Abstract
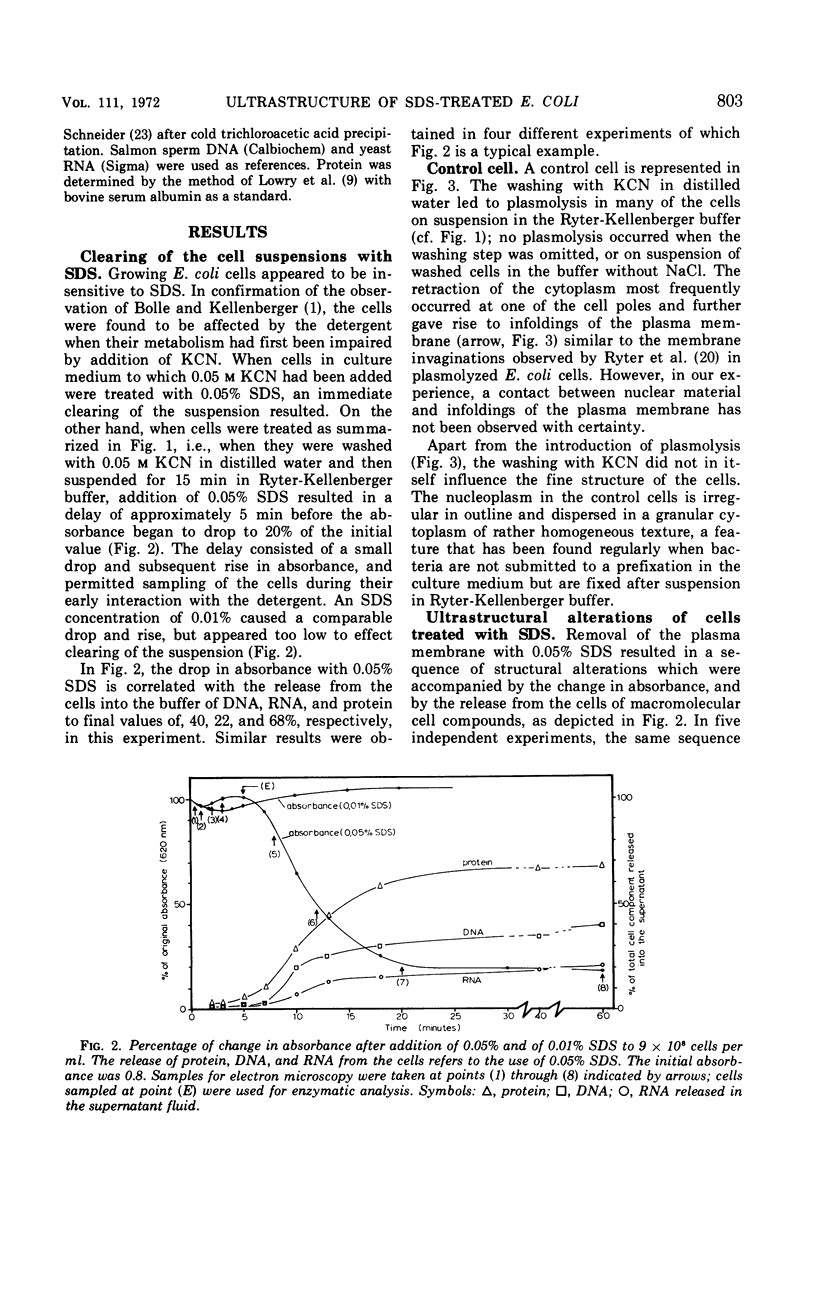
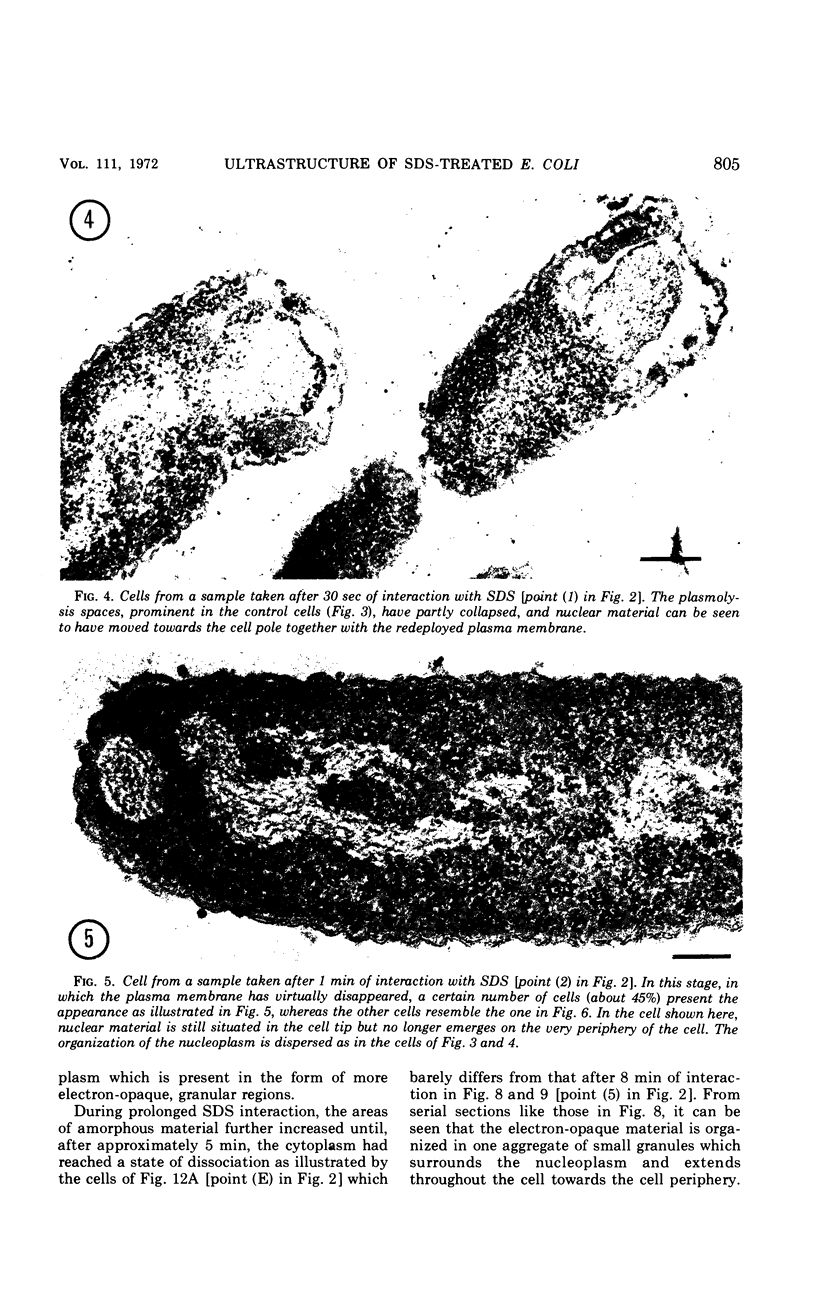
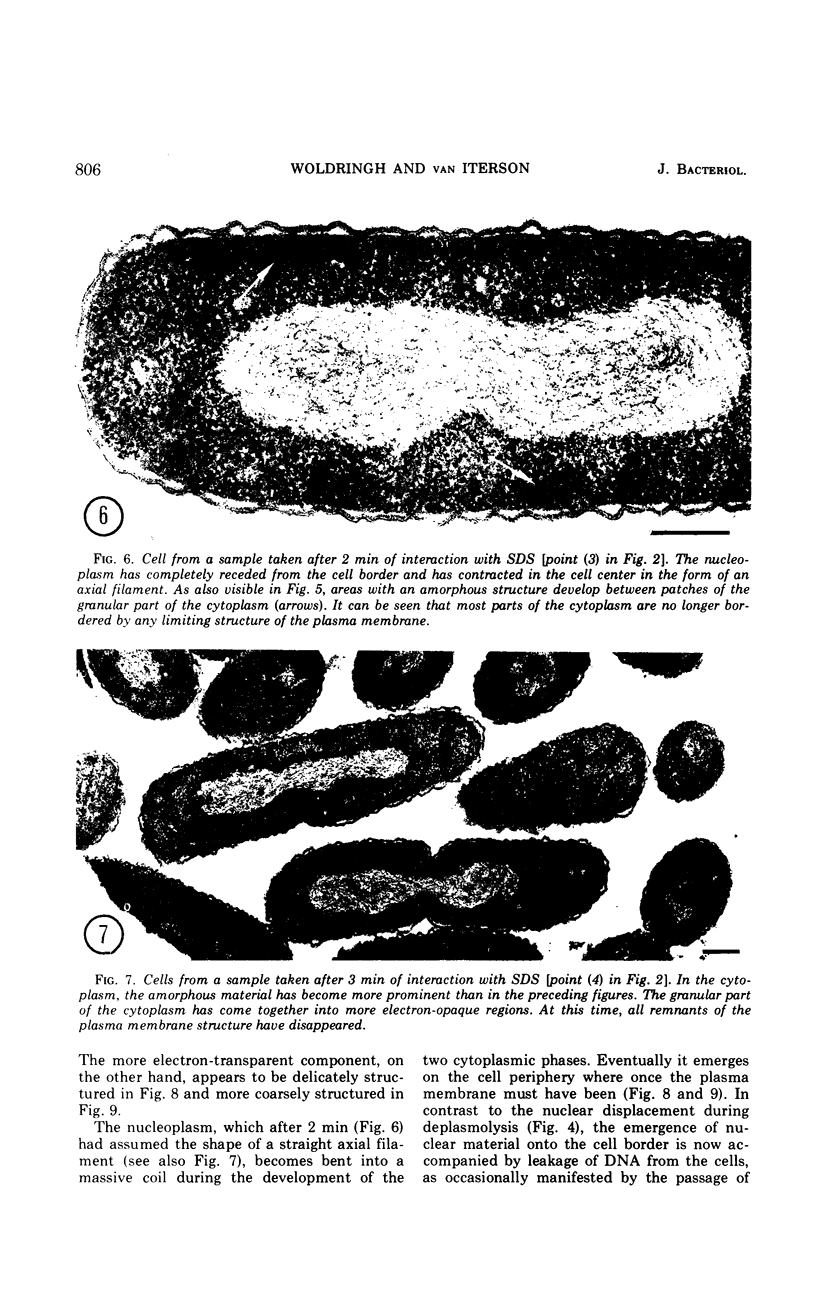
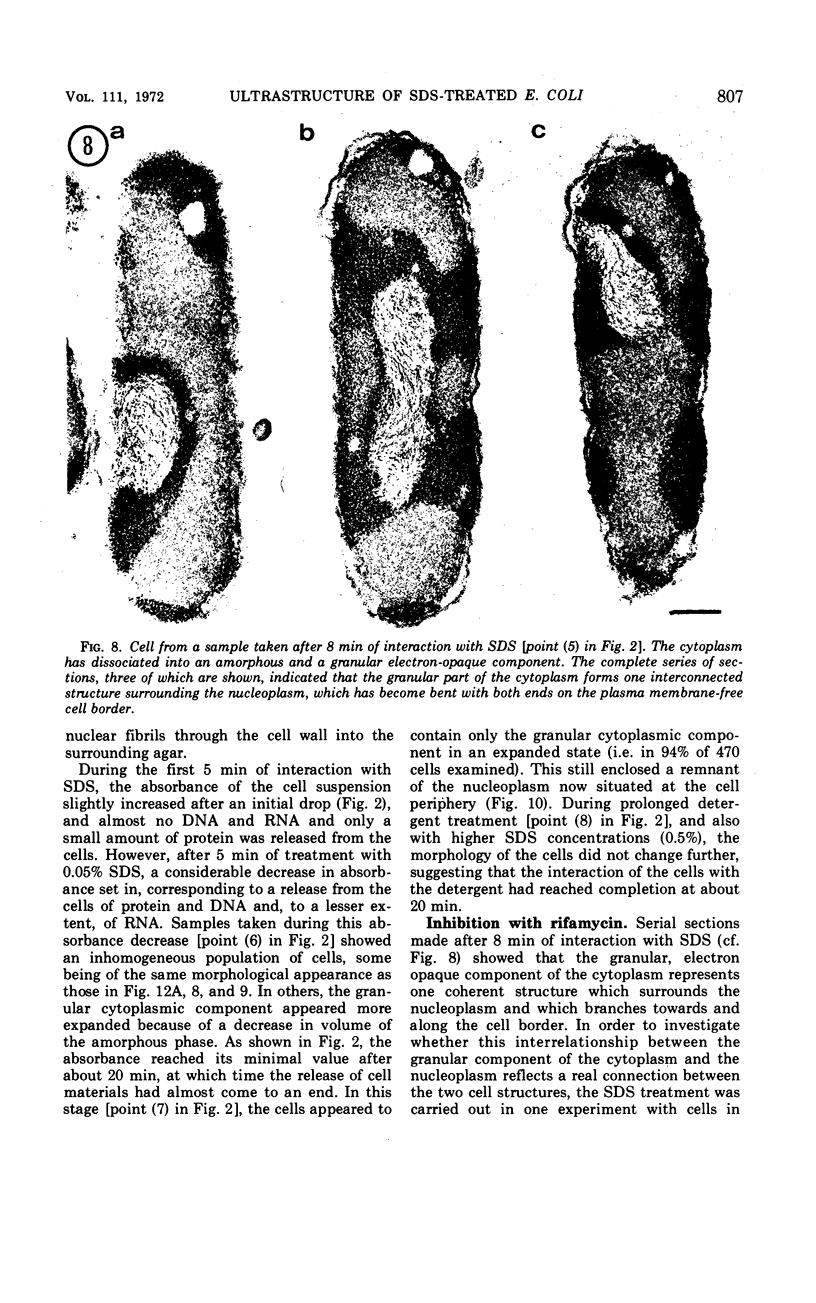
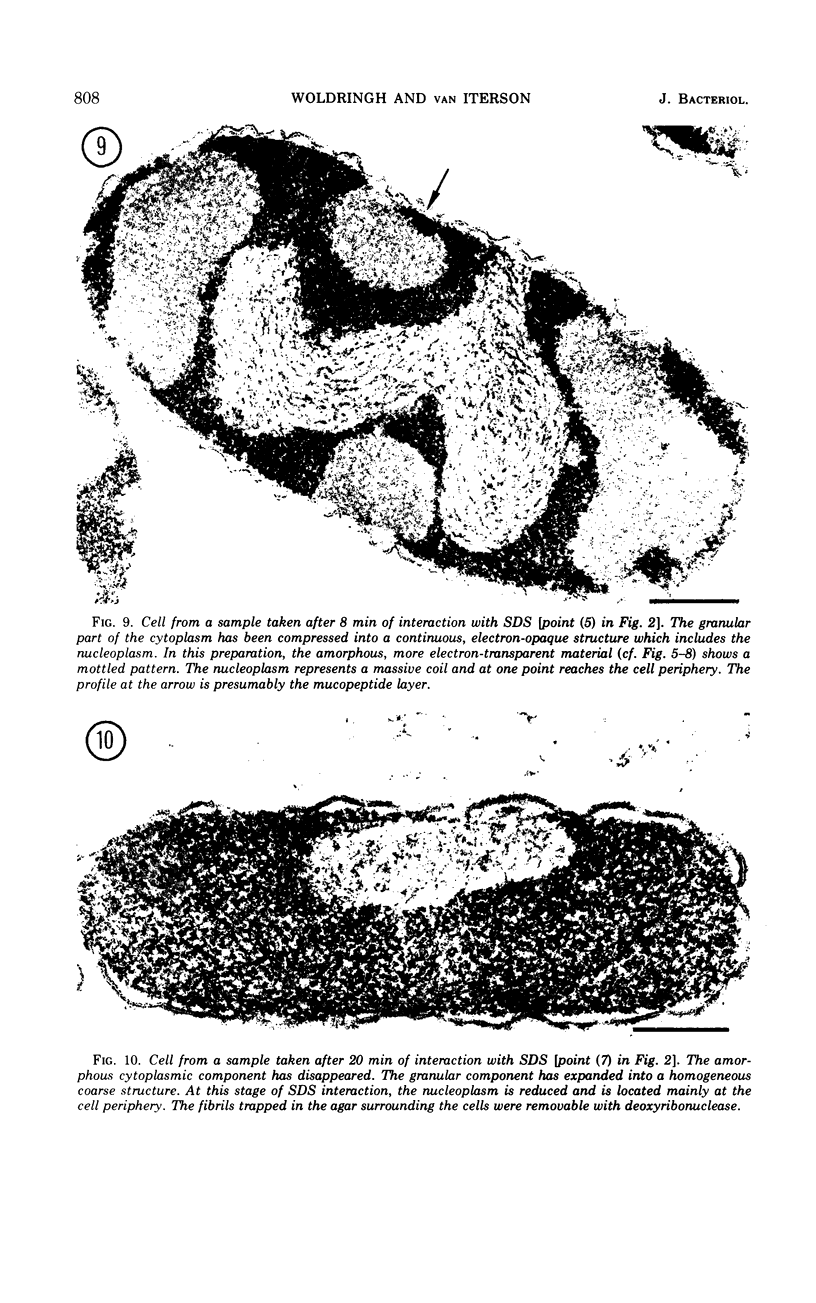
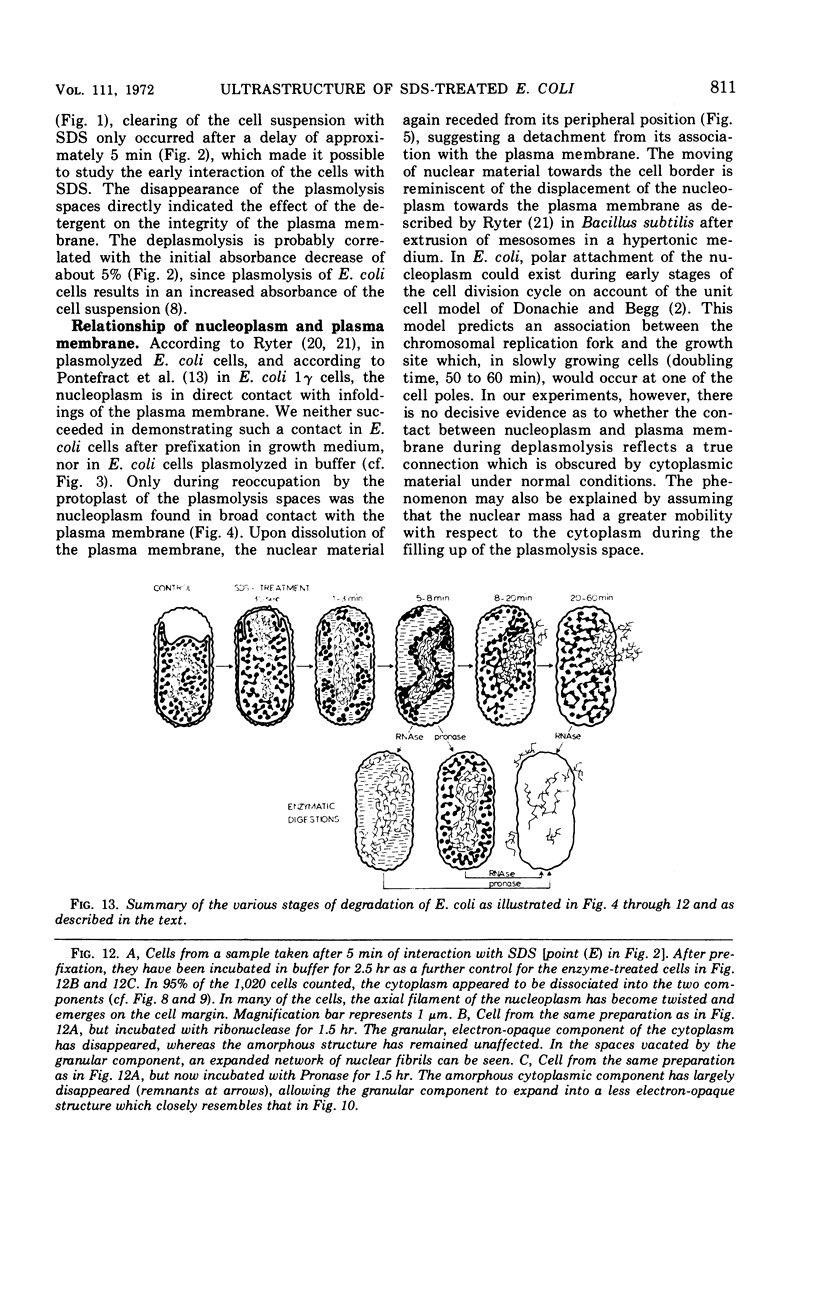
An electron microscopy study has been made of the effects of dissolution of the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on the organization of the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. The alterations observed in time course experiments were related to absorbance changes and to release of macromolecules from the cells. As the cells became plasmolyzed, under the conditions used, the first visible effect of SDS was a collapse of the plasmolysis spaces. This was accompanied by a displacement of the nuclear material which then appeared in broad