Abstract
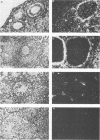
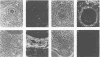
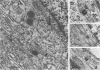
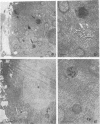
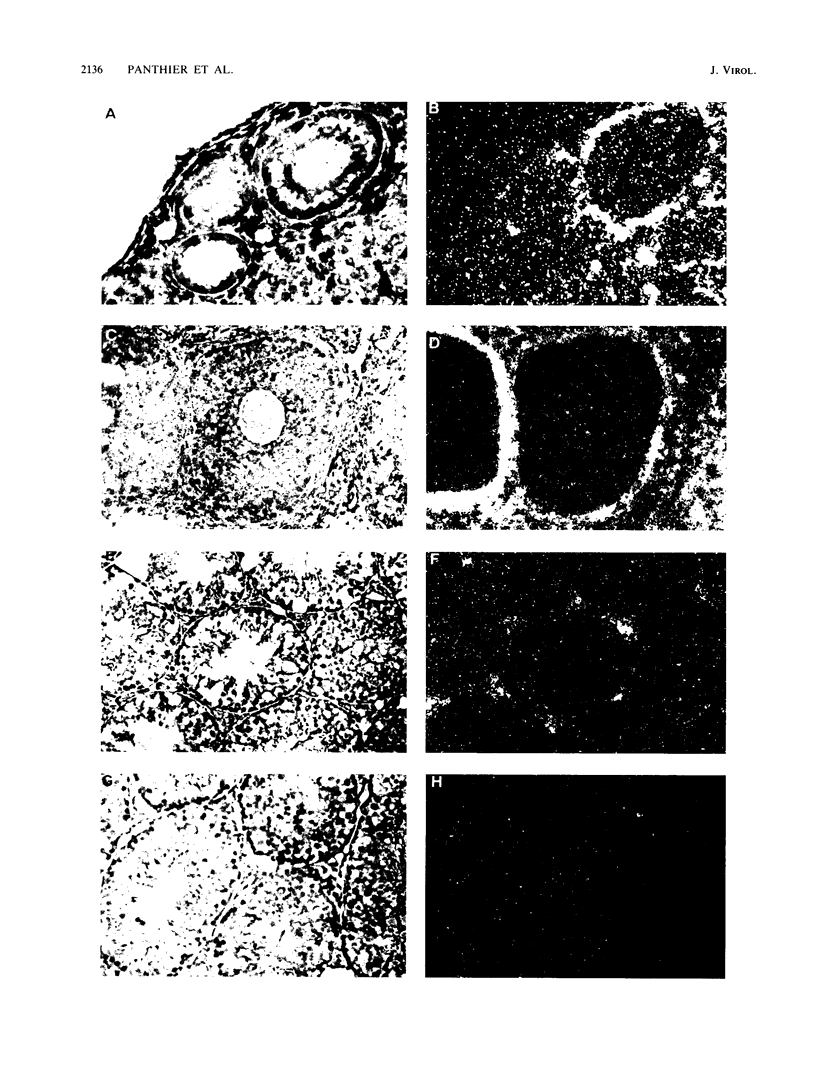
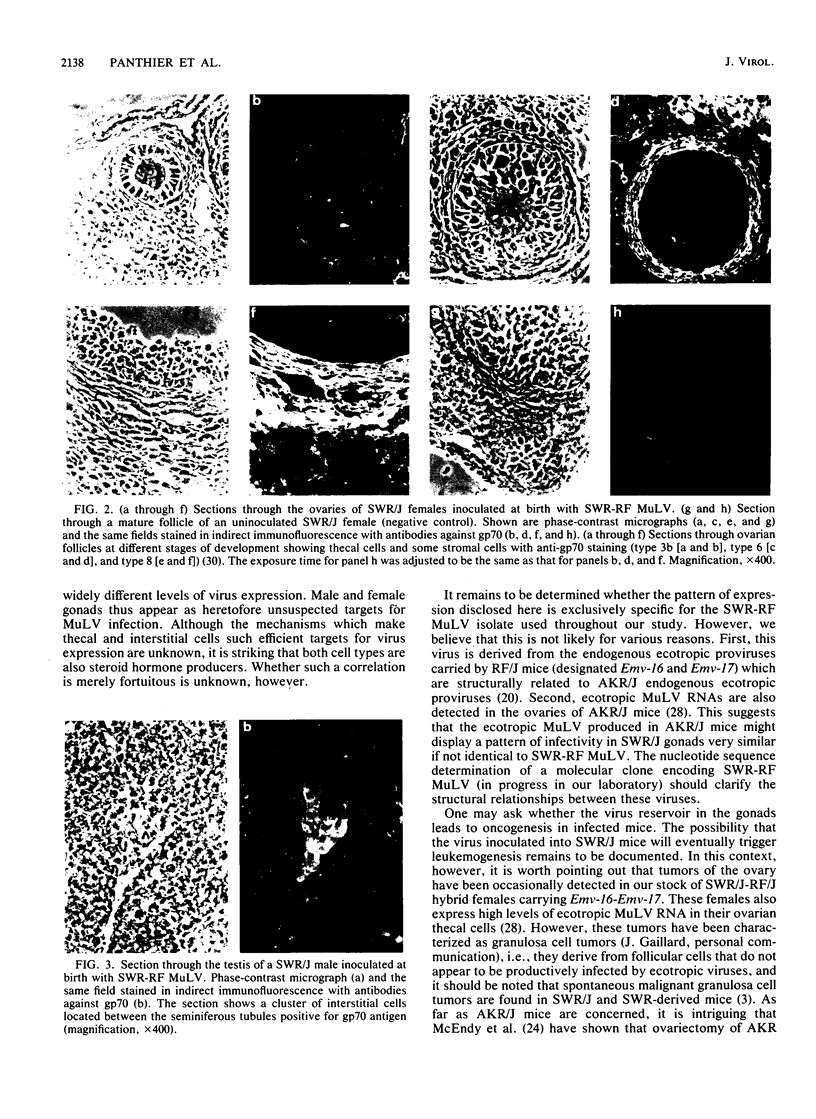
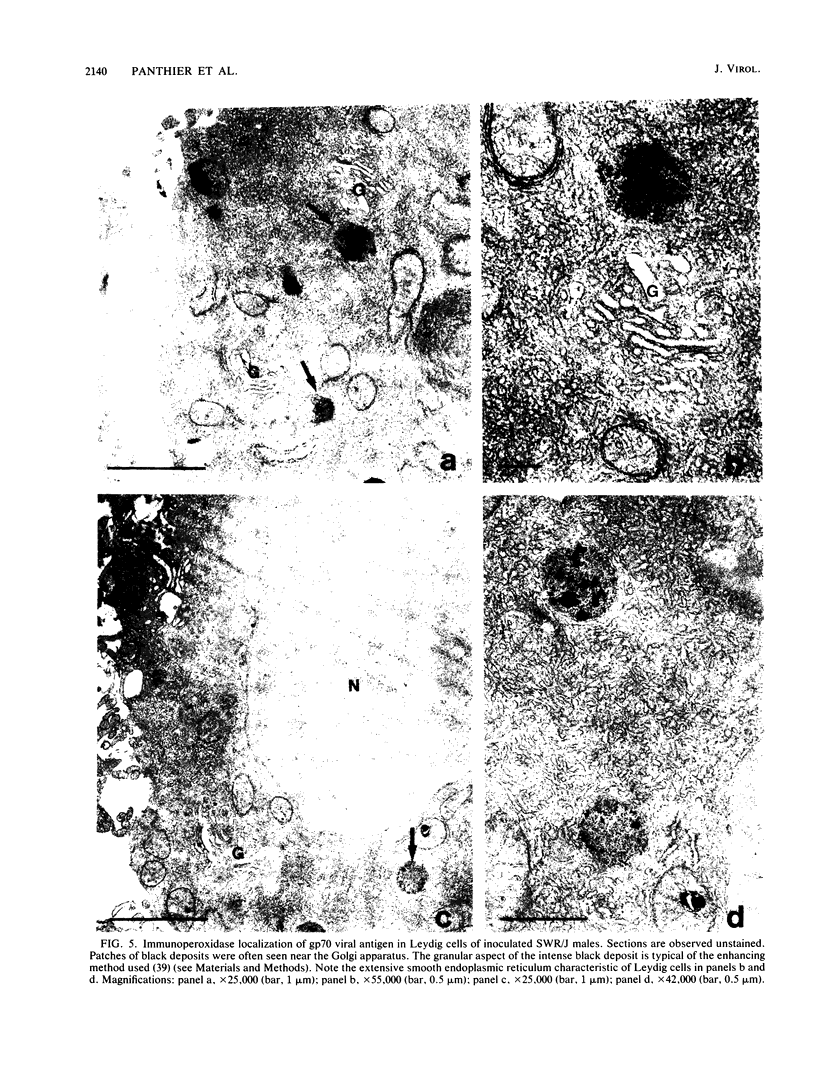
An ecotropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV) isolate has recently been shown to be able to infect the germ line or the early embryo or both when inoculated at birth to SWR/J females (J. J. Panthier, H. Condamine, and F. Jacob, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:1156-1160, 1988). We have used this isolate to further study this phenomenon. By using the techniques of RNA-RNA in situ hybridization, immunocytochemistry, and transmission electron microscopy, the identities of two important cell types that are infected by ecotropic MuLV in the gonads of inoculated mice were determined. These cells are the thecal cells surrounding the follicles in the ovary and the Leydig cells in the testis. Both types actively synthesize viral RNA and express a viral antigen. Furthermore, we documented the production of viral particles by the thecal cells. The expression of ecotropic MuLV by nonlymphoid cells in vivo may play a key role in the vertical transmission of these viruses by females as well as in their horizontal transmission.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basgall E. J., Soong M. M., Tompkins W. A. Visualization of cytoskeletal elements and associated retroviral antigens by immunogold transmission electron microscopy of detergent extracted cells. Scan Electron Microsc. 1986;(Pt 4):1419–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L. Genetic background affects integration frequency of ecotropic proviral sequences into the mouse germ line. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):693–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.693-701.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beamer W. G., Hoppe P. C., Whitten W. K. Spontaneous malignant granulosa cell tumors in ovaries of young SWR mice. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5575–5581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank K. J., Pincus T. Evidence that endogenous ecotropic virus is not expressed in AKR thymic lymphoid cells of chimeric hosts. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):458–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., Staal S. P., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Variation in the number of copies and in the genomic organization of ecotropic murine leukemia virus proviral sequences in sublines of AKR mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):629–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.629-640.