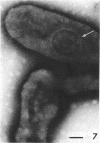
Abstract
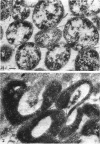
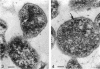
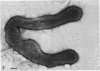
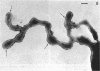
Four serologically distinct human T-mycoplasmas grown in liquid medium were studied in the electron microscope after ultrathin sectioning and negative staining. The morphology and ultrastructure of these strains was found to be essentially identical to that of other mycoplasmas; i.e., mainly spherical or ovoid cells were observed, but also short rod-shaped cells and filamentous, partly branched forms were noted. The cells were found to be enveloped by a triple-layered membrane, on the outer surface of which an electron-dense layer consisting of radiating hairlike structures was consistently present. In addition to ribosomes, now and then arranged in a regular geometric pattern, the ultrathin sections reveal vacuole-like structures in the interior of the cells.
Full text
PDF

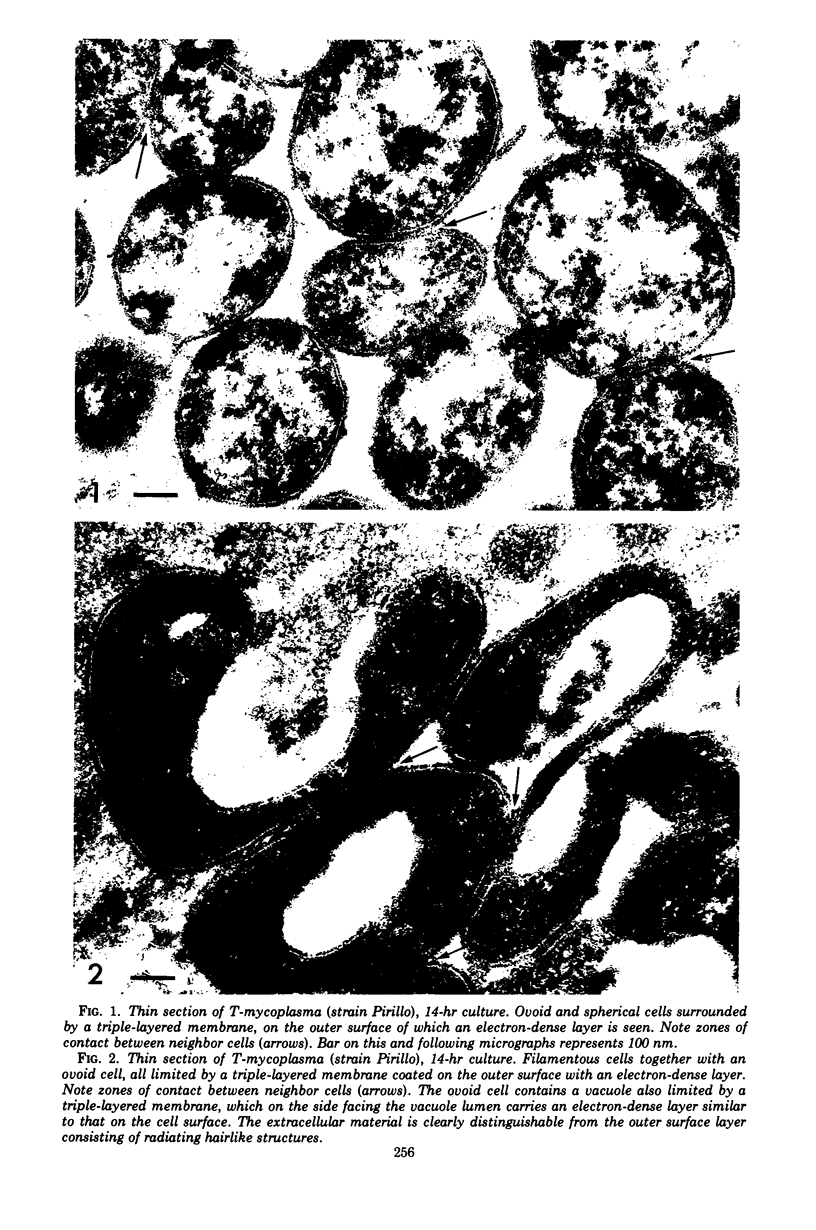
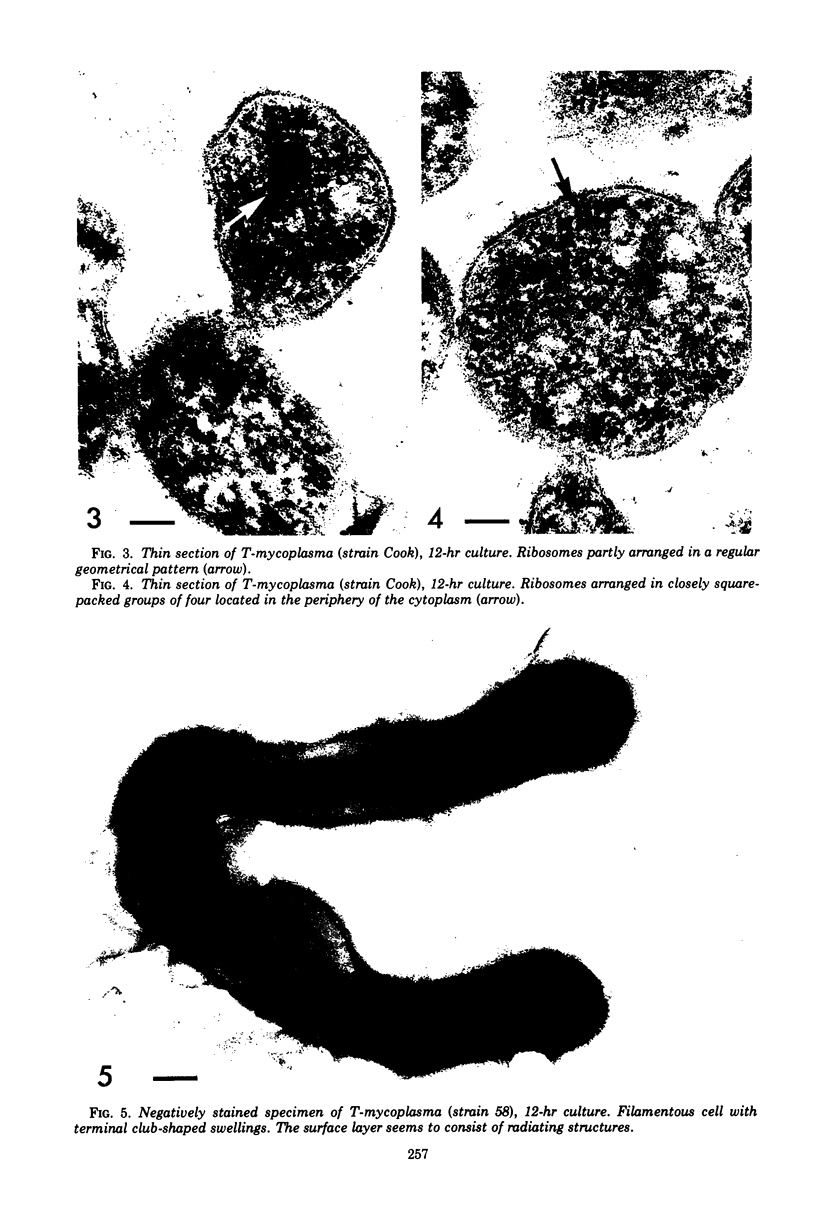


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. C., Stevens J. O., Florance E. R., Hampton R. O. Ultrastructure of Mycoplasma gallisepticum isolate 1056. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Nov;33(3):318–331. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Barile M. F. Ultrastructure of Mycoplasma hominis. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):180–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.180-192.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein-Ziv R. Cell division in Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Oct;15(10):1125–1128. doi: 10.1139/m69-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. P., Horne R. W. Electron microscopy of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma mycoides using the negative staining technique and their comparison with myxovirus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):190–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMERMUTH C. H., NIELSEN M. H., FREUNDT E. A., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF MYCOPLASMA SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:727–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.727-744.