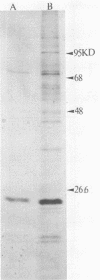
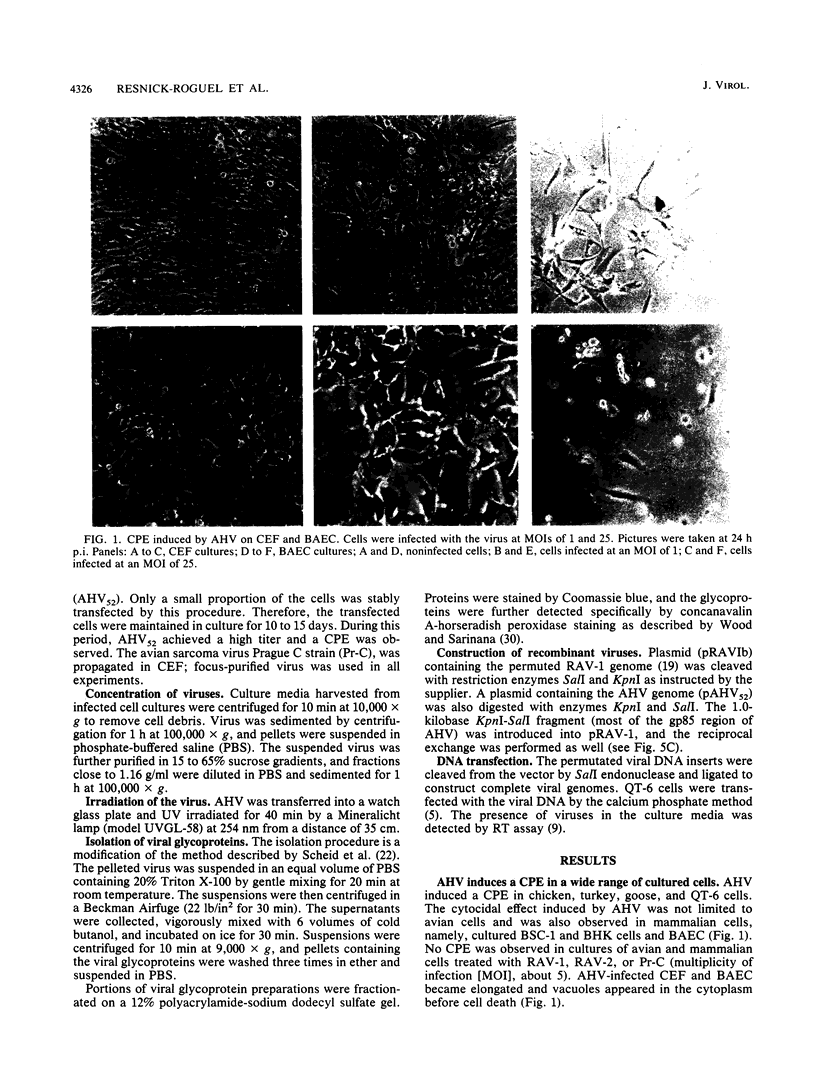
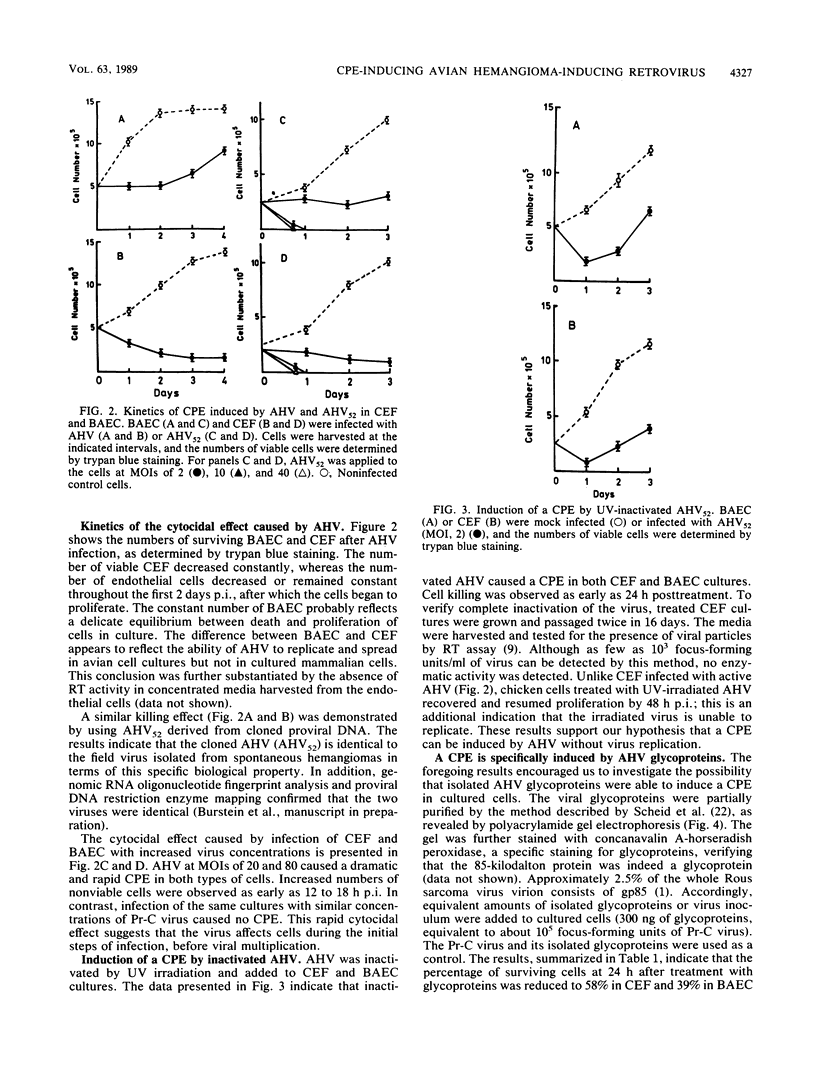
Abstract
We isolated a field strain of avian hemangioma retrovirus (AHV) which induces a cytopathic effect (CPE) on cultured avian and mammalian cells shortly after infection. The kinetics of cell killing were dependent on the multiplicity of infection. The CPE on avian and mammalian cells was independent of virus replication, because UV-irradiated virus led to cell death as well. Biochemical and genetic experiments indicated that AHV env gene products were responsible for the CPE. Partially purified AHV envelope glycoproteins (gp85), but not those of the Rous sarcoma virus Prague C strain, induced a CPE. Rous-associated virus type 1, in which the env region was replaced by the AHV gp85 region, induced a CPE on avian and mammalian cultured cells. Therefore, we suggest that CPE is induced by AHV via interaction between viral gp85 and the cell membrane. This mode of CPE is unique among avian sarcoma-leukemia viruses.
Full text
PDF
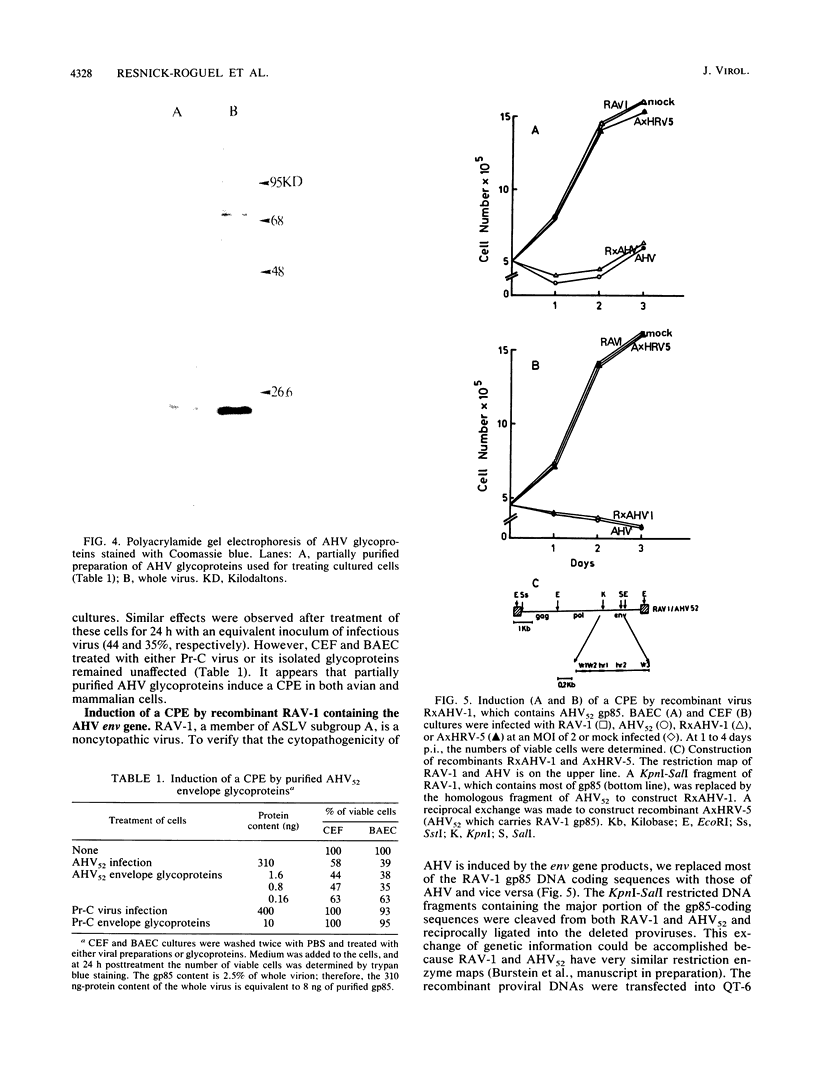


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolognesi D. P., Bauer H., Gelderblom H., Hüper G. Polypeptides of avian RNA tumor viruses. IV. Components of the viral envelope. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):551–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90545-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Blais B. P., Robinson H. L. Long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences, env, and a region near the 5' LTR influence the pathogenic potential of recombinants between Rous-associated virus types 0 and 1. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3431–3437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3431-3437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W., Scheid A. The role of viral glycoproteins in adsorption, penetration, and pathogenicity of viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):40–61. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Coffin J. M. Determinants for receptor interaction and cell killing on the avian retrovirus glycoprotein gp85. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90322-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J., Braun D., Birdwell C. Clonal growth of bovine vascular endothelial cells: fibroblast growth factor as a survival agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4120–4124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn A. Membrane effects of cytopathogenic viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1985;31:109–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Interaction of influenza virus hemagglutinin with target membrane lipids is a key step in virus-induced hemolysis and fusion at pH 5.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. J., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular DNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):356–367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.356-367.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Ensoli B., Markham P. D., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Kaposi's sarcoma cells: long-term culture with growth factor from retrovirus-infected CD4+ T cells. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):426–430. doi: 10.1126/science.3262925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedt G. W., Schinella R. A. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clinicopathologic study of 56 autopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Aug;109(8):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Gottlieb A. A., Garry R. F. Cell killing by ultraviolet-inactivated human immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):395–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Nakamura S., Biberfeld P., Kaplan M. H., Markham P. D., Larsson L., Gallo R. C. Angiogenic properties of Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells after long-term culture in vitro. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):430–433. doi: 10.1126/science.2459779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Neckameyer W. S., Hayward W. S., Smith R. E. Genetic determinants of neoplastic diseases induced by a subgroup F avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1203-1212.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasundaran M., Robinson H. L. A major mechanism of human immunodeficiency virus-induced cell killing does not involve cell fusion. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3114–3119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3114-3119.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Mechanisms of cell killing/cytopathic effects by nonhuman retroviruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):399–405. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Joy A. E., Temin H. M. Correlation between cell killing and massive second-round superinfection by members of some subgroups of avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):494–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.494-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Temin H. M. Cell killing by avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):713–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.713-721.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Ruscetti S. The spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) envelope gene, when introduced into mice in the absence of other SFFV genes, induces acute erythroleukemia. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2158–2163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2158-2163.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Sarinana F. O. The staining of sciatic nerve glycoproteins on polyacrylamide gels with concanavalin A-peroxidase. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90597-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]