Abstract
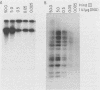
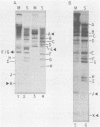
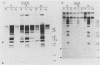
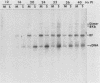
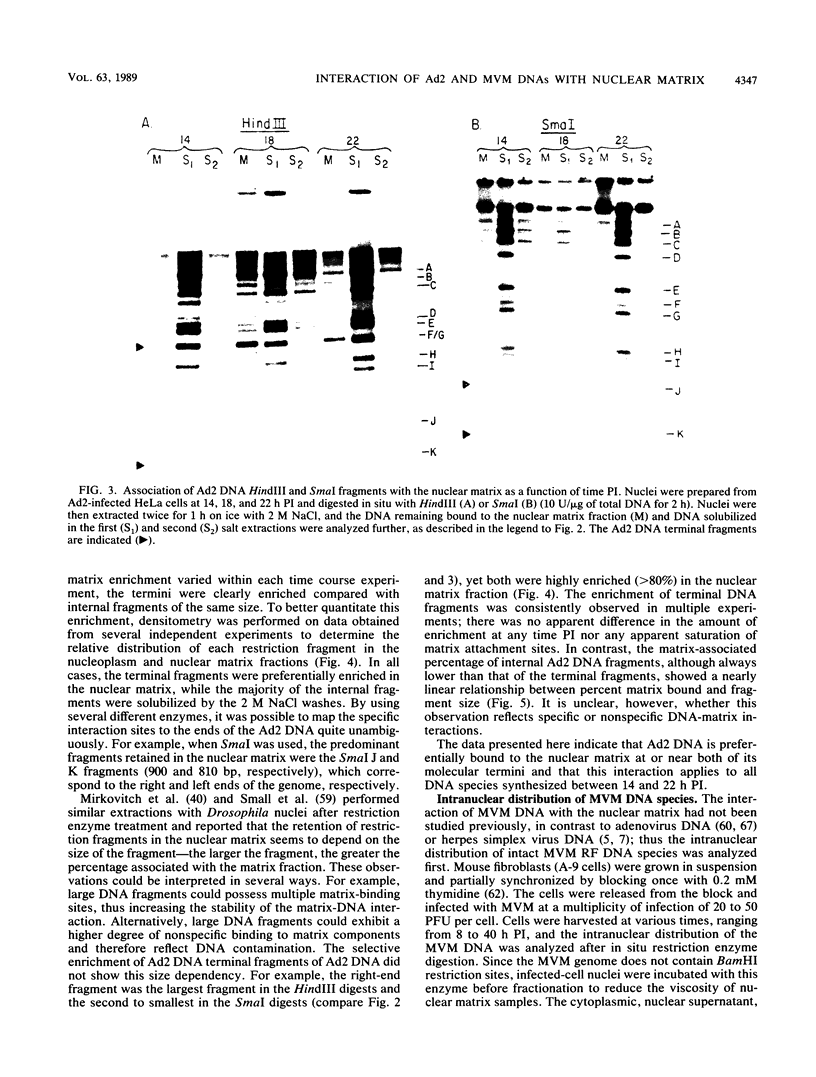
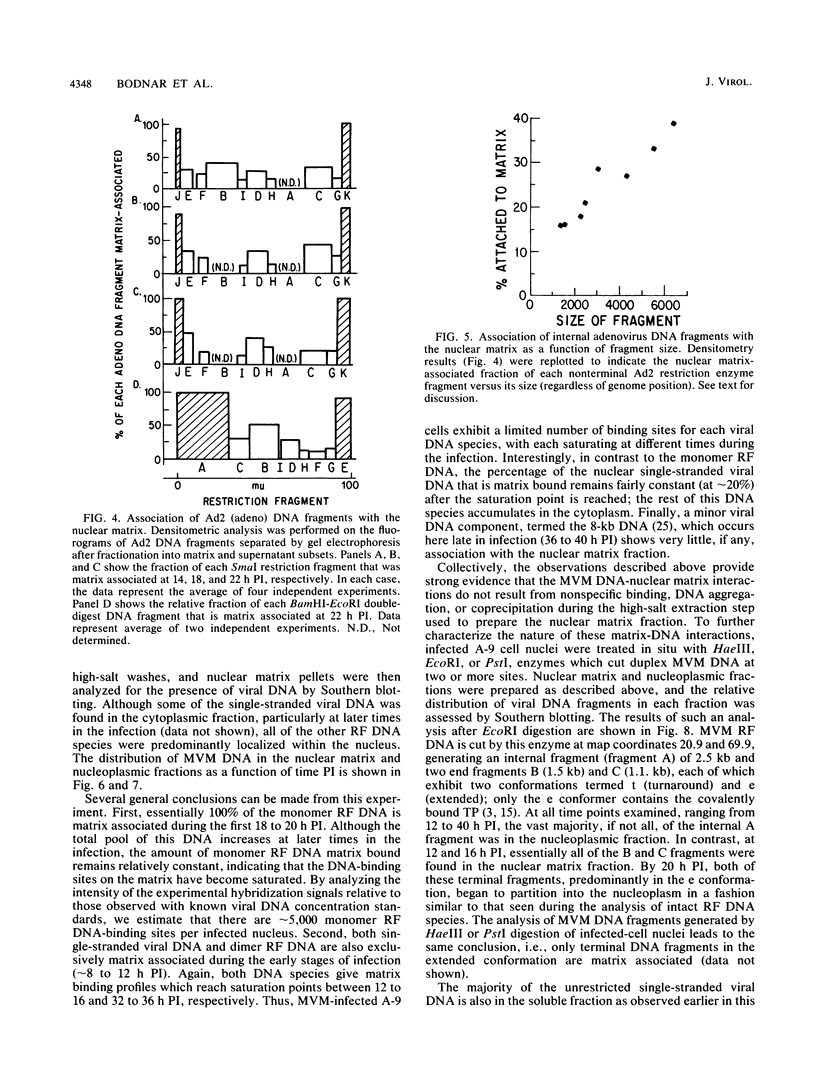
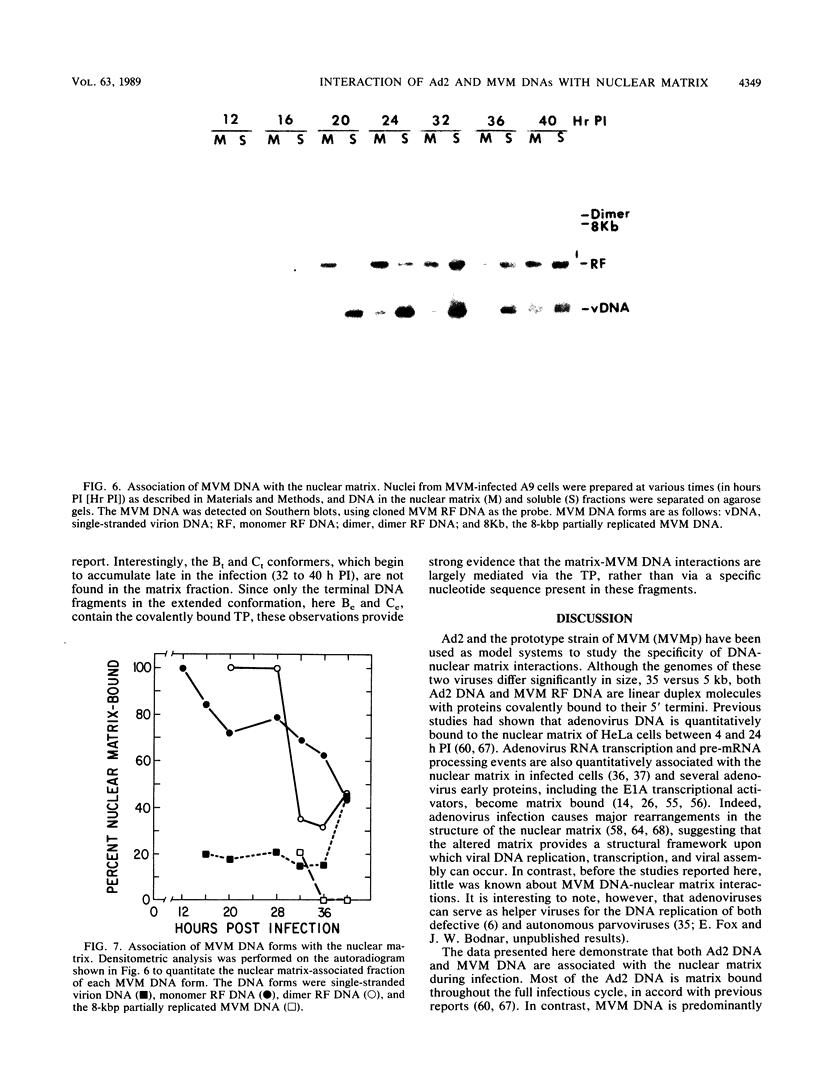
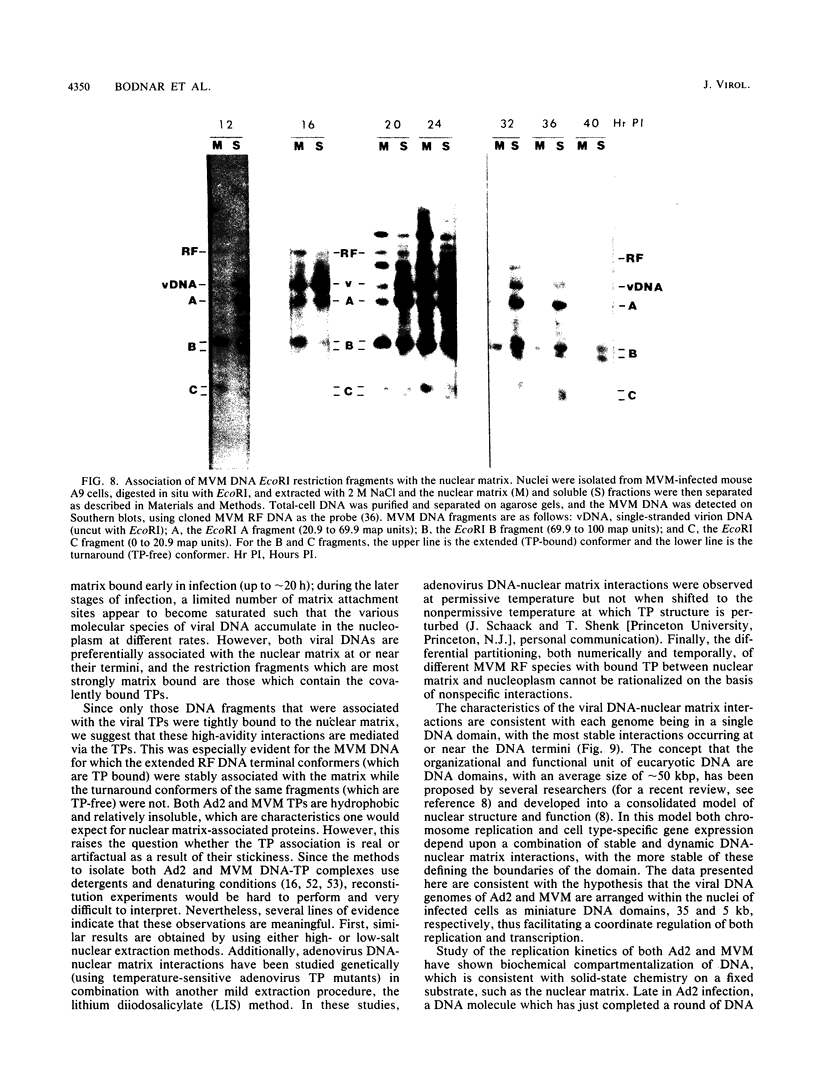
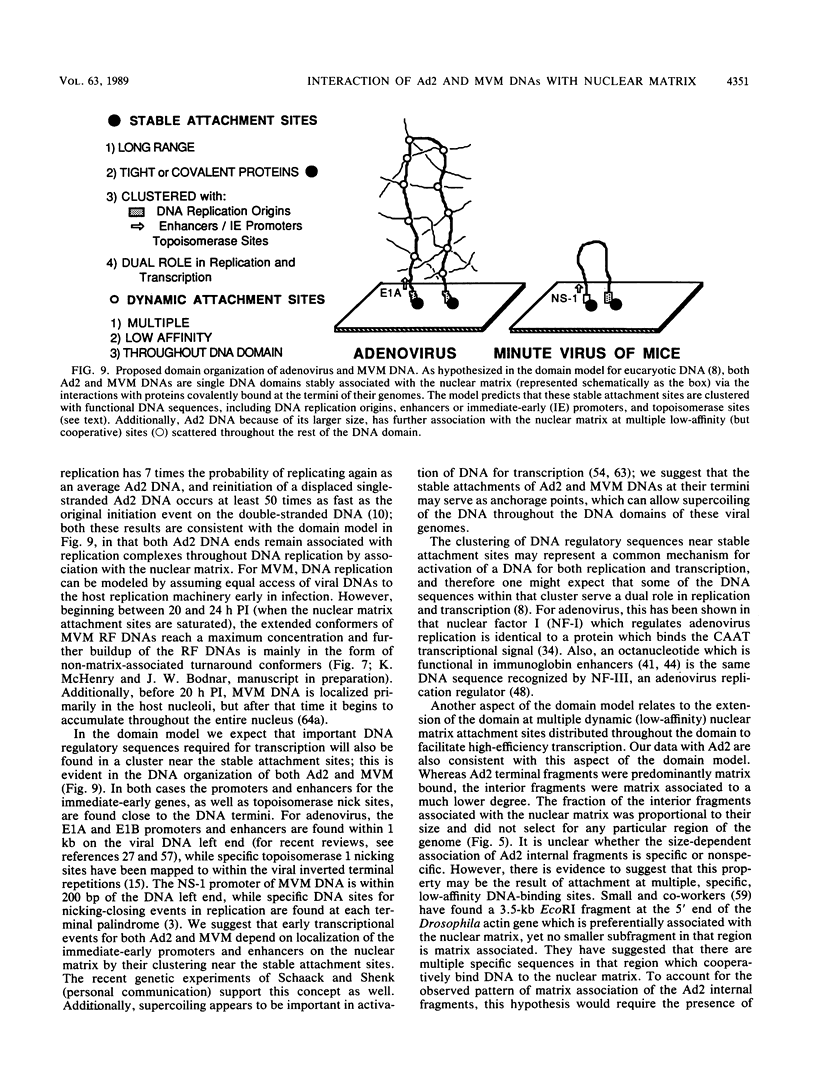
The interaction of viral genomes with the cellular nuclear matrix was studied by using adenovirus-infected HeLa cells and minute virus of mice (MVM)-infected A-9 cells. Adenovirus DNA was associated with the nuclear matrix both early and late in infection, the tightest interaction being with DNA fragments that contain the covalently bound 5'-terminal protein. Replicative forms of MVM DNA were also found to be exclusively matrix associated during the first 16 to 20 h of infection; at later times viral DNA species accumulated in the soluble nuclear fraction at different rates, suggesting a saturation of nuclear matrix-binding sites. MVM DNA fragments enriched in the matrix fraction were also derived from the terminal regions of the viral genome. However, only the subset of fragments which possess a covalently bound 5'-terminal protein (i.e., DNA fragments in which the 5' palindromic DNA sequences are in the extended duplex rather than the hairpin conformation) were matrix associated. These observations suggest that the DNA-matrix interactions are, at least in part, mediated by the viral terminal proteins. Since these proteins have previously been shown to be intimately involved in viral DNA replication, our results further indicate that an association with the nuclear matrix may be important for viral genome replication and possibly also for efficient gene transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aelen J. M., Opstelten R. J., Wanka F. Organization of DNA replication in Physarum polycephalum. Attachment of origins of replicons and replication forks to the nuclear matrix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1181–1195. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Structure and replication of minute virus of mice DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):751–762. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. Biological properties of the nuclear matrix: steroid hormone binding. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1982;38:133–195. