Abstract
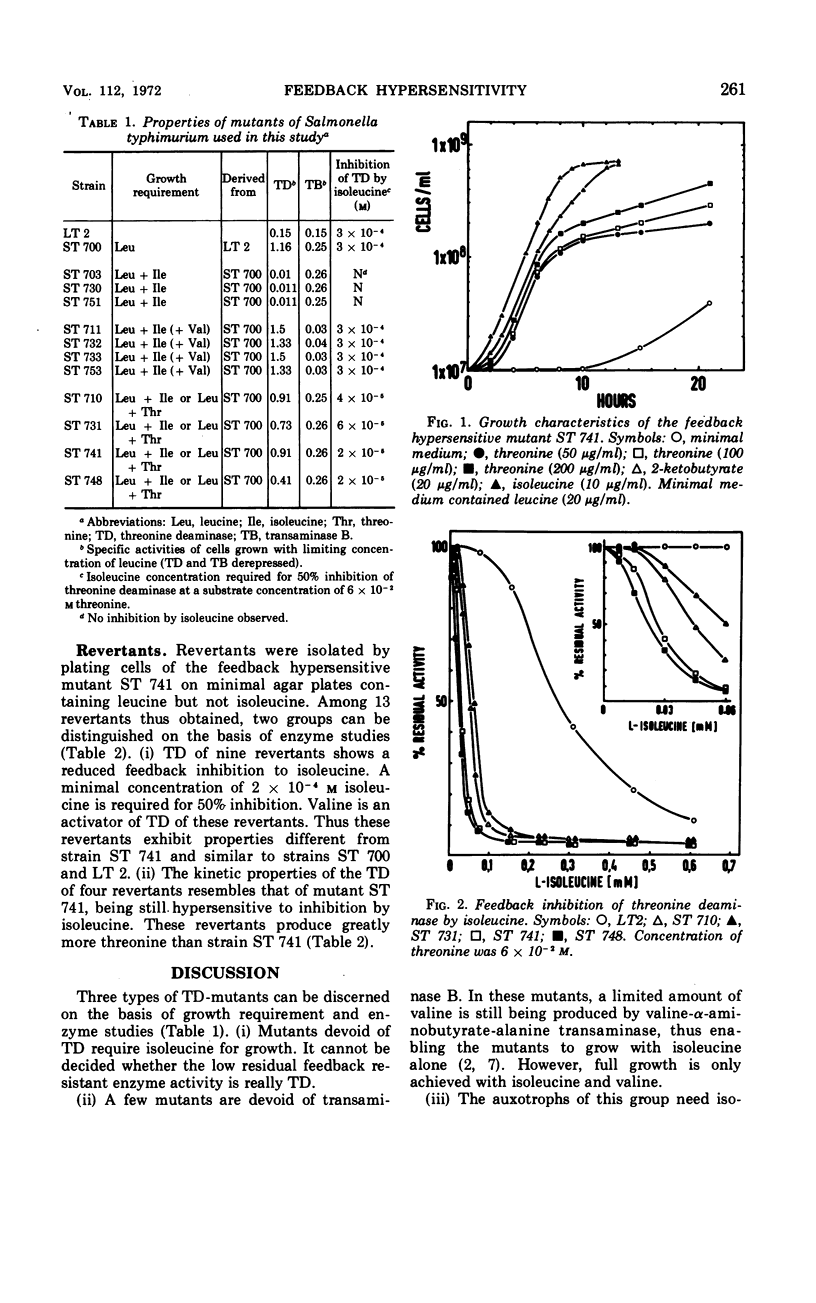
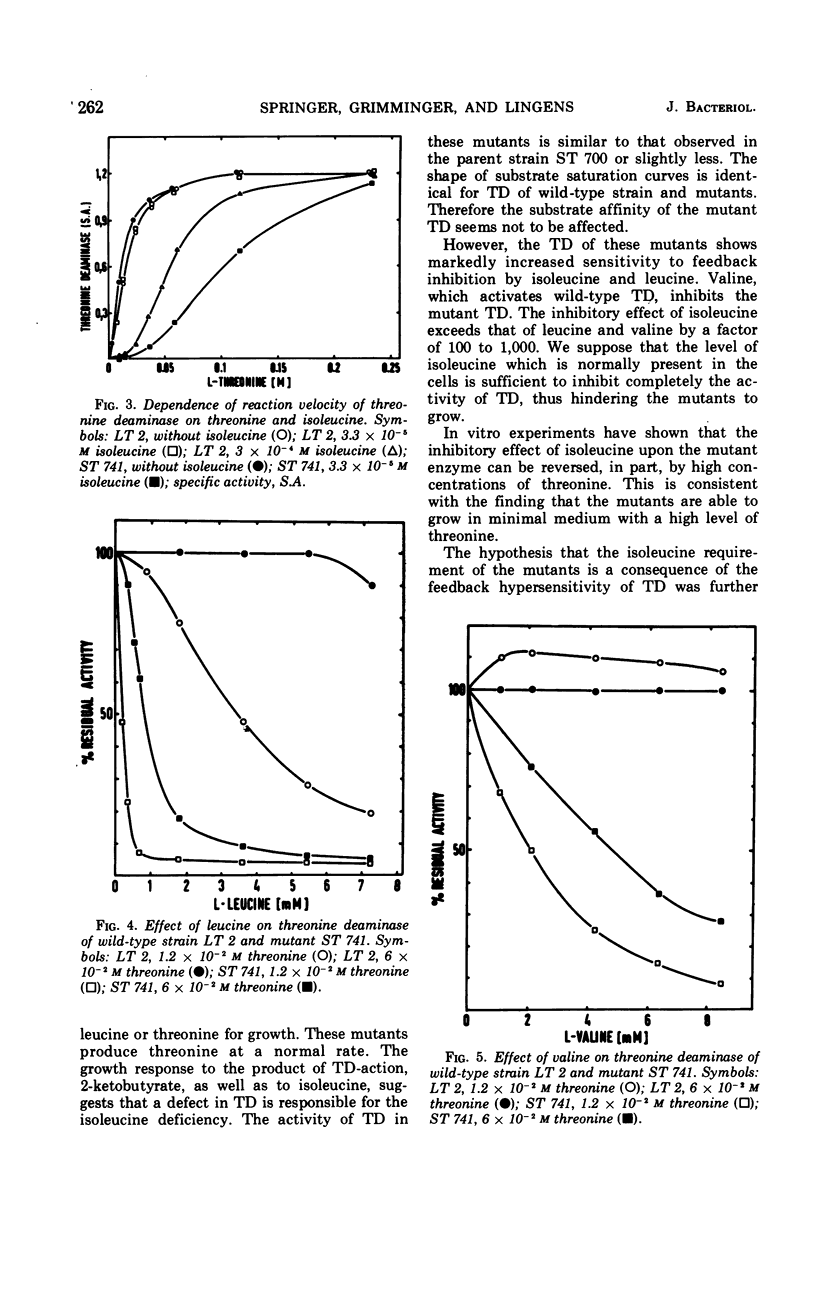
Isoleucine-deficient mutants of Salmonella typhimurium were isolated. Three groups of mutants can be discerned by their nutritional requirements and enzyme patterns. (i) Mutants which grow with isoleucine alone are devoid of biosynthetic threonine deaminase (TD). (ii) Mutants growing with isoleucine and valine are devoid of transaminase B. (iii) Mutants growing with either isoleucine or threonine have normal levels of TD. However, the sensitivity of this enzyme to feedback inhibition by isoleucine is greatly enhanced. The inhibitory effect of isoleucine can be counterbalanced by high concentrations of threonine. These results indicate that the production of isoleucine in the mutants is restricted to a low level not sufficient to support the growth of the cells. This hypothesis is confirmed by studies with revertants of an isoleucine-threonine mutant. In nine revertants, wild-type properties of TD have been restored. In four revertants, the hypersensitivity of TD is unchanged, but the strains produce a greatly enhanced quantity of threonine, which is excreted into the culture medium. It follows, that hypersensitivity of TD to inhibition by isoleucine is the cause of the nutritional requirement of isoleucine-threonine mutants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELBERG E. A., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. V. alpha-Ketoisovaleric acid accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. O., Zarlengo M. H. Threonine deaminase from Salmonella typhimurium. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer S. B., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XVI. Pattern of multivalent repression in strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1680–1684. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1680-1684.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimminger H., Lingens F. Alternate requirement for pyridoxine or isoleucine in mutants of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1969 Nov 12;5(3):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirard B. M., Ames B. N., Snell E. E. Salmonella typhimurium mutants with alternate requirements for vitamin B 6 or isoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):359–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.359-363.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDMAN D., MEISTER A. Transamination in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):591–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XIV. Effect of thiaisoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1666-1671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E., BROWN B. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. VII. A negative feedback mechanism controlling isoleucine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMBARGER H. E. Evidence for a negative-feedback mechanism in the biosynthesis of isoleucine. Science. 1956 May 11;123(3202):848–848. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3202.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Regulation of amino acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:323–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


