Abstract
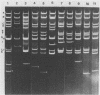
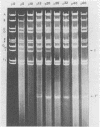
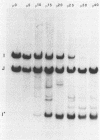
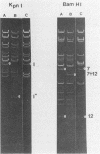
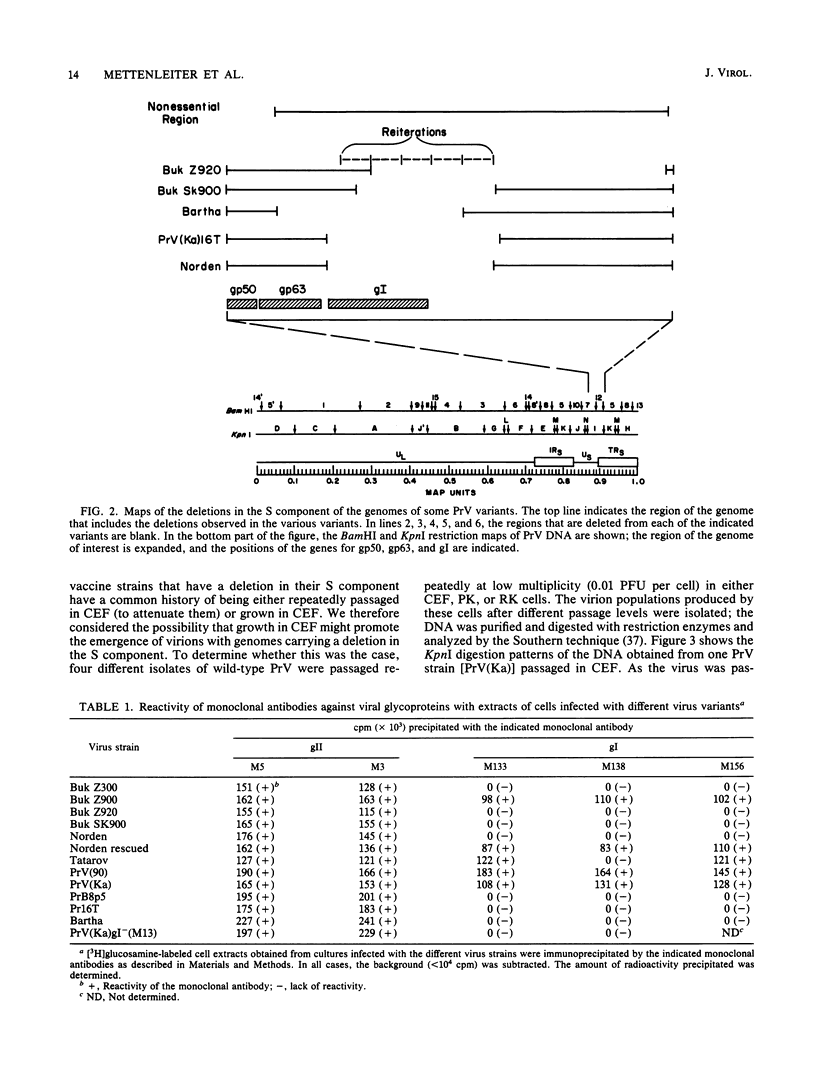
Several attenuated strains of pseudorabies virus contain genomes that carry a deletion in their short unique (Us) component. The sizes of the deletions are different in the various attenuated strains; the deletions may include part of one of the inverted repeats as well as part of the Us region of the genome. In most cases, the deletion includes the gene encoding the glycoprotein gI. The attenuated strains with a deletion in their S component have a common history of having been cultivated in chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEF). We show here that passage of wild-type virus in CEF promotes the emergence of populations of virions with a deletion in their S component. The emergence of these mutants is the result of their growth advantage over the wild type and is related to the lack of expression of gI, as shown by the following. (i) The Norden strain (which has a deletion in the Us) was marker rescued to restore an intact Us. The nonrescued Norden strain had a growth advantage over the rescued Norden strain in CEF. (ii) Passage of wild-type (gI+) virus in CEF but not in rabbit kidney or pig kidney cells resulted invariably in the emergence of virions whose genomes had a deletion in the S component. (iii) Passage of a gI- mutant in CEF did not result in the emergence of such virions. The emergence of virions with a deletion in their S component thus appears to be linked to gI expression. We conclude that gI is deleterious to the growth of pseudorabies virus in CEF and that this effect is cell type specific.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., DeMarchi J., Pendrys J., Veach R. A., Kaplan A. S. Proteins specified by the short unique region of the genome of pseudorabies virus play a role in the release of virions from certain cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):191–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.191-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Deatly A., Veach R. A., Blankenship M. L. Equalization of the inverted repeat sequences of the pseudorabies virus genome by intermolecular recombination. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. IV: analysis of concatemers. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Stehn B., Kaplan A. S. Fate of parental herpesvirus DNA. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):412–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A., van den Ouweland A., Quint W., van Oirschot J., Gielkens A. Presence of markers for virulence in the unique short region or repeat region or both of pseudorabies hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.89-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Harland J. Three mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2: one lacking the genes US10, US11 and US12 and two in which Rs has been extended by 6 kb to 0.91 map units with loss of Us sequences between 0.94 and the Us/TRs junction. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):1–18. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Wilkie N. M. One functional copy of the long terminal repeat gene specifying the immediate-early polypeptide IE 110 suffices for a productive infection of human foetal lung cells by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):179–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielkens A. L., Van Oirschot J. T., Berns A. J. Genome differences among field isolates and vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):69–82. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland J., Brown S. M. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2 (strain HG52). J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1305–1321. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S., VATTER A. E. A comparison of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladin B. F., Ihara S., Hampl H., Ben-Porat T. Pathway of assembly of herpesvirus capsids: an analysis using DNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):544–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Blankenship M. L., Ben-Porat T. Deletions in the genomes of pseudorabies virus vaccine strains and existence of four isomers of the genomes. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):970–979. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.970-979.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Gielkens A., Csobai I., Ben-Porat T. Evolution of pseudorabies virions containing genomes with an invertible long component after repeated passage in chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1772–1780. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1772-1780.