Abstract
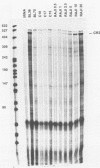
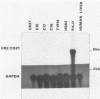
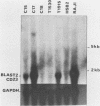
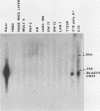
Anaplastic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells invariably harbor the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome, an association that is unique among human virus-associated cancers. Although EBV is able to replicate in epithelial cells, results with expression of the EBV receptor (complement receptor type 2 [CR2]; also called CD21) in normal and malignant epithelial cells are conflicting. We grew five different EBV-associated NPC tumors in nude mice, and by using a sensitive transcriptional assay, we detected a very weak transcription signal of the EBV receptor CR2 gene in these cells. This suggests that low levels of EBV receptor may be expressed by malignant epithelial nasopharyngeal cells. The gene coding for Blast2/CD23, a B-cell activation molecule induced by EBV, was transcribed in three of the transplanted NPC tumors. The soluble form of the Blast2/CD23 protein was also detected in medium taken from short-term cultures of the same NPC cell lines. In contrast to the lymphoid system, in which Blast2/CD23 expression is associated with EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA2) expression, no EBNA2 protein could be detected in these NPC epithelial cells. Our study represents the first demonstration of Blast2/CD23 expression in epithelial cells. As the soluble form of the Blast2/CD23 protein possesses growth factor activity associated with EBV-induced B-cell immortalization, these results suggest a possible role for this molecule in the pathogenesis of NPC.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adldinger H. K., Delius H., Freese U. K., Clarke J., Bornkamm G. W. A putative transforming gene of Jijoye virus differs from that of Epstein-Barr virus prototypes. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Aubry J. P., Peronne C., Wijdenes J., Banchereau J. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the human lymphocyte low affinity receptor for IgE: CD 23 is a low affinity receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2970–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Guillot O., Spits H., Blanchard D., Ishizaka K., Banchereau J. The low-affinity receptor for IgE (CD23) on B lymphocytes is spatially associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):57–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busson P., Braham K., Ganem G., Thomas F., Grausz D., Lipinski M., Wakasugi H., Tursz T. Epstein-Barr virus-containing epithelial cells from nasopharyngeal carcinoma produce interleukin 1 alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6262–6266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busson P., Ganem G., Flores P., Mugneret F., Clausse B., Caillou B., Braham K., Wakasugi H., Lipinski M., Tursz T. Establishment and characterization of three transplantable EBV-containing nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1988 Oct 15;42(4):599–606. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desgranges C., Wolf H., De-Thé G., Shanmugaratnam K., Cammoun N., Ellouz R., Klein G., Lennert K., Muñoz N., Zur Hausen H. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. X. Presence of epstein-barr genomes in separated epithelial cells of tumours in patients from Singapore, Tunisia and Kenya. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):7–15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Establishment of an epitheloid cell line and a fusiform cell line from a patient with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci Sin. 1978 Jan-Feb;21(1):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Barel M., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. gp140, the C3d receptor of human B lymphocytes, is also the Epstein-Barr virus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1490–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Lang C. M., Lee K. J., Schuller D. E., Jacobs D., McQuattie C. Attempt to infect nonmalignant nasopharyngeal epithelial cells from humans and squirrel monkeys with Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1085–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., de Thé G., Lenoir G., Ho J. H. Superinfection epithelial nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):960–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Ley S. C., Melamed M. D., English L. S., Hughes-Jones N. C. Immortalized B lymphocytes produce B-cell growth factor. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):145–147. doi: 10.1038/310145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herait P., Ganem G., Lipinski M., Carlu C., Micheau C., Schwaab G., De-The G., Tursz T. Lymphocyte subsets in tumour of patients with undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: presence of lymphocytes with the phenotype of activated T cells. Br J Cancer. 1987 Feb;55(2):135–139. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Hardie D. L., Ling N. R., Maclennan I. C. Human follicular dendritic cells (FDC): a study with monoclonal antibodies (MoAb). Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):205–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Inui S., Sato R., Barsumian E. L., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Kaisho T., Uchibayashi N., Hardy R. R., Hirano T. Molecular structure of human lymphocyte receptor for immunoglobulin E. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noro N., Yoshioka A., Adachi M., Yasuda K., Masuda T., Yodoi J. Monoclonal antibody (H107) inhibiting IgE binding to Fc epsilon R(+) human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1258–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynes M., Aubert J. P., Cohen J. H., Audouin J., Tricottet V., Diebold J., Kazatchkine M. D. Human follicular dendritic cells express CR1, CR2, and CR3 complement receptor antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2687–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter M., Boos H., Hirsch F., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Characterization of a latent protein encoded by the large internal repeats and the BamHI Y fragment of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):586–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Davis D. S., Young L. S., Hutt-Fletcher L., Tedder T. F., Rickinson A. B. Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Lemon S. M., Pagano J. S. A second site for Epstein-Barr virus shedding: the uterine cervix. Lancet. 1986 Nov 15;2(8516):1122–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Vesterinen E. H., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Walton L. A., Pagano J. S. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus in human epithelial cells infected in vitro. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):480–483. doi: 10.1038/306480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendeman S., Thorley-Lawson D. A. The activation antigen BLAST-2, when shed, is an autocrine BCGF for normal and transformed B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1637–1642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Mann K. P. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection provide a model for B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):45–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Nadler L. M., Bhan A. K., Schooley R. T. BLAST-2 [EBVCS], an early cell surface marker of human B cell activation, is superinduced by Epstein Barr virus. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3007–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Fearon D. T., Klickstein L. B., Wong W. W., Richards S. A., de Bruyn Kops A., Smith J. A., Weis J. H. Identification of a partial cDNA clone for the C3d/Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes: homology with the receptor for fragments C3b and C4b of the third and fourth components of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5639–5643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Clark D., Sixbey J. W., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human pharyngeal epithelia. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dawson C. W., Brown K. W., Rickinson A. B. Identification of a human epithelial cell surface protein sharing an epitope with the C3d/Epstein-Barr virus receptor molecule of B lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):786–794. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Yao Q. Y., Rooney C. M., Sculley T. B., Moss D. J., Rupani H., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W., Rickinson A. B. New type B isolates of Epstein-Barr virus from Burkitt's lymphoma and from normal individuals in endemic areas. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2853–2862. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa K., Kikutani H., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Yokota A., Nakamura H., Barsumian E. L., Hardy R. R., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. A B cell-specific differentiation antigen, CD23, is a receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon R) on lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2576–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]