Abstract
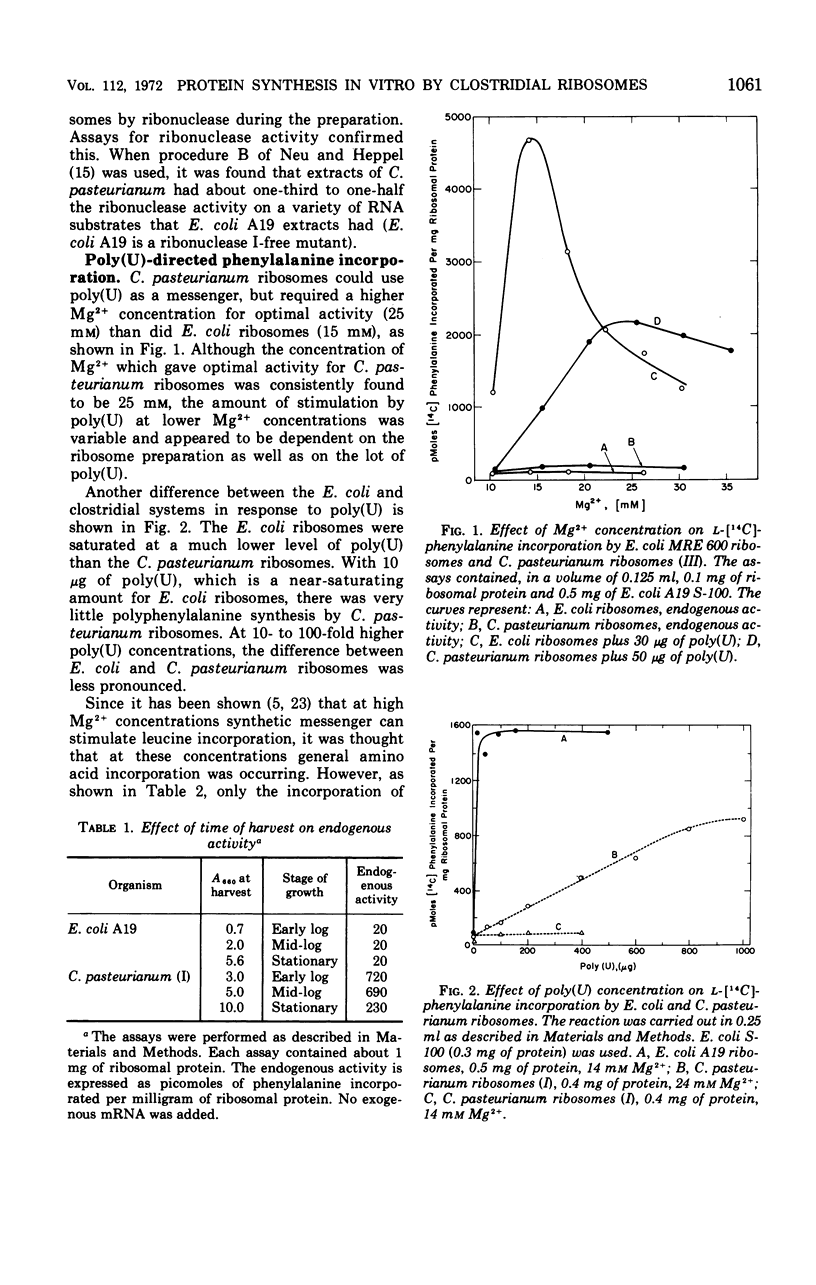
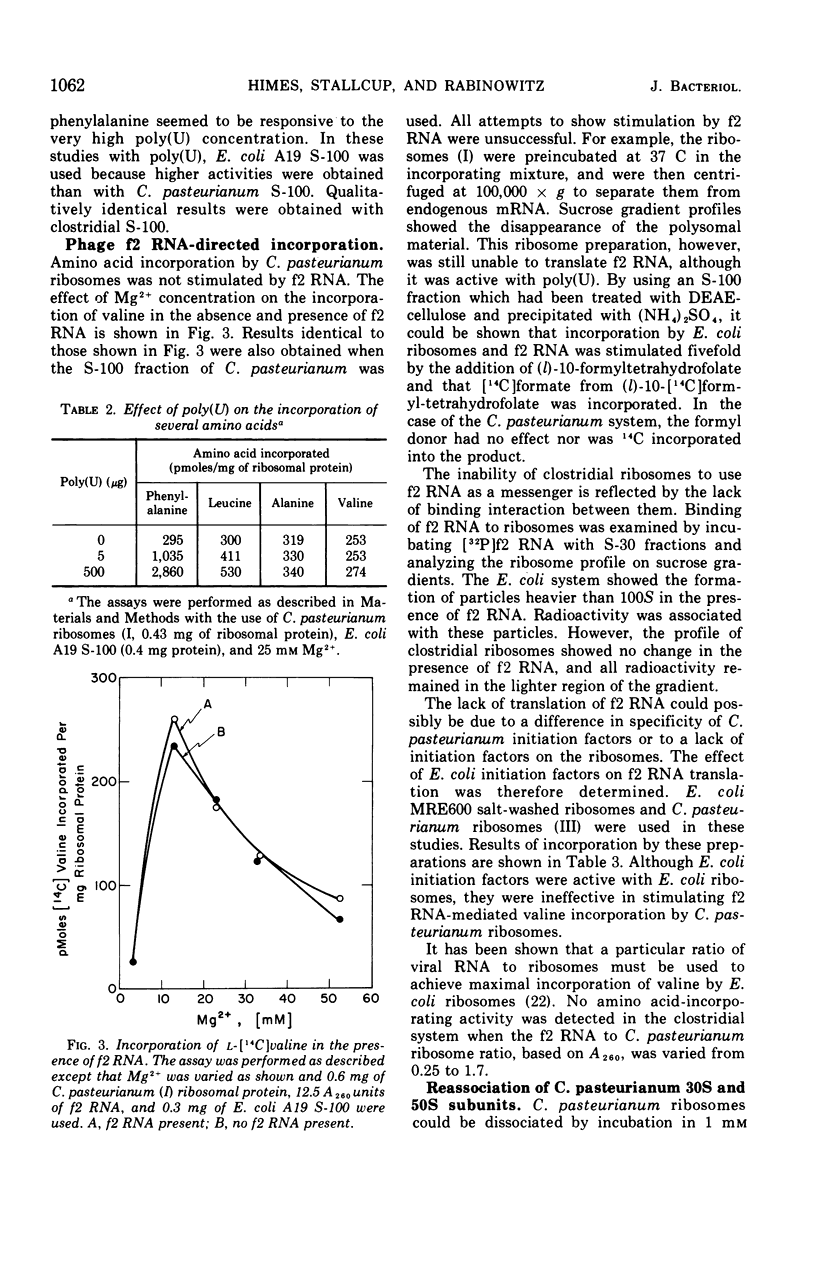
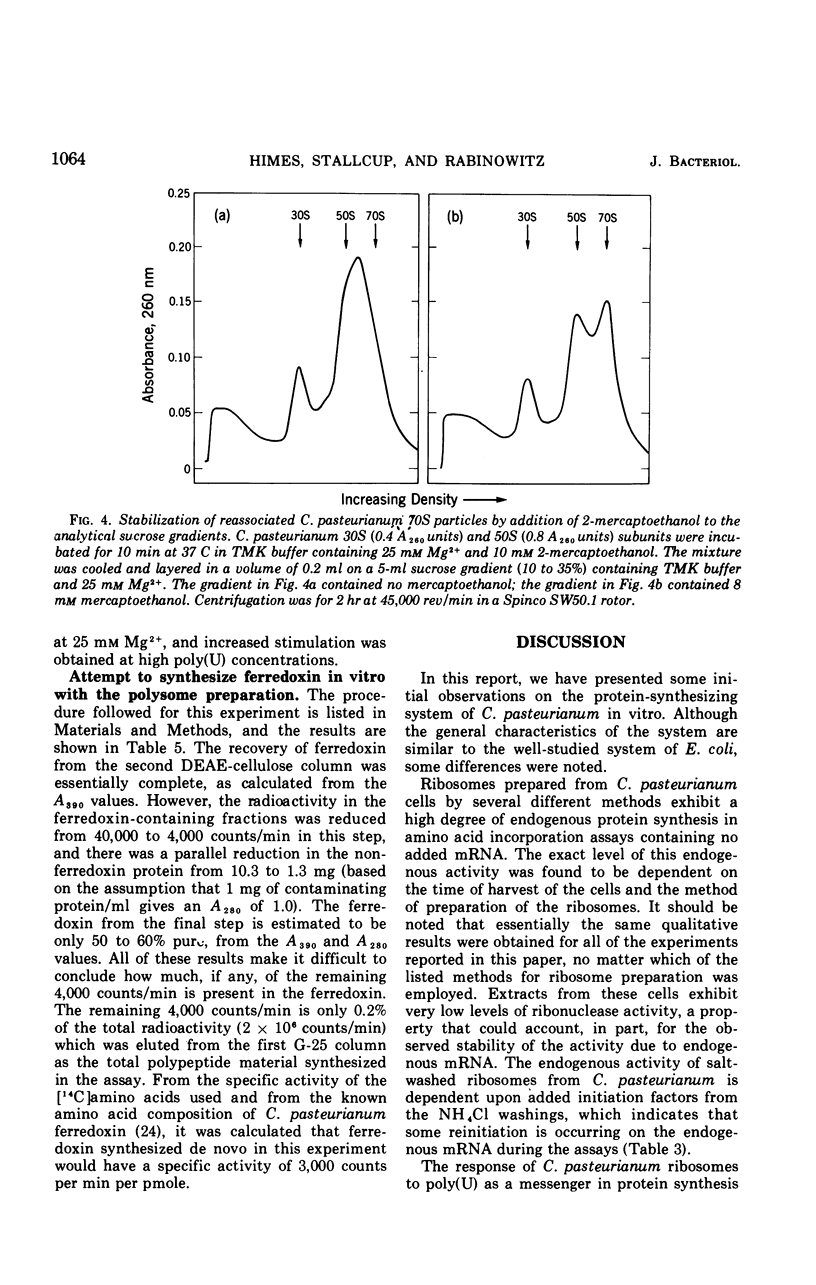
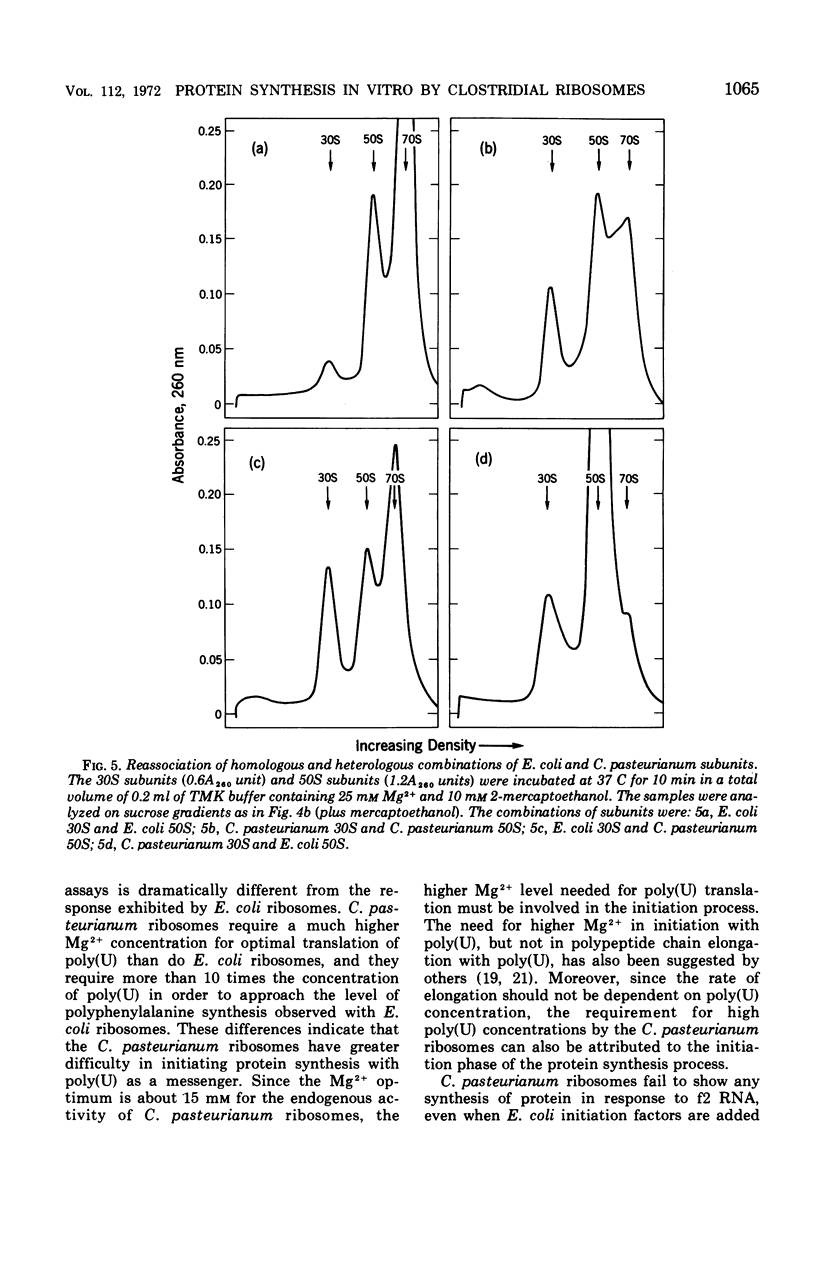
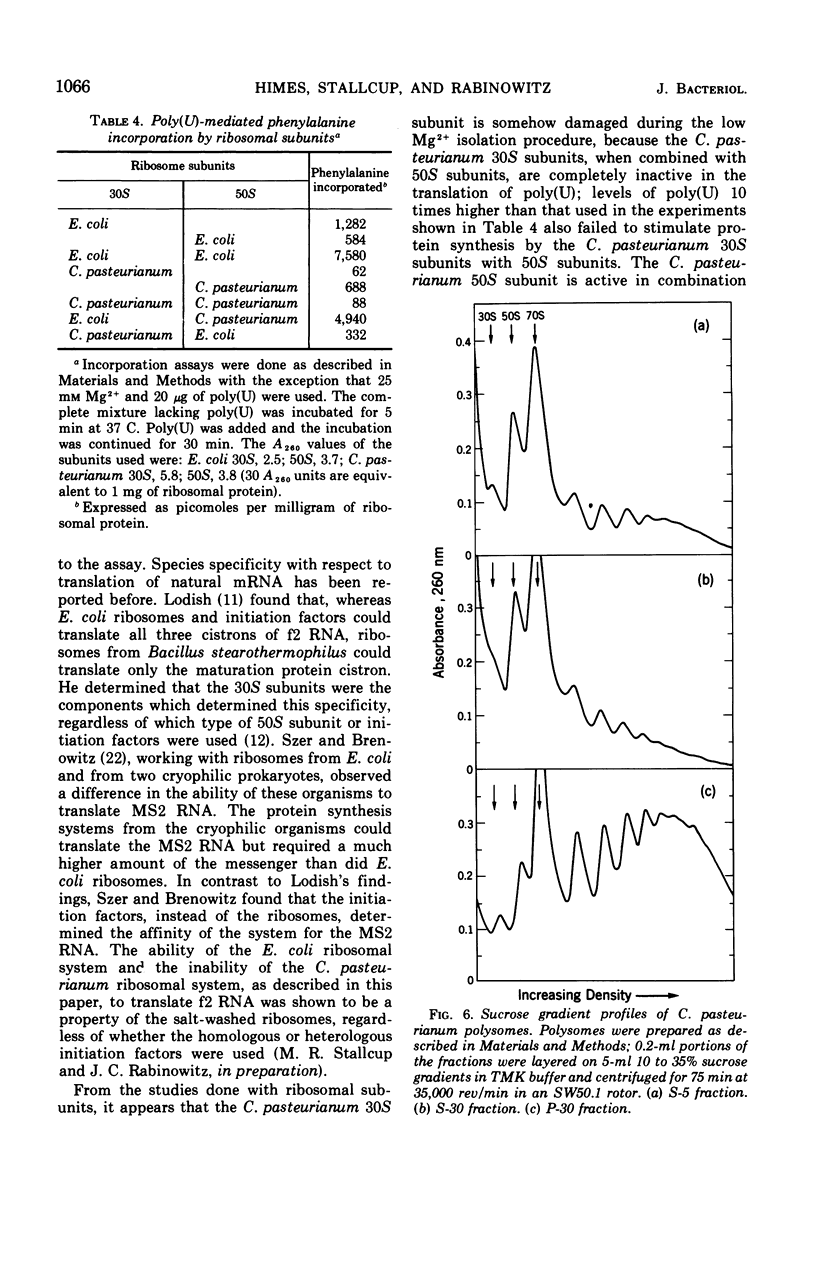
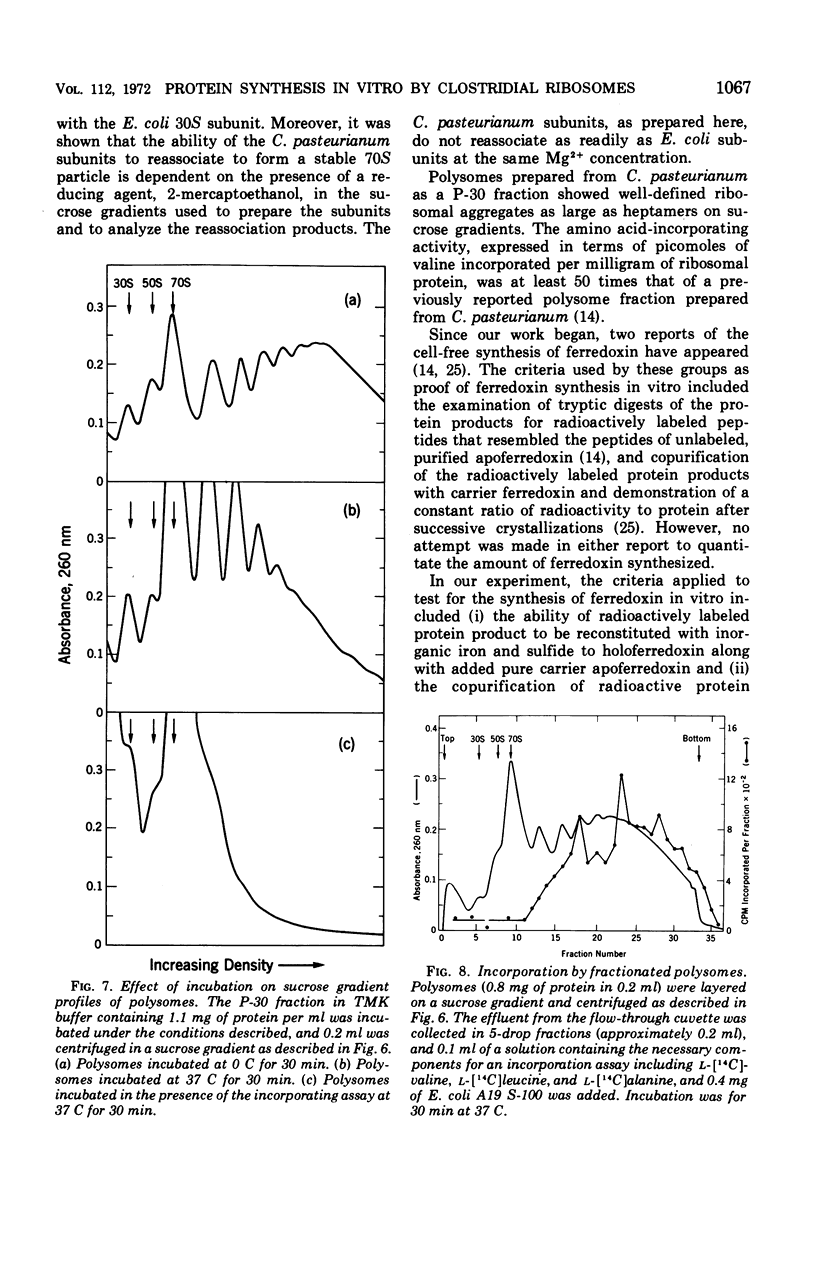
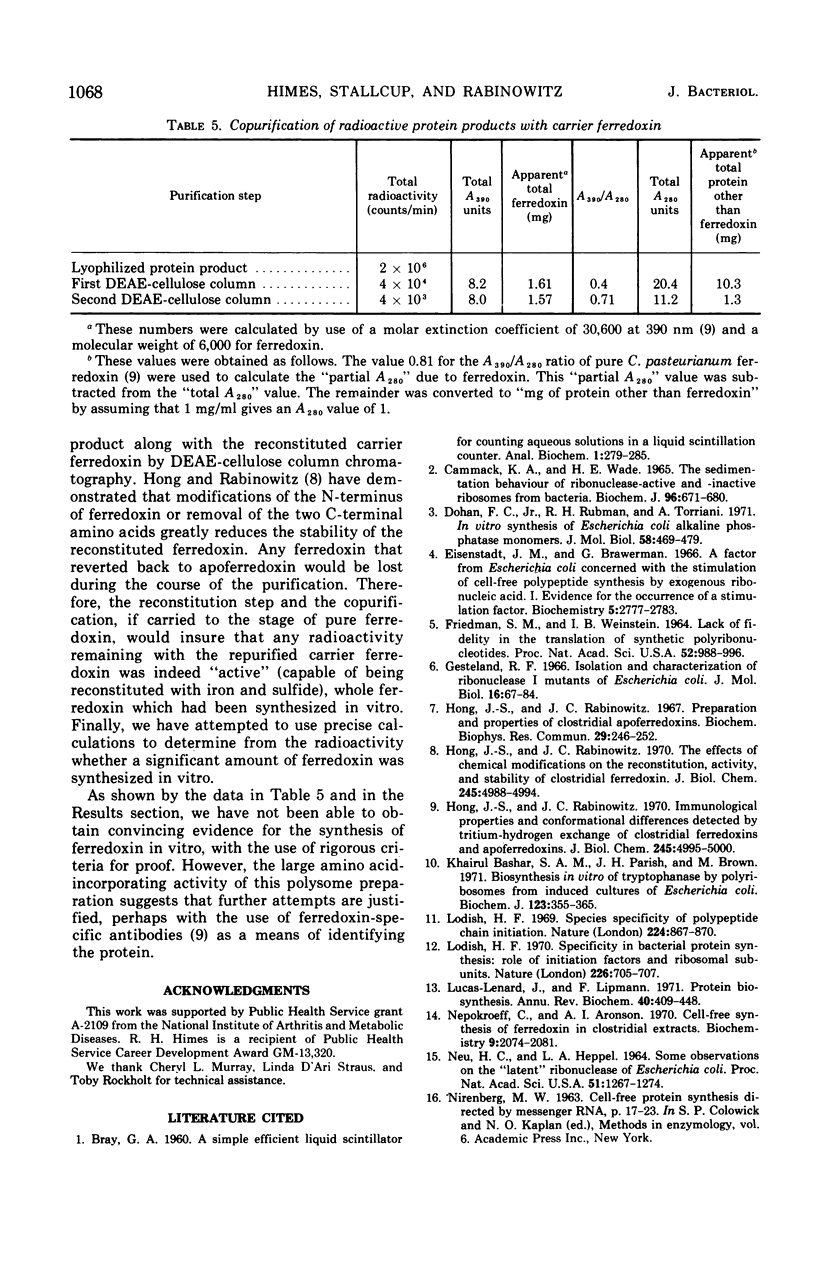
Ribosomes and polyribosomes from Clostridium pasteurianum were isolated and their activities were compared with those of ribosomes from Escherichia coli in protein synthesis in vitro. C. pasteurianum ribosomes exhibited a high level of activity due to endogenous messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA). For translation of polyuridylic acid [poly(U)], C. pasteurianum ribosomes required a higher concentration of Mg2+ and a much higher level of poly(U) than did E. coli ribosomes. Phage f2 RNA added to the system with C. pasteurianum ribosomes