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Watanabe S., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Genetic basis of the neurovirulence of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):198–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.198-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lukàcs N., Rziha H. J. Pseudorabies virus avirulent strains fail to express a major glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):307–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.307-311.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Thiel H. J., Rziha H. J. Variability of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein I expression. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T. Role of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI in virus release from infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2764-2769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Kaplan A. S., Ben-Porat T., Lomniczi B. Role of a structural glycoprotein of pseudorabies in virus virulence. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4030–4032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4030-4032.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul P. S., Mengeling W. L., Pirtle E. C. Differentiation of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus strains by restriction endonuclease analysis. Arch Virol. 1982;73(2):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01314727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Gierman T. M., Post L. E. Deletions in vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus and their effect on synthesis of glycoprotein gp63. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1166-1169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Use of lambda gt11 to isolate genes for two pseudorabies virus glycoproteins with homology to herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.185-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt K. B., Maré C. J., Hinz P. N. Differentiation of vaccine strains and field isolates of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus: thermal sensitivity and rabbit virulence markers. Arch Virol. 1979;60(1):13–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01318093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenberger K. L., Tabares E., Roizman B. Characterization of a viable, noninverting herpes simplex virus 1 genome derived by insertion and deletion of sequences at the junction of components L and S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2690–2694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKODA R. A modified pseudorabies virus suitable for immunization of cattle. Acta Virol. 1962 Mar;6:189–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKODA R., BRAUNER I., S'ADECKY E., SOMOGYIOVA J. IMMUNIZATION AGAINST AUJESZKY'S DISEASE WITH LIVE VACCINE. II. IMMUNIZATION OF PIGS UNDER LABORATORY CONDITIONS. Acta Virol. 1964 Mar;8:123–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKODA R., BRAUNER I., SADECKY E., MAYER V. IMMUNIZATION AGAINST AUJESZKY'S DISEASE WITH LIVE VACCINE. I. ATTENUATION OF VIRUS AND SOME PROPERTIES OF ATTENUATED STRAINS. Acta Virol. 1964 Jan;8:1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Roizman B. Cell-specific selection of mutants of a herpes simplex virus recombinant carrying deletions. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. Replication and virulence of pseudorabies virus mutants lacking glycoprotein gX. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.229-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umene K. Conversion of a fraction of the unique sequence to part of the inverted repeats in the S component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Harper L., Ben-Porat T. Molecular basis for interference of defective interfering particles of pseudorabies virus with replication of standard virus. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):308–317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.308-317.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuffa A., Banda I., Konrád J. Combined vaccination of mink against aujeszky's disease and botulism. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1972 Nov;19(9):728–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1972.tb00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuffa A. Immunization against Aujeszk's disease. VII. The use of a further modified virus for preventive vaccination of sheep. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Dec;201(4):423–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuffa A. Imunizácia proti Aujeszkého chorobe--izolovanie klónu avirulentneho pre králiky a morcatá a hodnotenie jeho imunogenity. Vet Med (Praha) 1971 Sep;16(9):525–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuffa A., Salaj J. Imunizácia proti Aujeszkého chorobe--imunogenita vysoko atenuovaného kmeńa Buk-TK-900-IV,a pre osipané. Vet Med (Praha) 1971;16(4):221–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]