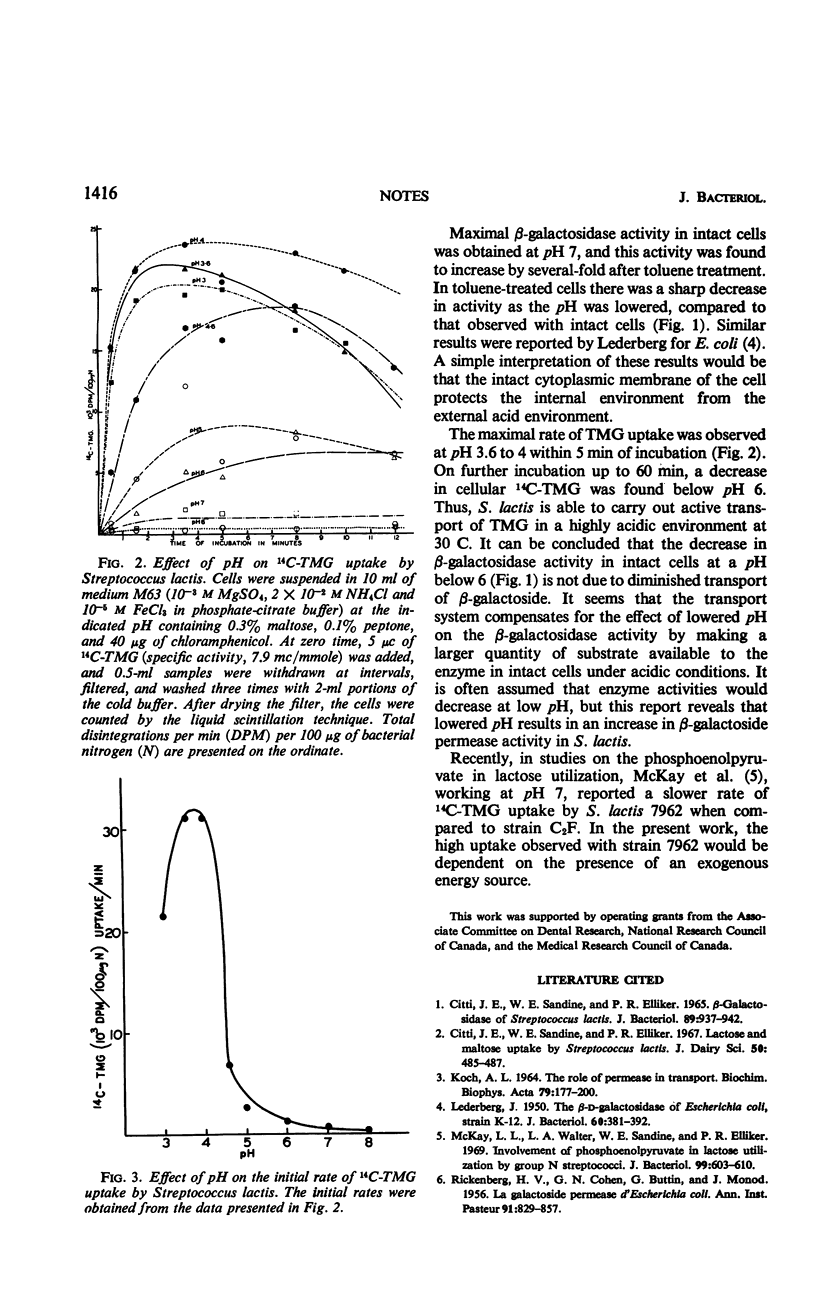
Maximal β-galactosidase activity in Streptococcus lactis was obtained at pH 7, but the maximal rate of thiomethyl-β-d-galactoside uptake was observed at pH 3.6 to 4. It is concluded that the decrease in β-galactosidase activity in intact cells at lowered pH is not due to diminished transport of β-galactoside.
