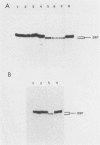
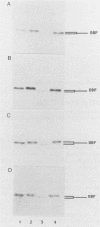
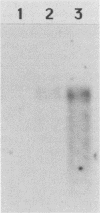
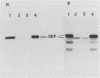
Abstract
The multifunctional adenovirus single-strand DNA-binding protein (DBP) is highly phosphorylated. Its phosphorylation sites are located in the amino-terminal domain of the protein, and its DNA- and RNA-binding activity resides in the carboxy-terminal half of the polypeptide. We have substituted cysteine or alanine for up to 10 of these potential phosphorylation sites by using oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Alteration of one or a few of these sites had little effect on the viability of virus containing the mutated DBP. However, when eight or more sites were altered, viral growth decreased significantly. This suggests that the overall phosphorylation state of the protein was more important than whether any particular site was modified. The reduction in growth correlated with both depressed DNA replication and expression of late genes. This reduction was probably the result of lower DBP accumulation in mutant-infected cells. Interestingly, although the stability of the mutated DBP was not affected, DBP synthesis and the level of its mRNA were depressed 5- to 10-fold for the underphosphorylated protein. These results suggest that DBP enhances its own expression and imply that phosphorylation of the DBP may be important for this function. Similarities to several eucaryotic transcriptional activators, which are composed of negatively charged activating domains and separate binding domains, are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Hardy M. M., Dunn J. J., Klessig D. F. Independent, spontaneous mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND3 that grow efficiently in monkey cells possess indentical mutations in the adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein gene. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):31–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.31-39.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Altered mRNA splicing in monkey cells abortively infected with human adenovirus may be responsible for inefficient synthesis of the virion fiber polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4023–4027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Posttranscriptional block to synthesis of a human adenovirus capsid protein in abortively infected monkey cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):31–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Synthesis of human adenovirus early RNA species is similar in productive and abortive infections of monkey and human cells. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):748–754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.748-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Klein H., Levine A. J., Horwitz M. S. A cleavage product of the adenovirus DNA binding protein is active in DNA replication in vitro. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod N. Phosphoproteins of adenovirus 2. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):366–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich A., Nevins J. R. The stability of early adenovirus mRNA is controlled by the viral 72 kd DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann E. A. DNA-binding properties of phosphorylated and dephosphorylated D2-T antigen, a simian-virus-40 T-antigen-related protein. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):495–501. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P., Lemay P., Blair G. E., Russell W. C. Characterization of adenovirus protein IX. J Gen Virol. 1979 Sep;44(3):783–800. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-3-783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brough D. E., Rice S. A., Sell S., Klessig D. F. Restricted changes in the adenovirus DNA-binding protein that lead to extended host range or temperature-sensitive phenotypes. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.206-212.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Blanton R. A. Possible role of the 72,000 dalton DNA-binding protein in regulation of adenovirus type 5 early gene expression. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):664–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.664-674.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Chinnadurai S., Brusca J. Physical mapping of a large-plaque mutation of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.623-628.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Chinnadurai S., Green M. Enhanced infectivity of adenovirus type 2 DNA and a DNA-protein complex. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):195–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.195-199.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleghon V. G., Klessig D. F. Association of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein with RNA both in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8947–8951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleghon V., Voelkerding K., Morin N., Delsert C., Klessig D. F. Isolation and characterization of a viable adenovirus mutant defective in nuclear transport of the DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2289–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2289-2299.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont D. J., Tremblay M. L., Branton P. E. Phosphorylation at serine 89 induces a shift in gel mobility but has little effect on the function of adenovirus type 5 E1A proteins. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):987–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.987-991.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friefeld B. R., Krevolin M. D., Horwitz M. S. Effects of the adenovirus H5ts125 and H5ts107 DNA binding proteins on DNA replication in vitro. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):380–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Mann K., Walter G. Removal of serine phosphates from simian virus 40 large T antigen increases its ability to stimulate DNA replication in vitro but has no effect on ATPase and DNA binding. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3373–3380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3373-3380.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa H., Kingston R. E., Sharp P. A. Inhibition of adenovirus early region IV transcription in vitro by a purified viral DNA binding protein. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):545–547. doi: 10.1038/302545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. S., Galos R., Williams J. Isolation of type 5 adenovirus mutants with a cold-sensitive host range phenotype: genetic evidence of an adenovirus transformation maintenance function. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):109–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Bellot F., Van Obberghen E., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Biological activities of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. M., Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Partial block to transcription of human adenovirus type 2 late genes in abortively infected monkey cells. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):378–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.378-385.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., FISCHER E. H. The phosphorylase b to a converting enzyme of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R. Sequence of the DNA-binding protein of a human subgroup E adenovirus (type 4): comparisons with subgroup A (type 12), subgroup B (type 7), and subgroup C (type 5). Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausing K., Scheidtmann K. H., Baumann E. A., Knippers R. Effects of in vitro dephosphorylation on DNA-binding and DNA helicase activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1258-1265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Structure-function relationships of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11051–11060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Anderson C. W. Block to multiplication of adenovirus serotype 2 in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1650–1668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1650-1668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Brough D. E., Cleghon V. Introduction, stable integration, and controlled expression of a chimeric adenovirus gene whose product is toxic to the recipient human cell. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1354–1362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T. Mutations that allow human Ad2 and Ad5 to express late genes in monkey cells map in the viral gene encoding the 72K DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Isolation of a variant of human adenovirus serotype 2 that multiplies efficiently on monkey cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1243–1246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1243-1246.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding adenovirus type 2 DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4493–4500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Levine A. J. The isolation and identification of the adenovirus group C tumor antigens. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Jörnvall H., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of the phosphorylated DNA-binding protein from adenovirus-type-2-infected cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Philipson L. Further characterization of the phosphate moiety of the adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):259–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade C. J., Tremblay M. L., Branton P. E. Mapping of a phosphorylation site in the 176R (19 kDa) early region 1B protein of human adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. C., Sarnow P., Girard M., Levine A. J. Host range temperature-conditional mutants in the adenovirus DNA binding protein are defective in the assembly of infectious virus. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):228–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90474-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Klessig D. F. Isolation and analysis of adenovirus type 5 mutants containing deletions in the gene encoding the DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):767–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.767-778.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Slavicek J. M., Schneider J. F., Jones N. C. Heterogeneity of adenovirus type 5 E1A proteins: multiple serine phosphorylations induce slow-migrating electrophoretic variants but do not affect E1A-induced transcriptional activation or transformation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1948–1955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1948-1955.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S. B., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of dephosphorylated A protein to SV40 DNA. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Chou W., Rodgers K. Phosphorylation downregulates the DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.888-894.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Gilead Z., Wold W. S., Green M. Immunofluorescence study of the adenovirus type 2 single-stranded DNA binding protein in infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):527–539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.527-539.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Ponticelli A., Berk A. J., Gaynor R. B. Genetic mapping of a major site of phosphorylation in adenovirus type 2 E1A proteins. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.14-22.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vliet P. C., Sussenbach J. S. An adenovirus type 5 gene function required for initiation of viral DNA replication. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkerding K., Klessig D. F. Identification of two nuclear subclasses of the adenovirus type 5-encoded DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):353–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.353-362.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., Brough D. E., Van der Lee F. M., Hoeben R. C., Verheijden G. F., Dooijes D., Klessig D. F., Sussenbach J. S. Characterization of adenovirus type 5 insertion and deletion mutants encoding altered DNA binding proteins. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):634–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos H. L., van der Lee F. M., Reemst A. M., van Loon A. E., Sussenbach J. S. The genes encoding the DNA binding protein and the 23K protease of adenovirus types 40 and 41. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Gay D. A., Pachter J. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated changes in stability of polyribosome-bound beta-tubulin mRNAs are specified by the first 13 translated nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1224–1235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amerongen H., van Grondelle R., van der Vliet P. C. Interaction between adenovirus DNA-binding protein and single-stranded polynucleotides studied by circular dichroism and ultraviolet absorption. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4646–4652. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]