contact with the redeployed plasma membrane. This initial displacement of nuclear material to the cell border may indicate an association between the nucleoplasm and the plasma membrane. Upon further dissolution of the plasma membrane, the nuclear material receded from the cell margin and contracted into an axial filament. Meanwhile, the cytoplasm dissociated into an amorphous, Pronase-sensitive component and an electron-opaque, granular one sensitive to ribonuclease. The latter represented one continuous area of ribosomal structures surrounding the nucleoplasm, an organization which did not occur when the cells were inhibited with rifamycin before SDS treatment. During prolonged SDS interaction, approximately 65% of the cellular protein, 25% of the ribonucleic acid and 40% of the deoxyribonucleic acid were released from the cells concomitant with the disappearance of the amorphous cytoplasmic part, expansion of the ribosomal aggregate, and rearrangement of the nuclear material at the cell periphery. The observations support the contention that all ribosomal structures bear a direct relationship with the nucleoplasm.
Full text
PDF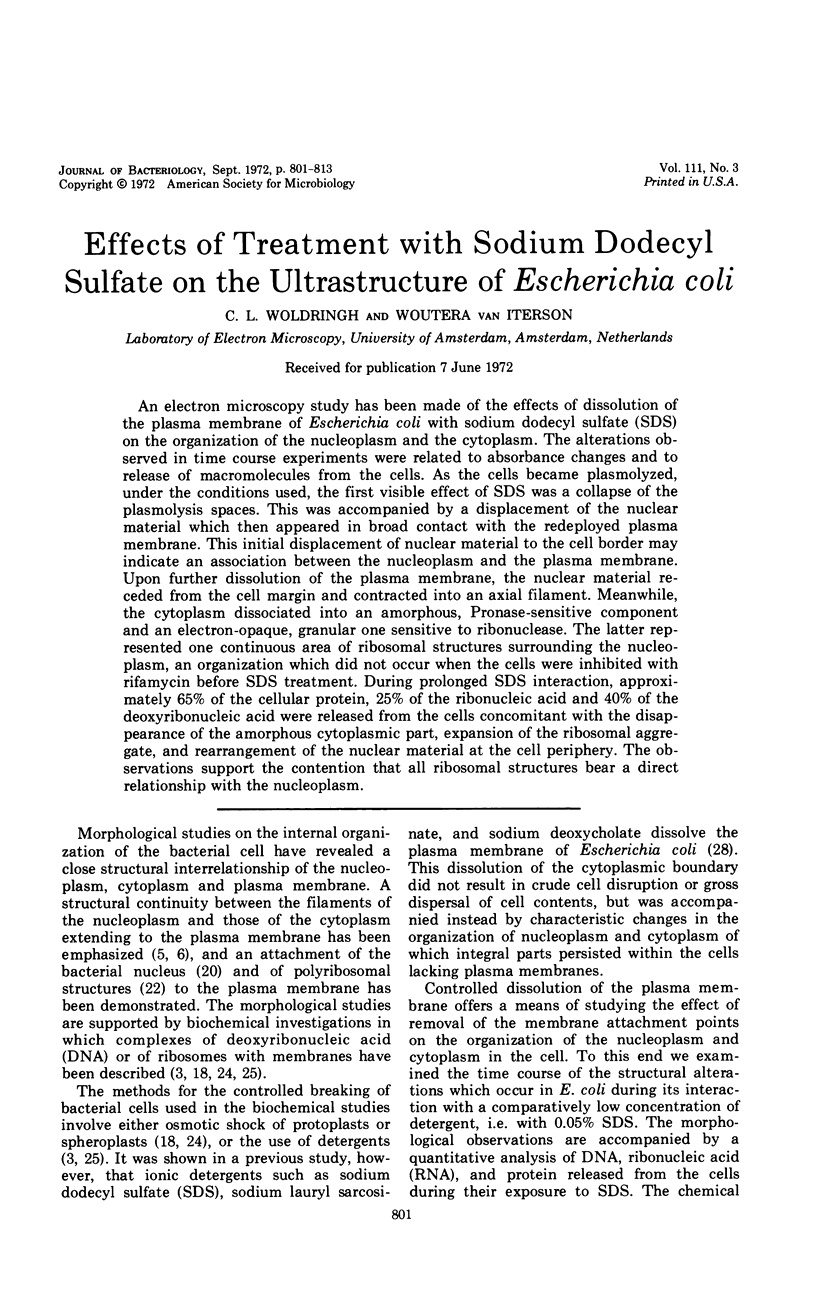






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLLE A., KELLENBERGER E. Etude de l'action du laurylsulfate de sodium sur E. coli. Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol. 1958;21(3):714–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D., Begg K. J. Growth of the bacterial cell. Nature. 1970 Sep 19;227(5264):1220–1224. doi: 10.1038/2271220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning U., Dennert G., Rehn K., Deppe G. Effects