Full text
PDF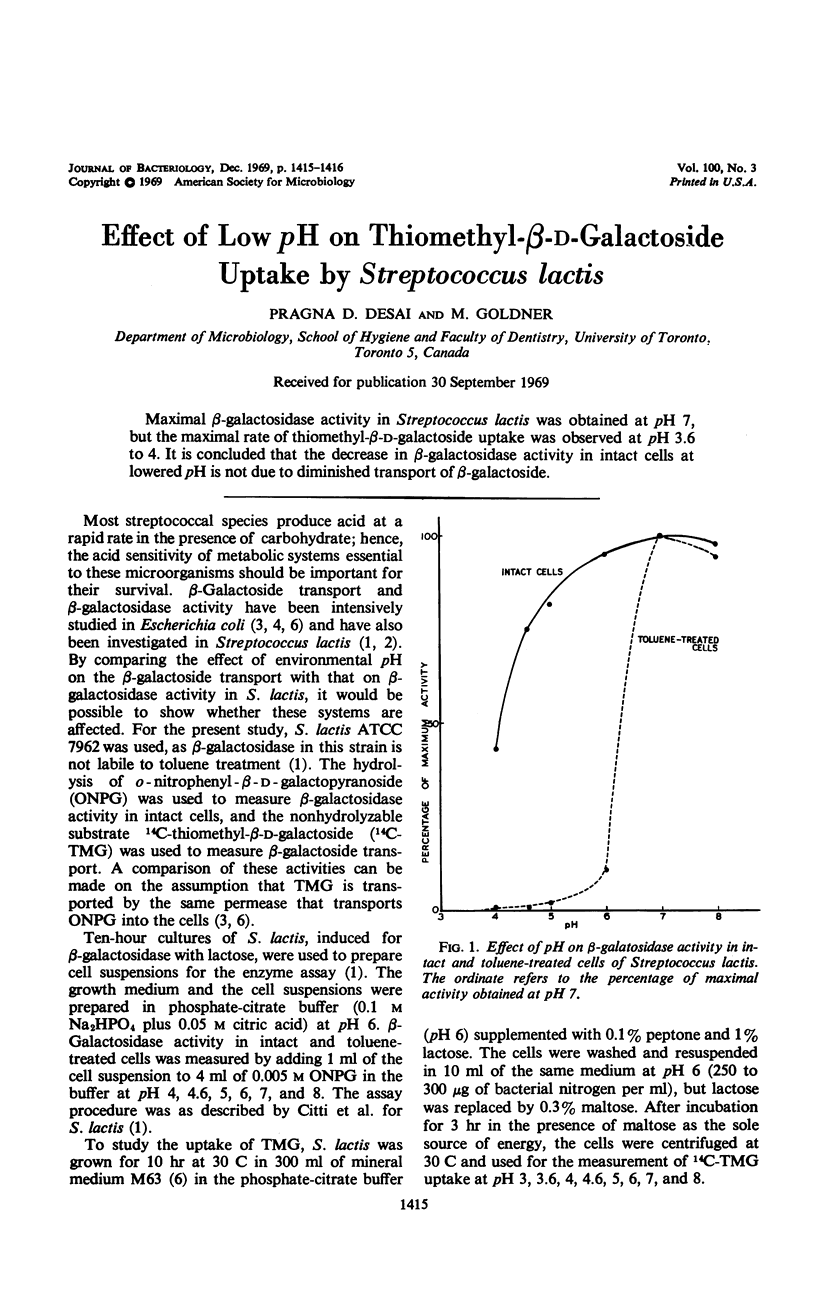
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTTIN G., COHEN G. N., MONOD J., RICKENBERG H. V. La galactoside-perméase d'Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Dec;91(6):829–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CITTI J. E., SANDINE W. E., ELLIKER P. R. BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF STREPTOCOCCUS LACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:937–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.937-942.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citti J. E., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Lactose and maltose uptake by Streptococcus lactis. J Dairy Sci. 1967 Apr;50(4):485–487. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(67)87451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH A. L. THE ROLE OF PERMEASE IN TRANSPORT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jan 27;79:177–200. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. The beta-d-galactosidase of Escherichia coli, strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Oct;60(4):381–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.4.381-392.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Walter L. A., Sandine W. E., Elliker P. R. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):603–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.603-610.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


