Abstract
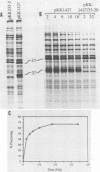
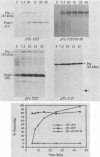
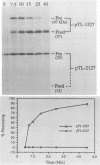
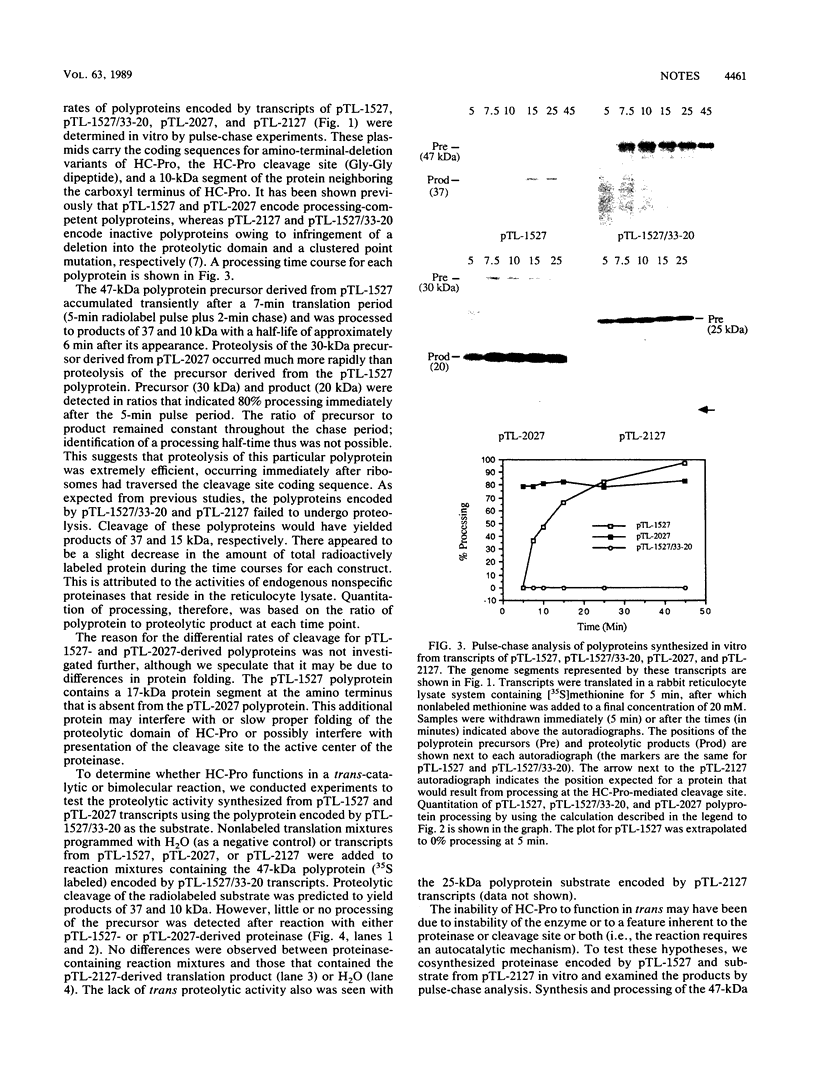
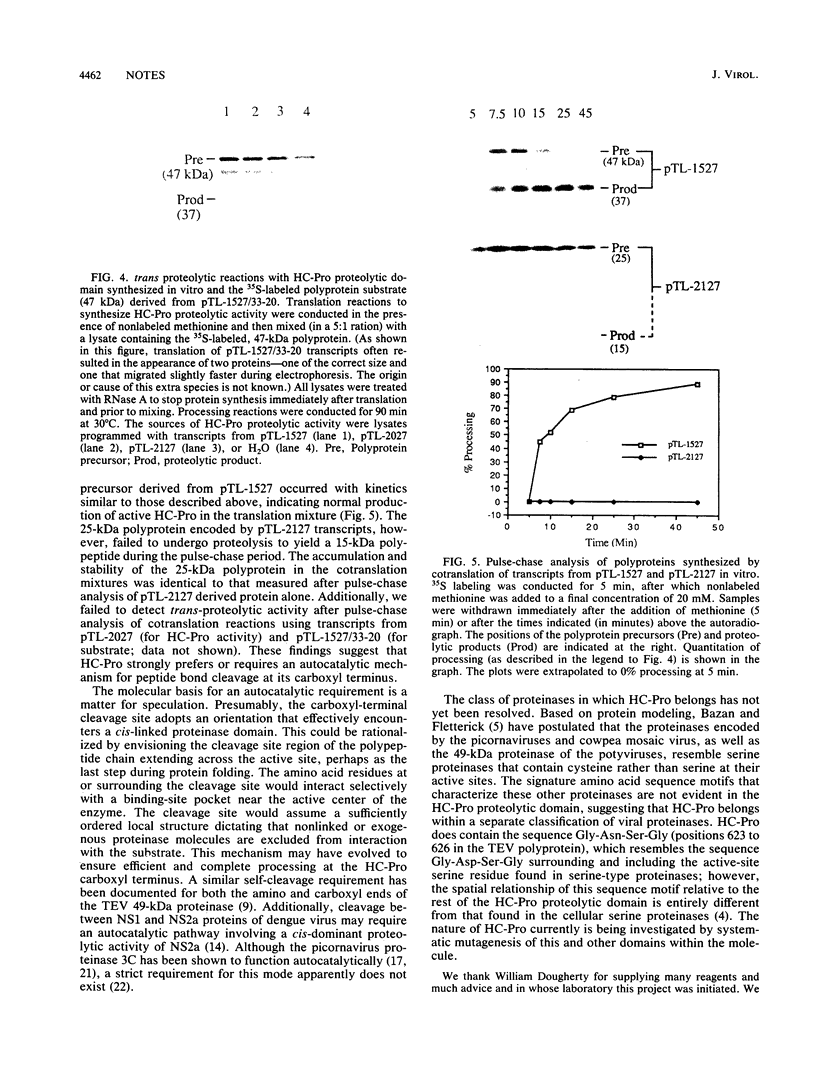
The virus-encoded proteins of tobacco etch virus (TEV), a plant potyvirus, arise by proteolytic processing of a large polyprotein precursor. The TEV genome codes for two proteinases, a 49-kilodalton proteinase and helper component proteinase (HC-Pro), which cleave the polyprotein at specific sites. The only known cleavage event catalyzed by HC-Pro occurs at the HC-Pro carboxyl terminus. The proteolytic activity of HC-Pro was analyzed by expression of the enzyme in bacterial and cell-free systems. The carboxyl-terminal domain of HC-Pro exhibited proteolytic activity in Escherichia coli with a processing half-time of approximately 100 s. The processing kinetics of HC-Pro expressed in vitro by cell-free transcription and translation was variable, depending on the presence or absence of TEV polypeptide sequences at the amino terminus of the proteolytic domain. Cleavage of the HC-Pro carboxyl terminus appeared to proceed exclusively by an autocatalytic mechanism; the proteinase synthesized in vitro exhibited little or no proteolytic activity when reacted with the HC-Pro cleavage site in trans or biomolecular reactions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison R. F., Sorenson J. C., Kelly M. E., Armstrong F. B., Dougherty W. G. Sequence determination of the capsid protein gene and flanking regions of tobacco etch virus: Evidence for synthesis and processing of a polyprotein in potyvirus genome expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3969–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Dougherty W. G. Mutational analysis of tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing: cis and trans proteolytic activities of polyproteins containing the 49-kilodalton proteinase. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2313–2320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2313-2320.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Parks T. D., Dougherty W. G. A second proteinase encoded by a plant potyvirus genome. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):365–370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. A viral cleavage site cassette: identification of amino acid sequences required for tobacco etch virus polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domier L. L., Franklin K. M., Shahabuddin M., Hellmann G. M., Overmeyer J. H., Hiremath S. T., Siaw M. F., Lomonossoff G. P., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. The nucleotide sequence of tobacco vein mottling virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5417–5430. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty W. G., Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Parks T. D. Biochemical and mutational analysis of a plant virus polyprotein cleavage site. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1281–1287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02942.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Chanock R., Lai C. J. Proper processing of dengue virus nonstructural glycoprotein NS1 requires the N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence and the downstream nonstructural protein NS2a. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1852–1860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1852-1860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Ariga H., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Expression of a cloned gene segment of poliovirus in E. coli: evidence for autocatalytic production of the viral proteinase. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann G. M., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. In vitro analysis of tobacco vein mottling virus NIa cistron: evidence for a virus-encoded protease. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Rueckert R. R. Evidence for intramolecular self-cleavage of picornaviral replicase precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):244–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.244-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E. A second protease of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.893-899.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y. C., Shih D. S. Cleavage of a viral polyprotein by a cellular proteolytic activity. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):547–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.547-551.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos P., Verver J., Jaegle M., Wellink J., van Kammen A., Goldbach R. Two viral proteins involved in the proteolytic processing of the cowpea mosaic virus polyproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1967–1985. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellink J., van Kammen A. Proteases involved in the processing of viral polyproteins. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1988;98(1-2):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01321002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. C., Van Frank R. M., Muth W. L., Burnett J. P. Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli producing biosynthetic human insulin proteins. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):687–689. doi: 10.1126/science.7036343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]