Abstract
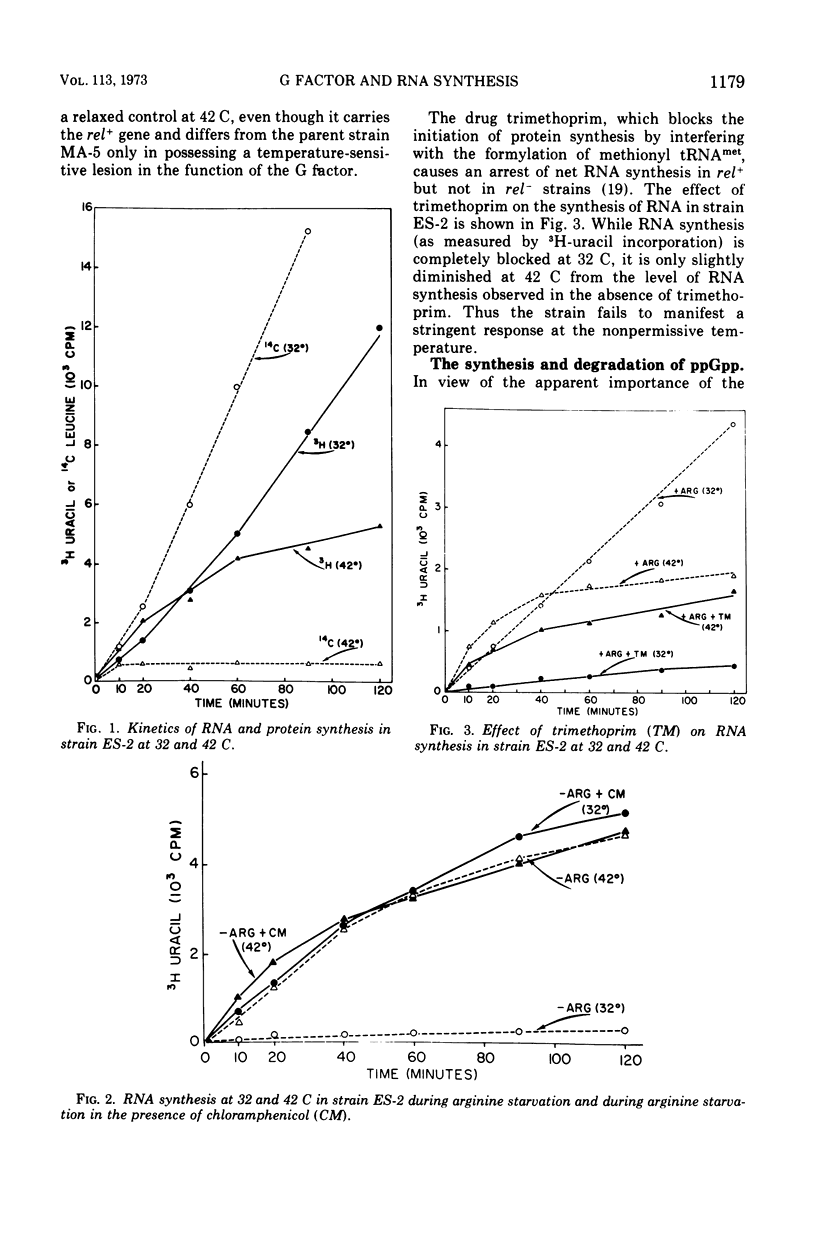
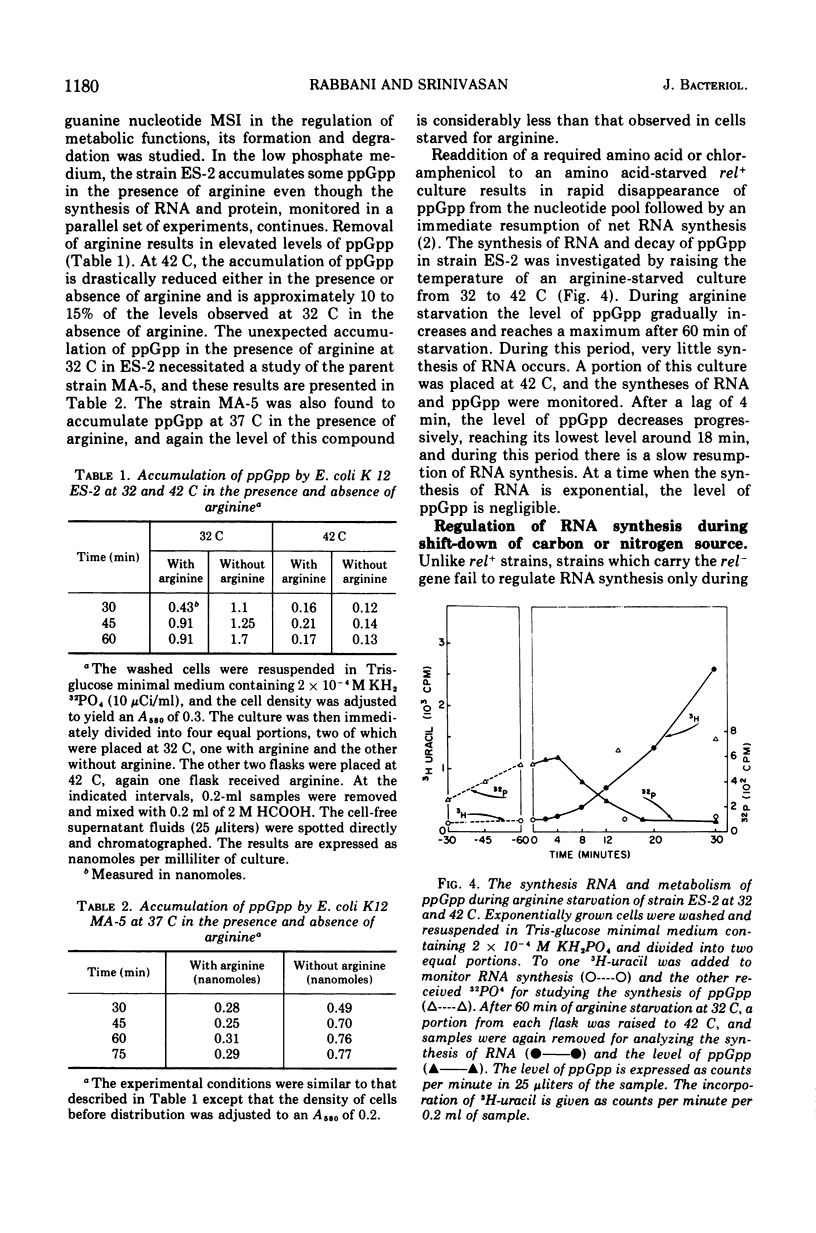
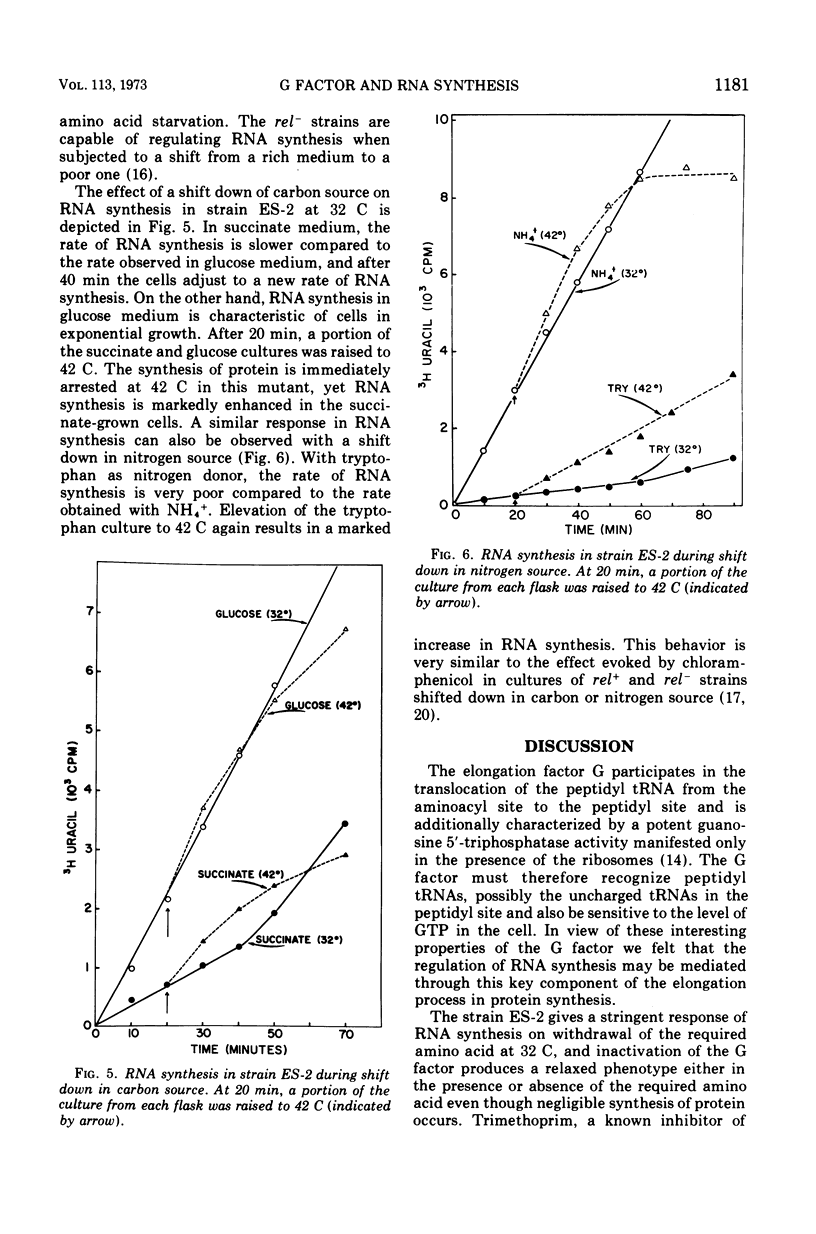
In an Escherichia coli rel+arg strain (ES-2) which carries a temperature-sensitive “G factor,” the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA) continues at the nonpermissive temperature (42 C) even though protein synthesis is terminated. However, at 32 C, the strain exhibits a stringent control of RNA synthesis in the absence of arginine. The stringent control of RNA synthesis imposed by trimethoprim (an inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis) at 32 C is released at the nonpermissive temperature. Even the diauxie lag in RNA synthesis, which is regulated independently of the allelic state of the rel gene, is overcome by inactivation of the G factor. The unusual guanosine nucleotide, guanosine 5′-diphosphate 2′ or 3′-diphosphate (ppGpp), is produced in small amounts during growth in strain ES-2. Withdrawal of arginine results in a greater accumulation of this compound at 32 C. At 42 C, the synthesis of ppGpp is abolished and is considerably lower than the level found in ES-2 under normal growth conditions. These results indicate that the translocation factor G plays an important role in the regulation of RNA synthesis and in the synthesis of ppGpp.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOREK E., ROCKENBACH J., RYAN A. Studies on a mutant of Escherichia coli with unbalanced ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1956 Mar;71(3):318–323. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.3.318-323.