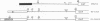Abstract
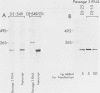
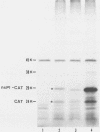
We have been studying defective interfering (DI) genomes of the RNA enveloped virus Sindbis virus. Deletion mapping of a DI cDNA demonstrated that only sequences at the 3' and 5' termini of the genome are required for the DI RNA to be biologically active. We constructed a series of cDNAs that transcribe DI RNAs differing only in 5'-terminal sequences. Two of the 5' termini identical to ones found in naturally occurring DI RNAs are the 5' terminus of the virion RNA (DI-549) and the first 142 nucleotides from the 5' terminus of the subgenomic 26S mRNA attached to the 5' terminus of the virion RNA (DI-15). The latter has a 42-nucleotide deletion from nucleotides 25 to 66 in the 26S RNA sequence. These DI RNA transcripts were biologically active, but one (DI-526) which did not have the 42-nucleotide deletion of DI-15 was not replicated. The DI RNA isolated after the presumed amplification of the DI-526 transcript had deleted the first 54 nucleotides of the 26S RNA sequences. The 5' terminus of Sindbis virion RNA contains a stem and loop region that is conserved among alphaviruses. An 11-nucleotide deletion in DI-549 that disrupted this stem and loop rendered this DI RNA inactive. In contrast, this same deletion in DI-15 and one that removed an additional 100 nucleotides of the virion 5' terminus did not prevent its amplification. We did not detect by computer analysis any common secondary structures among the biologically active DI RNAs that distinguished them from those RNAs that were not amplified. Our results support the conclusion that tertiary structure or the ability of the RNA to adapt its structure upon interaction with protein is important in the recognition process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Keene J. D., Schubert M. The origins of defective interfering particles of the negative-strand RNA viruses. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Engineered defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus express bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in avian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4811–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Weiss B. G., Tsiang M., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Deletion mapping of Sindbis virus DI RNAs derived from cDNAs defines the sequences essential for replication and packaging. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. Common and distinct regions of defective-interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):865–872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.865-872.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. RNAs from two independently isolated defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus contain a cellular tRNA sequence at their 5' ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3279–3283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Rice C. M., Dalgarno L., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sequence studies of several alphavirus genomic RNAs in the region containing the start of the subgenomic RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5235–5239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Comparative studies of the 3'-terminal sequences of several alpha virus RNAs. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90499-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. The 5'-terminal sequences of the genomic RNAs of several alphaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J. Origin and replication of defective interfering particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:151–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. II. Multiple forms of double-stranded RNA isolated from infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):615–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. Studies of defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus with and without tRNAAsp sequences at their 5' termini. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.38-44.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Rosenthal R., Schlesinger S. Establishment and maintenance of persistent infection by Sindbis virus in BHK cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):463–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.463-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. L., Jr, Tinoco I., Jr A dynamic programming algorithm for finding alternative RNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):299–315. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]