of oleate starvation in a fatty acid auxotroph of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):784–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.784-796.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles C. J. Salt induces changes of turbidity and volume of E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 3;229(5):154–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio229154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses R. E., Richardson C. C. Replication and repair of DNA in cells of Escherichia coli treated with toluene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):674–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontefract R. D., Bergeron G., Thatcher F. S. Mesosomes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.367-375.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P., Speyer J. Rifampicin inhibition of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in normal and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):376–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.376-389.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière J., Lederberg S., Granboulan P., Gros F. Structural sites of RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 28;46(3):413–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Jacob F. Etude morphologique de la liaison du noyau à la membrane chez E. coli et chez les protoplastes de B. subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jun;110(6):801–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESSINGER D., MARCHESTI V. T., KWAN B. C. BINDING OF RIBOSOMES TO CYTOPLASMIC RETICULUM OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:456–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.456-466.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Hanawalt P. C. Properties of the growing point region in the bacterial chromosome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 19;149(2):519–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay G. Y., Daniels M. J., Schaechter M. Isolation of a cell membrane-DNA-nascent RNA complex from bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD J. F., MURRAY R. G. The effects of the ionic environment on the chromatin structures of bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):245–260. doi: 10.1139/m56-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. Actions of the rifamycins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):290–309. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.290-309.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldringh C. L. Lysis of the cell membrane of Escherichia coli K12 by ionic detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):288–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90650-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iterson W. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. II. Bacterial cytoplasm. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):299–325. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.299-325.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iterson W. The fine structure of the ribonucleoprotein in bacterial cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1966 Mar;28(3):563–570. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]