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571138-8.50009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Abulafia R., Bratosin S. Herpes simplex virus and protein transport are associated with the cytoskeletal framework and the nuclear matrix in infected BSC-1 cells. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Labow M. A. Parvovirus gene regulation. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):601–614. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibor-Hardy V., Pouchelet M., St-Pierre E., Herzberg M., Simard R. The nuclear matrix is involved in herpes simplex virogenesis. Virology. 1982 Sep;121(2):296–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W. A domain model for eukaryotic DNA organization: a molecular basis for cell differentiation and chromosome evolution. J Theor Biol. 1988 Jun 22;132(4):479–507. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Jones C. J., Coombs D. H., Pearson G. D., Ward D. C. Proteins tightly bound to HeLa cell DNA at nuclear matrix attachment sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1567–1579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Pearson G. D. Kinetics of adenovirus DNA replication II. Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Ward D. C. Highly recurring sequence elements identified in eukaryotic DNAs by computer analysis are often homologous to regulatory sequences or protein binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1835–1851. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Weber J. Virion core-like organization of intranuclear adenovirus chromatin late in infection. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):306–310. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrì M. T., Micheli G., Graziano E., Pace T., Buongiorno-Nardelli M. The relationship between chromosomal origins of replication and the nuclear matrix during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jun;164(2):426–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee P. K., Flint S. J. Partition of E1A proteins between soluble and structural fractions of adenovirus-infected and -transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1018–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1018-1026.