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Murine leukemia virus proteins expressed on the surface of infected cells in culture. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):936–944. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.936-944.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W. Characterization of target cells for MCF viruses in AKR mice. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisselbrecht S., Blaineau C., Hurot M. A., Pozo F., Levy J. P. Prevalence of non-T-cells in the replication of the N-tropic, type C virus of young AKR mice. Cancer Res. 1978 Apr;38(4):939–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Germ-line MuLV reintegrations in AKR/J mice. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):865–868. doi: 10.1038/296865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. At least four viral genes contribute to the leukemogenicity of murine retrovirus MCF 247 in AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.158-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I., Enjuanes L., Lee J. C., Ihle J. N. Resistance of cultures of normal T cells to infection with murine type C viruses. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):483–487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.483-487.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. High frequency germline acquisition of ecotropic MuLV proviruses in SWR/J-RF/J hybrid mice. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling A. A., Crowell R. C., Connell R. S. Sperm-associated retroviruses in the mouse epididymis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Theodore T. S., Buckler C. E., Stimpfling J. H., Martin M. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Relationship between a retroviral germ line reintegration and a new mutation at the ashen locus in B10.F mice. Retroviral integration and an ashen mutation. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Wilson C. B., Villano B. C., McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Endogenous oncornaviral gene expression in adult and fetal mice: quantitative, histologic, and physiologic studies of the major viral glycorprotein, gp70. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):151–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Bernstein A. Linkage of the Fv-2 gene to a newly reinserted ecotropic retrovirus in Fv-2 congenic mice. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):471–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.471-477.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., Bedigian H. G., Shull M. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Comparative molecular genetic analysis of lymphomas from six inbred mouse strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.839-846.