Abstract
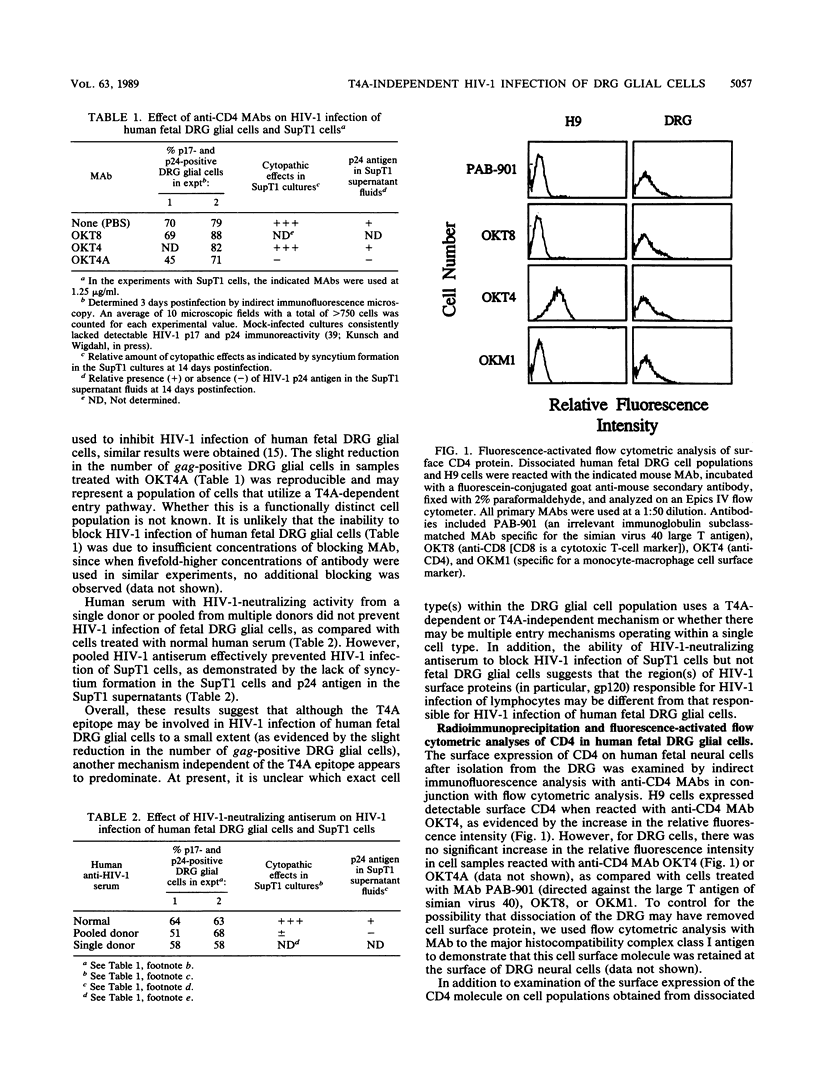
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) has been implicated in the generation of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated neurological dysfunction, and it is believed that the presence of CD4 in the nervous system may be involved in the susceptibility of selected neural cell populations to HIV-1 infection. We previously demonstrated (B. Wigdahl, R. A. Guyton, and P. S. Sarin, Virology 159:440-445, 1987) that glial cells derived from human fetal dorsal root ganglion (DRG) are susceptible to HIV-1 infection and subsequently express at least a fraction of the virus genome. In contrast to HIV-1 infection of CD4+ lymphocytes, which can be blocked by treatment with monoclonal antibodies directed against the HIV-1-binding region of CD4 (T4A epitope), treatment of human fetal DRG glial cells with similar antibodies resulted in only a slight reduction in HIV-1-specific gag antigen expression. In addition, preincubation of the HIV-1 inoculum prior to infection with HIV-1-neutralizing antiserum did not reduce HIV-1 gag antigen expression in these cells. Furthermore, we were unable to detect the synthesis or accumulation of the CD4 molecule in neural cell populations derived from DRG. However, a protected CD4-specific RNA fragment was detected in RNA isolated from human fetal DRG and spinal cord tissue by an RNase protection assay with a CD4-specific antisense RNA probe. RNA blot hybridization analysis of total cellular RNA isolated from human fetal DRG and spinal cord demonstrated specific hybridization to an RNA species that comigrated with the mature 3.0-kilobase CD4 mRNA as well as two unique CD4 RNA species with relative molecular sizes of approximately 5.3 and 6.7 kilobases. Furthermore, all three CD4-related RNA species were polyadenylated when isolated from human fetal spinal cord tissue. These data suggest that HIV-1 infection of human fetal DRG glial cells may proceed via a mechanism of viral entry independent of the T4A epitope of CD4.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asjö B., Ivhed I., Gidlund M., Fuerstenberg S., Fenyö E. M., Nilsson K., Wigzell H. Susceptibility to infection by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) correlates with T4 expression in a parental monocytoid cell line and its subclones. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew B. J., Rosenblum M., Price R. W. AIDS dementia complex and primary HIV brain infection. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Dec;20(2-3):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofinis G., Papadaki L., Sattentau Q., Ferns R. B., Tedder R. HIV replicates in cultured human brain cells. AIDS. 1987 Dec;1(4):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Dalgleish A. G., Exley M., Whitby D., Hogg N. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of monocytic and T-lymphocytic cells: receptor modulation and differentiation induced by phorbol ester. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):44–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Sakai K., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Susceptibility of human glial cells to infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Stevenson M., Volsky D. J. Expression of the T4 molecule (AIDS virus receptor) by human brain-derived cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81478-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. G., Flanigan T. P., Walsh F. S. Cell-surface antigens of human fetal brain and dorsal root ganglion cells in tissue culture. Adv Neurol. 1982;36:435–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funke I., Hahn A., Rieber E. P., Weiss E., Riethmüller G. The cellular receptor (CD4) of the human immunodeficiency virus is expressed on neurons and glial cells in human brain. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1230–1235. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Leonard J. M., Dutko F., Koenig S., Khillan J., Meltzer M. S. Immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection in the central nervous system. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S78–S81. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Laughlin M. A., Hoxie J. A., Wigdahl B., Gonzalez-Scarano F. CD4-independent infection of human neural cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2527-2533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. M., Farrar W. L., Pert C. B. Autoradiographic localization of T4 antigen, the HIV receptor, in human brain. Int J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;32(3-4):687–693. doi: 10.3109/00207458709043323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Pomerantz R. J., Kaplan J. C. Pathogenesis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):278–286. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Schooley R. T., Kaplan J. C., Allan J. D., Groopman J. E., Resnick L., Felsenstein D., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1493–1497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Clements G. B., Brown S. M. Differential susceptibility of human neural cell types in culture to infection with herpes simplex virus. Brain. 1983 Mar;106(Pt 1):101–119. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
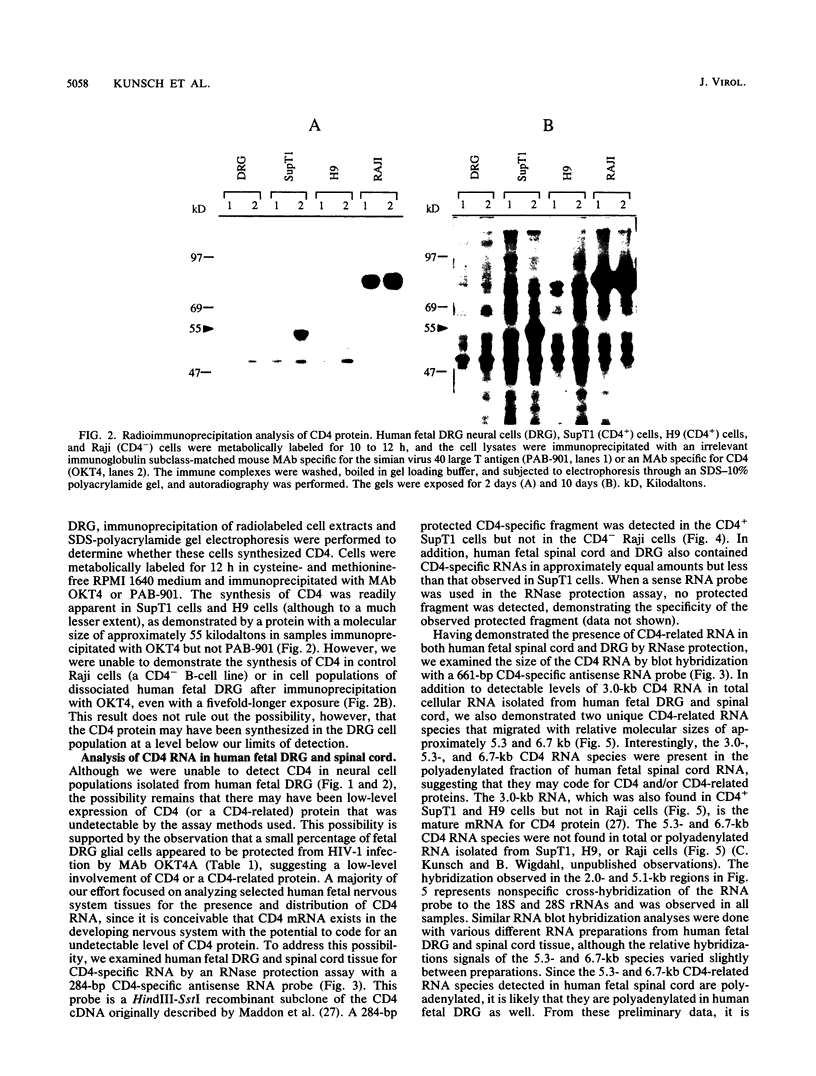