gave no significant stimulation of protein synthesis in a homologous system or with E. coli initiation factors. The 30S and 50S subunits prepared from C. pasteurianum ribosomes reassociated less readily than subunits from E. coli. The ability of the C. pasteurianum subunits to reassociated was found to be dependent upon the presence of a reducing agent during preparation and during analysis of the reassociation products. In heterologous combinations, E. coli 30S subunits associated readily with C. pasteurianum 50S subunits to form 70S particles, but C. pasteurianum 30S subunits and E. coli 50S subunits did not associate. In poly(U) translation, E. coli 30S subunits were active in combination with 50S subunits from either E. coli or C. pasteurianum, but C. pasteurianum 30S subunits were not active in combination with either type of 50S subunits. Polyribosomes prepared from C. pasteurianum were very active in protein synthesis, and well-defined ribosomal aggregates as large as heptamers could be seen on sucrose gradients. An attempt was made to demonstrate synthesis in vitro of ferredoxin.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashar S. A., Parish J. H., Brown M. Biosynthesis in vitro of tryptophanase by polyribosomes from induced cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):355–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1230355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohan F. C., Jr, Rubman R. H., Torriani A. In vitro synthesis of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase monomers. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt J. M., Brawerman G. A factor from Escherichia coli concerned with the stimulation of cell-free polypeptide synthesis by exogenous ribonucleic acid. I. Evidence for the occurrence of a stimulation factor. