Abstract
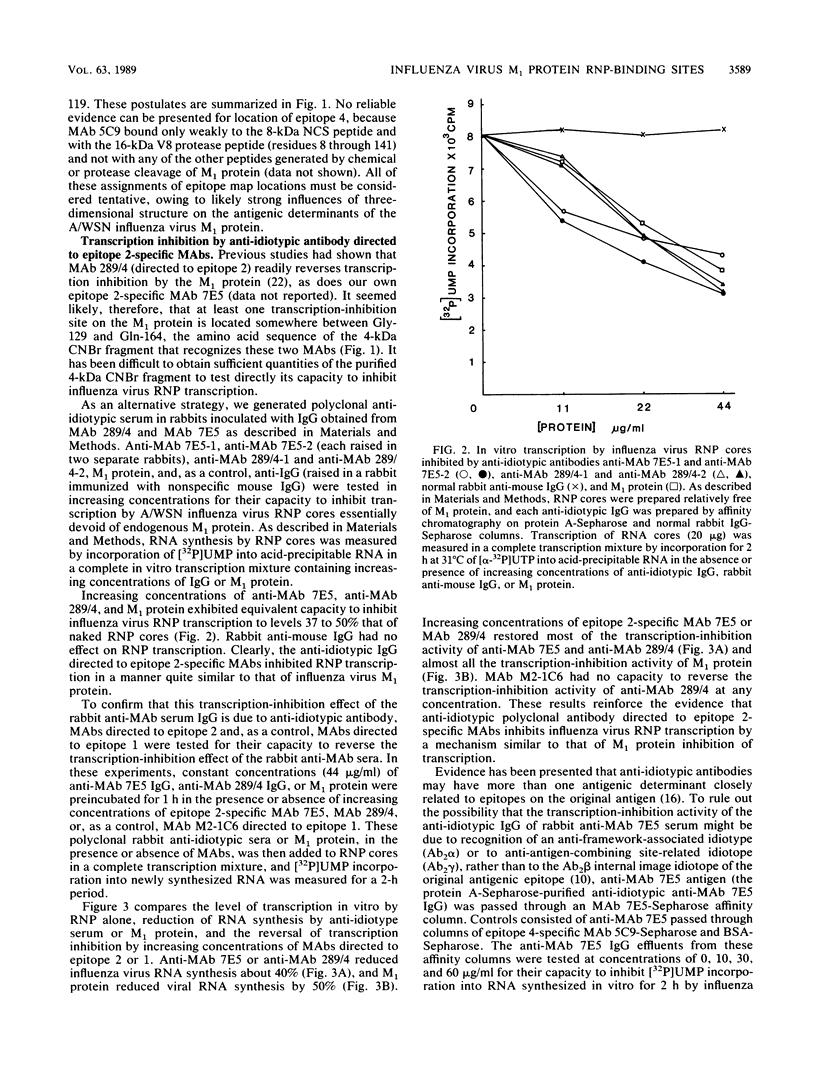
We have undertaken by biochemical and immunological experiments to locate the region of the matrix (M1) protein responsible for down-regulating endogenous transcription of A/WSN/33 influenza virus. A more refined map of the antigenic determinants of the M1 protein was obtained by binding of epitope-specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to chemically cleaved fragments. Epitope 2-specific MAb 289/4 and MAb 7E5 reverse transcription inhibition by M1 protein and react with a 4-kilodalton cyanogen bromide fragment extending from amino acid Gly-129 to Gln-164. Anti-idiotype serum immunoglobulin G prepared in rabbits immunized with MAb 289/4 or MAb 7E5 mimicked the action of M1 protein by inhibiting transcription in vitro of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein cores. This transcription-inhibition activity of anti-MAb 7E5 immunoglobulin G and anti-MAb 289/4 immunoglobulin G could be reversed by MAb 7E5 and MAb 289/4 or could be removed by MAb 7E5-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Transcription of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein was inhibited by one of three synthetic oligopeptides, a nonodecapeptide SP3 with an amino acid sequence corresponding to Pro-90 through Thr-108 of the M1 protein. Of all the structural proteins of influenza virus, only NP and M1 showed strong affinity for binding viral RNA or other extraneous RNAs. The 4-kilodalton cyanogen bromide peptide (Gly-129 to Gln-164), exhibited marked affinity for viral RNA, the binding of which was blocked by epitope 2-specific MAb 7E5 but not by MAbs directed to three other epitopes. Viral RNA also bound strongly to the nonodecapeptide SP3 and rather less well to anti-idiotype anti-MAb 7E5; these latter viral RNA-binding reactions were only slightly blocked by preincubation of anti-MAb 7E5 or SP3 with MAb 7E5. These experiments suggest the presence of at least two RNA-binding sites, which also serve as transcription-inhibition sites, centered around amino acid sequences 80 through 109 (epitope 4?) and 129 through 164 (epitope 2) of the 252 amino acid M1 protein of A/WSN/33 influenza virus. A hydropathy plot of the M1 protein calculated by free-energy transfer suggests that the two hydrophilic transcription-inhibition RNA-binding domains are brought into close proximity by an alpha-helix-forming intervening hydrophobic domain.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen H., McCauley J., Waterfield M., Gething M. J. Influenza virus RNA segment 7 has the coding capacity for two polypeptides. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):548–551. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Air G. M. Nucleotide sequence coding for the N-terminal region of the matrix protein influenza virus. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher D. J., Kharitonenkov I. G., Zakomirdin J. A., Grigoriev V. B., Klimenko S. M., Davis J. F. Incorporation of influenza virus M-protein into liposomes. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.586-590.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulton G. N., Greene M. I. Idiotypic mimicry of biological receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:253–280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A., Frangione B. Insertion of influenza M protein into the viral lipid bilayer and localization of site of insertion. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):323–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.323-328.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriades A. Interaction of influenza M protein with viral lipid and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):470–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.470-479.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The gene structure and replication of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:467–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Zebedee S. L., Richardson C. D. Influenza virus M2 protein is an integral membrane protein expressed on the infected-cell surface. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisonoff A., Lamoyi E. Implications of the presence of an internal image of the antigen in anti-idiotypic antibodies: possible application to vaccine production. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 Dec;21(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. R., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Mapping regions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus which bind to ribonucleocapsids, liposomes, and monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.860-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Gross J., Oxford J. S. The intracellular distribution of influenza virus matrix protein and nucleoprotein in infected cells and their relationship to haemagglutinin in the plasma membrane. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1859–1872. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehnke P. C., Mason A. M., Hood S. J., Lister R. M., Johnson J. E. A "zinc-finger"-type binding domain in tobacco streak virus coat protein. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley J. B., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Antigenicity, function, and conformation of synthetic oligopeptides corresponding to amino-terminal sequences of wild-type and mutant matrix proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2569–2577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2569-2577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. P., Pal R., Fox J. W., Wagner R. R. Functional and antigenic domains of the matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.239-246.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Growth restriction of influenza A virus by M2 protein antibody is genetically linked to the M1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1061–1065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2762-2772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvonarjev A. Y., Ghendon Y. Z. Influence of membrane (M) protein on influenza A virus virion transcriptase activity in vitro and its susceptibility to rimantadine. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):583–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.583-586.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyke K. L., Yewdell J. W., Reck L. J., Murphy B. R. Antigenic characterization of influenza A virus matrix protein with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):248–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.248-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