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., Hollander H., Mills J., Kaminsky L. Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Molineaux S. M., Maddon D. E., Zimmerman K. A., Godfrey M., Alt F. W., Chess L., Axel R. Structure and expression of the human and mouse T4 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9155–9159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Hunkapiller T. L3T4 and the immunoglobulin gene superfamily: new relationships between the immune system and the nervous system. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:109–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00529.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M. The AIDS dementia complex: some current questions. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S27–S33. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumarola-Sune T., Navia B. A., Cordon-Cardo C., Cho E. S., Price R. W. HIV antigen in the brains of patients with the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol. 1987 May;21(5):490–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L., diMarzo-Veronese F., Schüpbach J., Tourtellotte W. W., Ho D. D., Müller F., Shapshak P., Vogt M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D. Intra-blood-brain-barrier synthesis of HTLV-III-specific IgG in patients with neurologic symptoms associated with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1498–1504. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Dorsett D., York D., Bohan C., Anand R. Human immunodeficiency virus replication in human brain cells. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1988;99(1-2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01311031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Eskin T. A., Benn S., Angerer R. C., Angerer L. M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazeux R., Brousse N., Jarry A., Henin D., Marche C., Vedrenne C., Mikol J., Wolff M., Michon C., Rozenbaum W. AIDS subacute encephalitis. Identification of HIV-infected cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):403–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B. L., Ziegler R. J., Sneve M., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus latency and reactivation in isolated rat sensory neurons. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Guyton R. A., Sarin P. S. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of the developing human nervous system. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):440–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Kunsch C. Role of HIV in human nervous system dysfunction. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):369–374. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Smith C. A., Traglia H. M., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus latency in isolated human neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6217–6221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Smith D. H., Lasky L. A., Theodore T. S., Earl P. L., Moss B., Capon D. J., Martin M. A. In vitro mutagenesis identifies a region within the envelope gene of the human immunodeficiency virus that is critical for infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.139-147.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