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2777–2783. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S. M., WEINSTEIN I. B. LACK OF FIDELITY IN THE TRANSLATION OF SYNTHETIC POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:988–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Rabinowitz J. C. Immunological properties and conformational differences detected by tritium-hydrogen exchange of clostridial ferredoxins and apoferredoxins. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4995–5000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Rabinowitz J. C. The effects of chemical modifications on the reconstitution, activity, and stability of clostridial ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4988–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J., Rabinowitz J. C. Preparation and properties of clostridial apoferredoxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Oct 26;29(2):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90595-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Species specificity of polypeptide chain initiation. Nature. 1969 Nov 29;224(5222):867–870. doi: 10.1038/224867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Specificity in bacterial protein synthesis: role of initiation factors and ribosomal subunits. Nature. 1970 May 23;226(5247):705–707. doi: 10.1038/226705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEU H. C., HEPPEL L. A. SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE "LATENT" RIBONUCLEASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1267–1274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepokroeff C., Aronson A. I. Cell-free synthesis of ferredoxin in clostridial extracts. Biochemistry. 1970 May 12;9(10):2074–2081. doi: 10.1021/bi00812a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL M., HIATT H. H. MAGNESIUM REQUIREMENT FOR THE FORMATION OF AN ACTIVE MESSENGER RNA-RIBOSOME-S-RNA COMPLEX. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:467–475. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz J. Preparation and properties of clostridial ferredoxins. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:431–446. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARIN P. S., ZAMECNIK P. C. ON THE STABILITY OF AMINOACYL-S-RNA TO NUCLEOPHILIC CATALYSIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:653–655. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZER W., OCHOA S. COMPLEXING ABILITY AND CODING PROPERTIES OF SYNTHETIC POLYNUCLEOTIDES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jun;8:823–834. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Noll H. Conformational changes in ribosomes during protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Brenowitz J. Translation of MS2 RNA by ribosomes from different bacterial species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1154–1160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Nakashima T., Benson A., Mower H., Tasunobu K. T. The amino acid sequence of Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1666–1681. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trakatellis A. C., Schwartz G. The biosynthesis of ferredoxin in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):436–441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