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Gallant J. Two compounds implicated in the function of the RC gene of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):838–841. doi: 10.1038/221838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. IV. Relevance of unusual phosphorylated compounds from amino acid-starved stringent strains. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3133–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E., Schlessinger D., Gurgo C. Synthesis, no synthesis, or synthesis and degradation of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in various Escherichia coli strains starved for an amino acid. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):66–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.66-72.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Broda P. Physiology and genetics of the "ribonucleic acid control" locus in escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):206–226. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.206-226.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL D. G., NEIDHARDT F. C. Use of chloramphenicol to study control of RNA synthesis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:96–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J., Irr J., Cashel M. The mechanism of amino acid control of guanylate and adenylate biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5812–5816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Block R., Gilbert W., Weber K. MSI and MSII made on ribosome in idling step of protein synthesis. Nature. 1972 Aug 18;238(5364):381–384. doi: 10.1038/238381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. In vitro transcription of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1972 Feb 11;235(5337):329–333. doi: 10.1038/235329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Cashel M., Gallant J. On the regulation of guanosine tetraphosphate levels in stringent and relaxed strains of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4381–4385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Kjeldgaard N. O. Metabolism of guanosine tetraphosphate in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 24;28(3):316–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., FRAENKEL D. G. Metabolic regulation of RNA synthesis in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:63–74. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C. Properties of a bacterial mutant lacking amino acid control of RNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 26;68:365–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson D., Gillespie D. Stringent response of RNA synthesis in E. coli produced by a temperature shift-up. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90843-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih A. Y., Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. On the relation between ribonucleic acid synthesis and peptide chain initiation in E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1599–1605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokawa Y., Sokawa J., Kaziro Y. Function of the rel gene in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 3;234(44):7–10. doi: 10.1038/newbio234007a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G., Cheong L., Gefter M. DNA-directed cell-free synthesis of biologically active transfer RNA: su + 3 tyrosyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2195–2197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