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASCA J. M., PARKS V. R. A ROUTINE TECHNIQUE FOR DOUBLE-STAINING ULTRATHIN SECTIONS USING URANYL AND LEAD SALTS. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:157–161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., TOMASSINI N., HAYFLICK L. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF A MYCOPLASMA (NEGRONI) ISOLATED FROM HUMAN LEUKEMIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:517–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.517-523.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANILOFF J., MOROWITZ H. J., BARRNETT R. J. STUDIES OF THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND RIBOSOMAL ARRANGEMENTS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM A5969. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:139–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Morowitz H. J., Barrnett R. J. Ultrastructure and Ribosomes of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):193–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.193-204.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. B., Lyons M. J. Phase-contrast and electron microscopy of murine strains of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1750–1763. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1750-1763.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E. L'inclusion au polyester pour l'ultramicrotomie. J Ultrastruct Res. 1958 Dec;2(2):200–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(58)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Pfendt E. A., Hayflick L. Sterol requirements of T-strain mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):323–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.323-330.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard M. C. Cultivation and properties of T-strains of mycoplasma associated with nongonococcal urethritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Williams M. H., Haig D. A. The isolation and comparative biological and physical characteristics of T-mycoplasmas of cattle. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):33–46. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. H. Electron microscopy of T-strains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):397–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]