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Condamine H., Jacob F. Inoculation of newborn SWR/J females with an ecotropic murine leukemia virus can produce transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1156–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. The development of the mouse ovary from birth to maturity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 Sep;62(1):98–116. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0620098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Li J. S. Studies with inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing indicate a functional role for complex sugars in the transport and proteolysis of Friend mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia virus envelope proteins. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):196–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Kalil J., Zilber M. T., Fellous M., Lévy D. Identification of a viral antigen recognized by H-2-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes on a murine leukemia virus-induced tumor. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2551–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Cuypers T., Maandag E. R., Selten G., Berns A. Generation of AKR mink cell focus-forming viruses: a conserved single-copy xenotrope-like provirus provides recombinant long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.432-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Quax W., van der Putten H., Berns A. Characterization of AKR murine leukemia virus sequences in AKR mouse substrains and structure of integrated recombinant genomes in tumor tissues. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDALI G., DESORMEAUX B., JULIARD L. Action d'hormones mâles et femelles sur la leucémogenès des souris AkR. Bull Assoc Fr Etud Cancer. 1956 Oct-Dec;43(4):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Kozak C. A. Germ-line reinsertions of AKR murine leukemia virus genomes in Akv-1 congenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4871–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pincus T. Quantitative studies of naturally occurring murine leukemia virus infection of AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):429–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Taylor B. A., Weinberg R. A. Continuing germ line integration of AKV proviruses during the breeding of AKR mice and derivative recombinant inbred strains. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.165-175.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus W. Imidazole increases the sensitivity of the cytochemical reaction for peroxidase with diaminobenzidine at a neutral pH. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 May;30(5):491–493. doi: 10.1177/30.5.6176617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]