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. C., Pearson G. D. Site-specific nicking within the adenovirus inverted terminal repetition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1489–1500. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Bodnar J. W., Polvino-Bodnar M., Ward D. C. Identification and characterization of a protein covalently bound to DNA of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1094–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1094-1104.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Mapping sequences in loops of nuclear DNA by their progressive detachment from the nuclear cage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2895–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R. The nucleoskeleton: artefact, passive framework or active site? J Cell Sci. 1988 May;90(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E., Groff D. E., Fedor M. J. Adenovirus chromatin structure at different stages of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1094–1105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Mullenders L. H., Wanka F. Analysis of the attachment of replicating DNA to a nuclear matrix in mammalian interphase nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):219–230. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Wenink P. W., Poddighe J. Permanent attachment of replication origins to the nuclear matrix in BHK-cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3241–3249. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerig C., McMaster G., Sogo J., Bruggmann H., Beard P. Nucleoprotein complexes of minute virus of mice have a distinct structure different from that of chromatin. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):817–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.817-824.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Déry C. V., Toth M., Brown M., Horvath J., Allaire S., Weber J. M. The structure of adenovirus chromatin in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2671–2684. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Gloor G. Characterization of a metastable, partially replicated dimeric intermediate of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):621–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.621-625.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer J., Winnacker E. L. Adenovirus DNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;111:41–64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69549-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., Hermoso J. M., García J. A., García E., López R., Salas M. Formation of a covalent complex between the terminal protein of pneumococcal bacteriophage Cp-1 and 5'-dAMP. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):31–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.31-35.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W. Identification of proteins tightly bound to herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):254–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Cook P. R. Replication occurs at a nucleoskeleton. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledinko N., Hopkins S., Toolan H. Relationship between potentiation of H-1 growth by human adenovirus 12 and inhibition of the 'helper' adenovirus by H-1. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):19–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loc P. V., Strätling W. H. The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme gene co-map with the boundaries of the chromatin domain. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Eekelen C. A., Reinders R. J., Berns A. J., van Venrooij W. J. Adenoviral heterogeneous nuclear RNA is associated with the host nuclear matrix during splicing. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E., Hagebols A. M., van Venrooij W. On the localization and transport of specific adenoviral mRNA-sequences in the late infected HeLa cell. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6131–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Godwin J., Mason D. W., Brazell I. A., Cook P. R. DNA is replicated at the nuclear cage. J Cell Sci. 1980 Dec;46:365–386. doi: 10.1242/jcs.46.1.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocikat R., Falkner F. G., Mertz R., Zachau H. G. Upstream regulatory sequences of immunoglobulin genes are recognized by nuclear proteins which also bind to other gene regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8829–8844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Pienta K. J., Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. The role of the nuclear matrix in the organization and function of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:457–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Jones S. D., Bond B., Yamamoto K. R. The immunoglobulin octanucleotide: independent activity and selective interaction with enhancers. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1498–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.3029871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Hanawalt P. C. Isolation of DNA replication complexes from uninfected and adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinard M. F., Simard R., Bibor-Hardy V. DNA-binding proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected BHK cell nuclear matrices. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):727–735. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Chen L. B., Knipe D. M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. V., Kekelidze M. G., Lukanidin E. M., Scherrer K., Georgiev G. P. Replication origins are attached to the nuclear skeleton. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):8189–8207. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.8189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. V., Mantieva V. L., Georgiev G. P. The similarity of DNA sequences remaining bound to scaffold upon nuclease treatment of interphase nuclei and metaphase chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1713–1735. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Russell W. C., Bellet A. J., Robinson A. J. Identification of a protein linked to the ends of adenovirus DNA. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. J., Bodnar J. W., Coombs D. H., Pearson G. D. Replicating adenovirus 2 DNA molecules contain terminal protein. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):143–158. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Structure of the two distinct types of minichromosomes that are assembled on DNA injected in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):923–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Hearing P., Anderson C. W., Reich N., Levine A. J. Identification and characterization of an immunologically conserved adenovirus early region 11,000 Mr protein and its association with the nuclear matrix. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):565–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90389-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt R. C., Fahnestock M. L., Lewis J. B. Differential nuclear localization of the major adenovirus type 2 E1a proteins. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.247-255.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Williams J. Genetic analysis of adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;111:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69549-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons T., Heywood P., Hodge L. D. Intranuclear site of replication of adenovirus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 5;89(3):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D., Nelkin B., Vogelstein B. The association of transcribed genes with the nuclear matrix of Drosophila cells during heat shock. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2413–2431. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Berezney R., Brewster J. M., Rekosh D. Properties of adenoviral DNA bound to the nuclear matrix. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1197–1202. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thilly W. G. Maintenance of perpetual synchrony in HeLa S3 culture: theoretical and empirical approaches. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;14:273–285. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Rozijn R. H., Spies F. Localization of adenovirus DNA replication in KB cells. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton T. H., Moen P. T., Jr, Fox E., Bodnar J. W. Interactions of minute virus of mice and adenovirus with host nucleoli. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3651–3660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3651-3660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Hyman R. W., Davidson N. Electron microscopic mapping of proteins bound to herpes simplex virus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3427–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younghusband H. B., Maundrell K. Adenovirus DNA is associated with the nuclear matrix of infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):705–713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.705-713.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Z. H., Nickerson J. A., Krochmalnic G., Penman S. Alterations in nuclear matrix structure after adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1007–1018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1007-1018.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]