Abstract
Transient expression assays were used to investigate the restriction of Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV) expression in undifferentiated mouse F9 embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells. We previously reported that the MoMuLV long terminal repeat (LTR) is inactive in undifferentiated F9EC cells due to inactivity of the tandemly repeated MoMuLV transcriptional enhancers. Others suggested that the inactivity was due to the presence of negative regulatory elements that interact with the MoMuLV tandem repeats. Two heterologous enhancer sequences that are active in undifferentiated F9 EC cells were inserted into the MoMuLV LTR: the B enhancers from the F101 variant of polyomavirus and a cellular enhancer sequence isolated from EC cells that we previously identified. The chimeric LTRs were then fused to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene and tested for expression by transfection into F9 EC or NIH 3T3 cells. Insertion of these enhancers either upstream or downstream of the MoMuLV tandem repeats resulted in transcriptionally active LTRs in undifferentiated EC cells, which did not support the existence of negative regulatory elements interacting with the tandem repeats. In our previous MoMuLV enhancer deletion constructs, the GC-rich sequences downstream from the tandem repeats were also deleted, which might have contributed to the inactivity in EC cells. However, restoration of the GC-rich sequences did not yield an active LTR. The experiments also suggested that the EC cellular enhancer was preferentially active in undifferentiated EC cells and inactive in NIH 3T3 cells. The possibility of negative regulatory sequences in the vicinity of the MoMuLV primer-binding site was tested by inserting MoMuLV sequences from +30 to +419 base pairs into the LTR-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene constructs downstream of the transcriptional start site. Transient expression assays confirmed that these sequences reduced expression from functional LTRs in undifferentiated F9 EC cells but reduced expression significantly less in NIH 3T3 cells. Moreover, equivalent sequences from myeloproliferative sarcoma virus did not exhibit this effect. These results supported restriction of MoMuLV expression in undifferentiated F9 EC cells at two levels, inactivity of the MoMuLV enhancers and interaction of negative regulatory factors in the vicinity of the primer-binding site.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos R., Villarreal L. P. An SV40 deletion mutant accumulates late transcripts in a paranuclear extract. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control of the mouse prealbumin (transthyretin) gene: both promoter sequences and a distinct enhancer are cell specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4697–4708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Mittal S., Chute H., Chao E., Pattengale P. K. Rearrangements and insertions in the Moloney murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat alter biological properties in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):204–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.204-214.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz T., Hilberg F., Seliger B., Stocking C., Ostertag W. Retroviral mutants efficiently expressed in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3292–3296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Linney E. Polyoma mutants that productively infect F9 embryonal carcinoma cells do not rescue wild-type polyoma in F9 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Wu F. K., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Interactions of cellular proteins involved in the transcriptional regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3761–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Mittal S., Davis B. R., Fan H. Generation of infectious Moloney murine leukemia viruses with deletions in the U3 portion of the long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4634–4640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilberg F., Stocking C., Ostertag W., Grez M. Functional analysis of a retroviral host-range mutant: altered long terminal repeat sequences allow expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Vasseur M., Montreau N., Yaniv M., Blangy D. Polyoma DNA sequences involved in control of viral gene expression in murine embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):720–722. doi: 10.1038/290720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollek R., Stocking C., Smadja-Joffe F., Ostertag W. Molecular cloning and characterization of a leukemia-inducing myeloproliferative sarcoma virus and two of its temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.717-724.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Donerly S. DNA fragments from F9 PyEC mutants increase expression of heterologous genes in transfected F9 cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh T. P., Sievert L. L., Scott R. W. Proviral sequences that restrict retroviral expression in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3775–3784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Yokota Y., Ishida H., Sugahara T. Independent mechanisms involved in suppression of the Moloney leukemia virus genome during differentiation of murine teratocarcinoma cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1105–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekikawa K., Levine A. J. Isolation and characterization of polyoma host range mutants that replicate in nullipotential embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1100–1104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
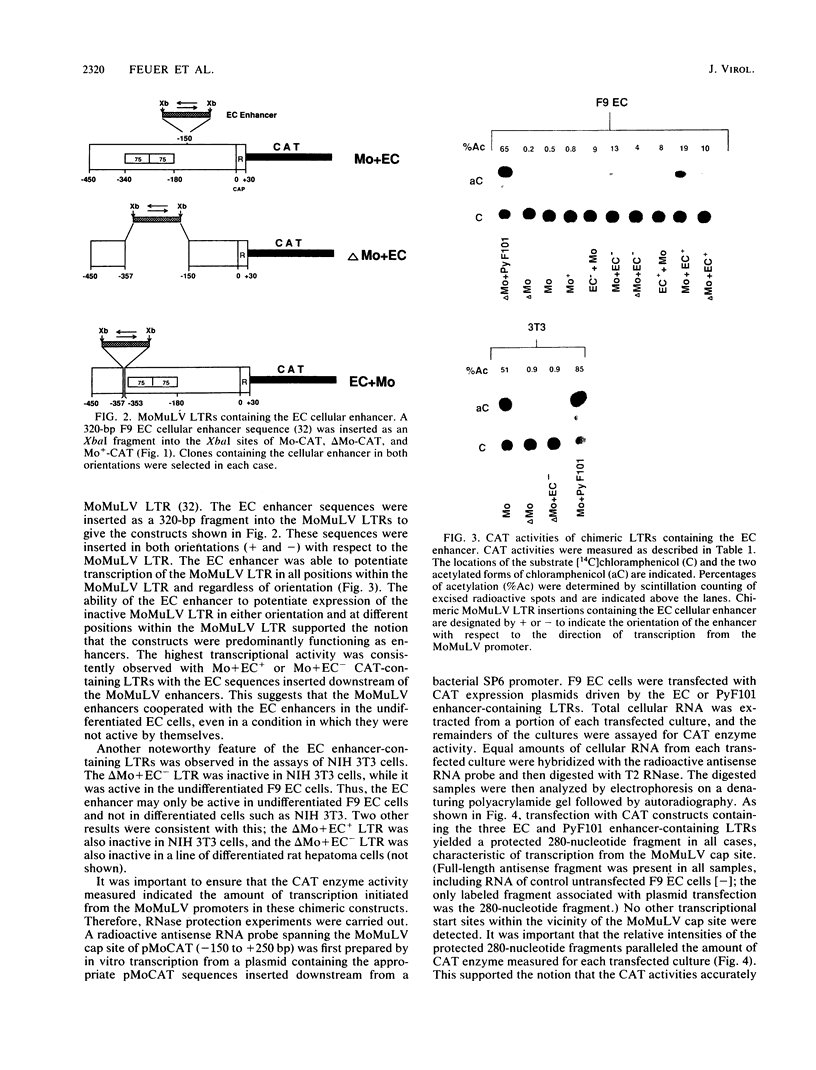
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo M., Gilboa E., Sherman M. I. Isolation of embryonal carcinoma cell lines that express integrated recombinant genes flanked by the Moloney murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo M., Tanaka M. A cellular enhancer of retrovirus gene expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3748–3752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N. M., Weiss R. A., Martin G. R., Lowy D. R. Virus infection of murine teratocarcinoma stem cell lines. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Barklis E., Ostertag W., Jaenisch R. Two distinct sequence elements mediate retroviral gene expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2742–2746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2742-2746.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. Alterations in binding characteristics of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer factor. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):218–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.218-225.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]