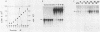Abstract
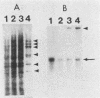
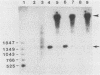
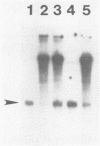
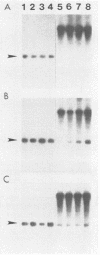
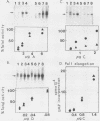
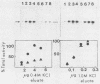
Synthesis of rRNA by RNA polymerase I is almost completely inhibited soon after infection of human cells with poliovirus. We show that extracts prepared from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells are severely inhibited in their ability to transcribe from a human rDNA promoter compared with extracts from mock-infected cells. Two lines of evidence presented here suggest that a specific transcriptional activity required for rDNA transcription in vitro is impaired in virus-infected cells. First, fractionation of individual transcriptional components by phosphocellulose chromatography and subsequent reconstitution experiments showed that the specific transcriptional activity of fraction C (0.8 M KCl eluate) from virus-infected cells was reduced three- to fourfold relative to that isolated from mock-infected cells. The activities of other transcription factors needed for in vitro transcription from the rDNA promoter were unaffected. Second, fraction C derived from mock-infected cells specifically restored transcription in extracts prepared from virus-infected cells. Fraction C contained both a nonspecific RNA polymerase I elongation activity and a specific factor activity which was needed for accurate transcription initiation. It is the specific transcriptional activity and not the nonspecific chain elongation activity of fraction C that is affected in cells infected with poliovirus.
Full text
PDF



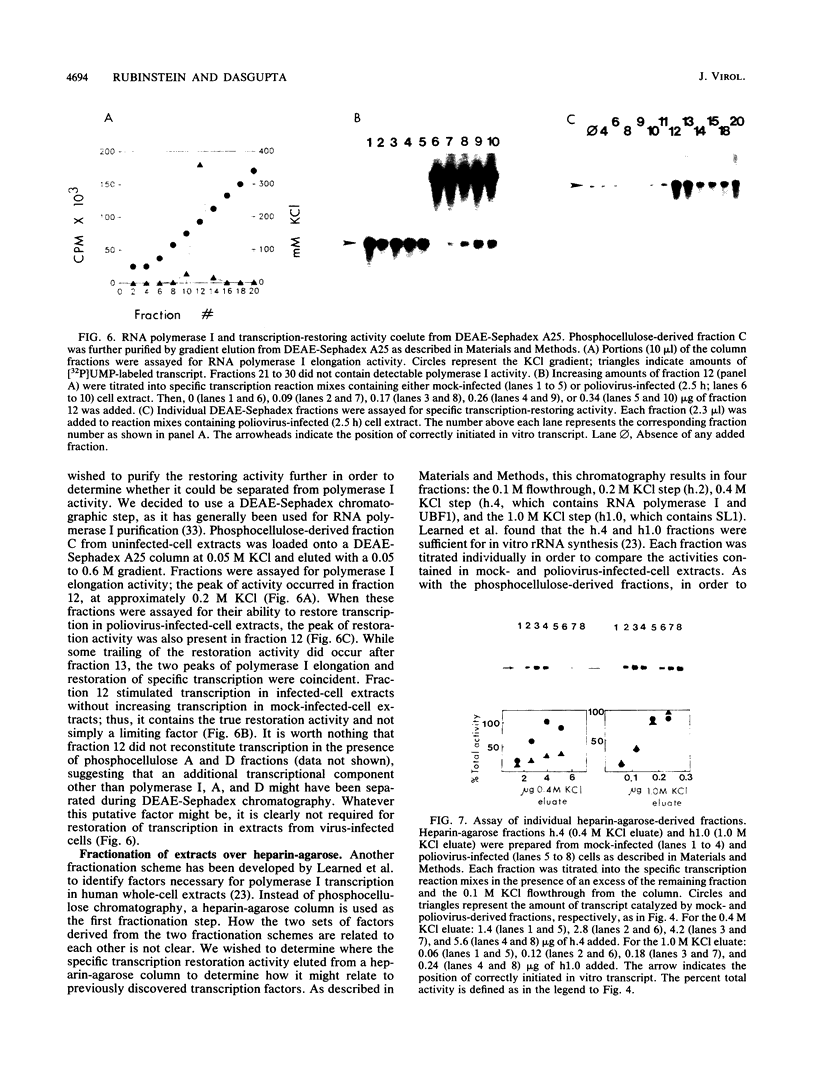


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apriletti J. W., Penhoet E. E. Cellular RNA synthesis in normal and mengovirus-infected L-929 cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):603–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apriletti J. W., Penhoet E. E. Recovery of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activities from L cells after mengovirus infection. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. P., Learned R. M., Jantzen H. M., Tjian R. Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1192–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.3413483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttgereit D., Pflugfelder G., Grummt I. Growth-dependent regulation of rRNA synthesis is mediated by a transcription initiation factor (TIF-IA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8165–8180. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Gokal P. K., Lawther R. P., Thompson E. A., Jr Glucocorticoid inhibition of initiation of transcription of the DNA encoding rRNA (rDNA) in lymphosarcoma P1798 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):718–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA: glucocorticoid effects upon initiation and elongation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3357–3369. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavannaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Inhibition of transcription during glucocorticoid-mediated inhibition of proliferation of lymphosarcoma P1798 cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9768–9773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras G., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Ehrenfeld E. HeLa cell nucleolar RNA synthesis after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. Inhibition of transcription factor activity by poliovirus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90397-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Wides R. J., Sollner-Webb B. Eucaryotic transcription complexes are specifically associated in large sedimentable structures: rapid isolation of polymerase I, II, and III transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1582–1590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradkin L. G., Yoshinaga S. K., Berk A. J., Dasgupta A. Inhibition of host cell RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription by poliovirus: inactivation of specific transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3880–3887. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal P. K., Cavanaugh A. H., Thompson E. A., Jr The effects of cycloheximide upon transcription of rRNA, 5 S RNA, and tRNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Skinner J. A. Efficient transcription of a protein-coding gene from the RNA polymerase I promoter in transfected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):722–726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Specific transcription of mouse ribosomal DNA in a cell-free system that mimics control in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PETERSON J. A. NUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DURING POLIOVIRUS INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:556–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Nagamine M., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Formation of the transcription initiation complex on mammalian rDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3418–3427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S., Dasgupta A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor inactivated in poliovirus-infected cells copurifies with transcription factor TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3175–3182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B., Chow N., Lively M., Powers J. Virus-specified protease in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2992–2995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Cordes S., Tjian R. Purification and characterization of a transcription factor that confers promoter specificity to human RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1358–1369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Learned T. K., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. T. Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Tjian R. In vitro transcription of human ribosomal RNA genes by RNA polymerase I. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Arnheim N. Species-specific rDNA transcription is due to promoter-specific binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):221–227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Matsui T., Muramatsu M. The mechanism of decrease in nucleolar RNA synthesis by protein synthesis inhibition. J Biochem. 1979 Mar;85(3):807–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Dasgupta A. Activation of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase in HeLa cells after poliovirus infection does not result in increased phosphorylation of eucaryotic initiation factor-2. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1781–1787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1781-1787.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C., Tjian R. Multiple control elements involved in the initiation of SV40 late transcription. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(5):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lawrence C., Thach R. E., Roeder R. G. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. II. Effect on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.611-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Culotta V. C., Sollner-Webb B. Factors and nucleotide sequences that direct ribosomal DNA transcription and their relationship to the stable transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3451–3462. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rDNA is regulated by an activated subform of RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):873–883. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN E. F., HEETER M., DARNELL J. E. RNA synthesis in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]